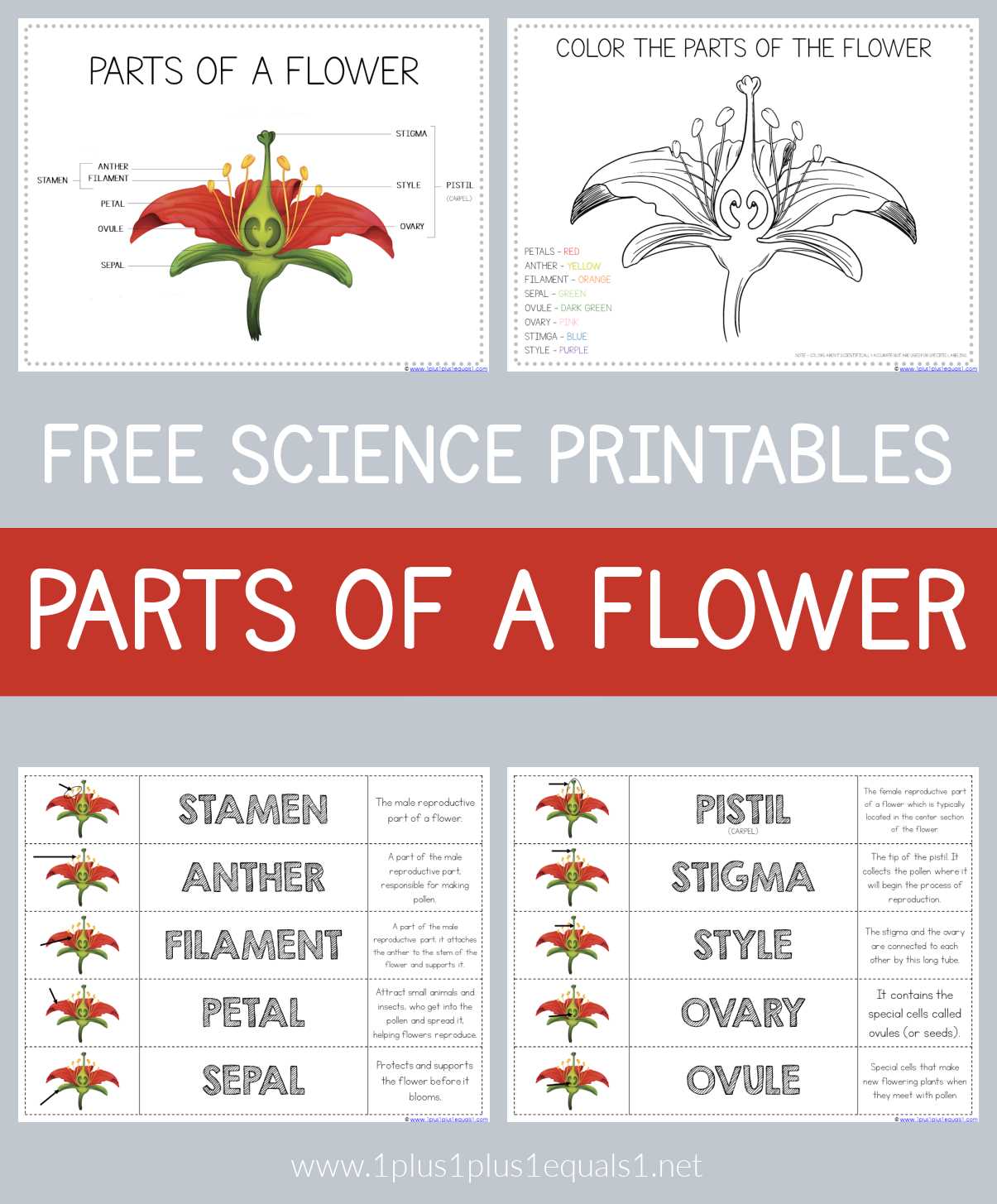
In the realm of botany, the intricate design of blooms plays a crucial role in the life cycle of plants. Each component contributes to reproduction and survival, showcasing nature’s ingenuity. Through careful observation, we can appreciate the delicate balance and functionality of these elements.
By exploring the various sections, we uncover their unique roles and significance. From the outermost layers that attract pollinators to the inner mechanisms ensuring fertilization, each section serves a specific purpose. Understanding these intricacies allows us to delve deeper into the fascinating world of flora.
Ultimately, this exploration enhances our appreciation for the natural world and encourages a greater respect for the diversity of life that surrounds us. By recognizing the complexities within each bloom, we can cultivate a more profound connection to our environment.
Understanding the Flower Structure
The intricate design of reproductive structures in plants plays a crucial role in their life cycle and the continuation of species. Each component is specialized, serving distinct functions that contribute to the overall process of reproduction. By examining these elements closely, one can appreciate the complexity and elegance inherent in nature’s arrangements.
At the heart of this biological marvel are various components that facilitate pollination, seed development, and genetic diversity. The outer layers often protect more delicate inner sections, while specific features attract pollinators, ensuring successful transfer of pollen. Each feature interacts harmoniously with others, highlighting a well-coordinated system essential for thriving ecosystems.
Understanding these components not only enhances our knowledge of botany but also underscores the importance of these organisms in our environment. Their roles extend beyond mere reproduction; they are integral to food webs, habitats, and even cultural practices. The study of these structures reveals the interconnectedness of life and the vital contributions plants make to our planet.
In summary, the study of reproductive forms reveals a fascinating interplay of structure and function. Appreciating these natural designs invites a deeper respect for the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Key Components of a Flower
This section explores the essential elements that constitute a blossom, emphasizing their roles in reproduction and attraction. Understanding these components provides insight into the intricate design and function of nature’s creations.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Petals | Colorful structures that attract pollinators through their vibrant hues and patterns. |
| Stamens | The male reproductive organs, consisting of anthers and filaments, responsible for producing pollen. |
| Pistils | The female reproductive part, comprising stigma, style, and ovary, crucial for fertilization. |
| Sepals | Leaf-like structures that protect the developing blossom and often support the petals. |
Role of Petals in Pollination
Petals serve a crucial function in the reproductive processes of many plants. Their vibrant colors, unique shapes, and enticing fragrances play a vital role in attracting various pollinators. By enhancing visibility and appeal, these structures facilitate the transfer of pollen, ensuring successful reproduction and genetic diversity.
Attraction of Pollinators
The striking appearance of petals is often the first point of contact for potential pollinators. Key aspects include:
- Color: Bright and contrasting hues catch the attention of insects and birds, drawing them closer.
- Shape: Specific formations can guide pollinators to the reproductive parts, increasing the likelihood of successful pollen transfer.
- Fragrance: Pleasant scents can lure in various species, enhancing the chance of interaction.
Facilitation of Pollination Process
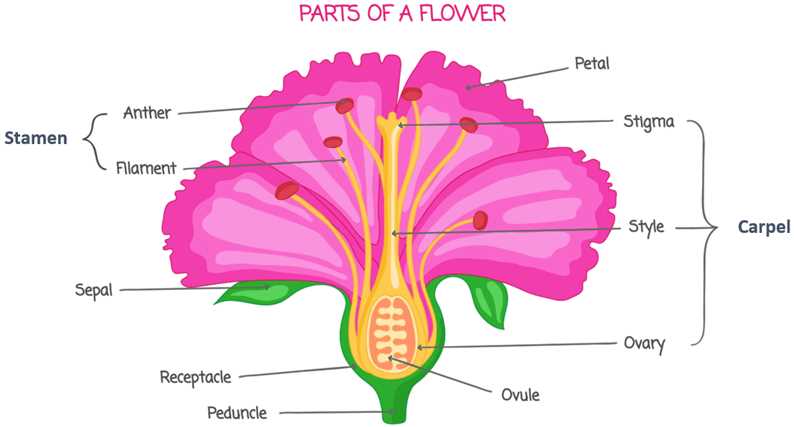
Beyond attraction, petals contribute to the mechanics of pollination:
- Support: They provide a stable platform for pollinators to land while accessing nectar.
- Guidance: The structure can direct pollinators toward the pollen and ovary, ensuring efficient transfer.
- Protection: Petals may shield delicate reproductive organs from harsh environmental conditions and pests.
Through these functions, petals play an indispensable role in the lifecycle of many plant species, significantly impacting their reproductive success and survival.
Function of Sepals Explained
Sepals play a crucial role in the development and protection of reproductive structures. These components serve as a protective layer during early growth stages, ensuring the integrity of more delicate elements.
- Protection: They shield the inner organs from environmental factors and potential damage.
- Support: Offering structural stability, they help maintain the arrangement of the reproductive organs.
- Photosynthesis: In some species, they can contribute to the photosynthetic process, aiding overall plant health.
- Attraction: They may enhance the visual appeal, indirectly influencing pollinator behavior.
Understanding the significance of these structures provides deeper insights into the complex interactions within plant biology.
The Importance of Stamen
The reproductive structures of plants play a crucial role in the process of pollination and the continuation of species. Among these components, one specific element stands out for its essential function in facilitating fertilization. Understanding this role sheds light on the intricate relationships within ecosystems and the significance of plant biology.
This particular structure is primarily responsible for producing pollen, which is vital for the transfer of genetic material between individuals. By attracting various pollinators, it ensures that the process of reproduction can occur efficiently. The effectiveness of this element can directly influence the diversity and health of plant populations.
Moreover, the design and arrangement of this structure can impact the overall reproductive success of a species. Factors such as shape, size, and position can determine how easily pollinators access the pollen, highlighting the adaptive strategies plants employ in response to their environments.
In summary, the significance of this reproductive structure extends beyond individual species; it contributes to broader ecological networks and supports the intricate balance of life. Recognizing its importance helps in appreciating the complexities of nature and the interdependence of living organisms.
Exploring the Pistol’s Role
The pistol serves as a crucial component in the reproductive system of flowering plants. Its significance extends beyond mere structure, playing a vital part in the processes of fertilization and seed production. Understanding its function is essential for grasping how plants propagate and thrive in diverse environments.
Structure and Function
The pistol comprises several key elements that work together to facilitate reproduction:
- Stigma: The receptive surface where pollen grains land and germinate.
- Style: The elongated structure that connects the stigma to the ovary, guiding the pollen tube.
- Ovary: The chamber that houses the ovules, which develop into seeds upon fertilization.
Importance in Plant Reproduction
The role of the pistol is paramount in ensuring successful reproduction. Its components contribute to the following processes:
- Pollen Capture: The stigma’s surface is specially adapted to trap pollen, facilitating fertilization.
- Pollen Tube Growth: The style supports the growth of the pollen tube, allowing sperm cells to reach the ovules.
- Seed Development: The ovary protects and nurtures the fertilized ovules until they mature into seeds.
In conclusion, the pistol’s intricate structure and vital functions underscore its essential role in the reproductive success of flowering plants. Understanding this component provides valuable insights into plant biology and ecology.
Types of Flowers and Their Parts
Exploring the diverse world of blooms reveals a fascinating array of structures and characteristics that define them. Each variant showcases unique attributes, contributing to the intricate tapestry of nature. Understanding these distinctions enhances our appreciation of their beauty and function in the ecosystem.
Classification of Blossoms
- Annuals: Thrive in one growing season.
- Perennials: Return year after year.
- Biennials: Complete their life cycle in two years.
Key Structures
- Petals: Attract pollinators with their colors.
- Sepals: Protect the bud before blooming.
- Stamen: Male reproductive component.
- Pistil: Female reproductive structure.
How Flowers Attract Pollinators
The vibrant colors and captivating scents of plants play a crucial role in enticing various creatures that aid in reproduction. These visual and olfactory signals create a compelling invitation, ensuring that essential interactions occur for the continuation of species. Through a combination of aesthetics and aroma, these living organisms effectively communicate their readiness to engage with potential partners.
Additionally, timing is key; many species release their alluring fragrances during specific times when their preferred pollinators are most active. This synchronization ensures that the opportunity for interaction is optimized, further solidifying the bond between the two. As a result, the strategies utilized by plants are intricate and carefully honed through evolutionary processes.
Life Cycle of a Flower
The journey of a blossoming plant involves several fascinating stages, each crucial for its development and reproduction. Understanding this progression reveals the intricate processes that sustain plant life and contribute to the ecosystem.
-
Seed Stage:
The process begins with a seed, which contains the genetic material necessary for growth. Seeds remain dormant until conditions are favorable for germination.
-
Germination:
When moisture and warmth are present, the seed absorbs water, swells, and eventually breaks open. This marks the start of the growth phase.
-
Seedling Stage:
A young plant, known as a seedling, emerges from the soil. During this phase, it develops roots and leaves, establishing itself in its environment.
-
Mature Plant:
As the plant grows, it enters maturity. This stage is characterized by the development of structures necessary for reproduction.
-
Reproductive Phase:
During this period, the plant produces blossoms, which are essential for pollination and fertilization. This phase ensures the continuation of the species.
-
Seed Production:
After pollination, seeds are formed within the blossoms. Once mature, these seeds are dispersed, beginning the cycle anew.
Each stage of this remarkable journey is interconnected, highlighting the beauty and complexity of nature’s design. Understanding this life cycle helps us appreciate the role of plants in our world.
Common Flowering Plants to Know
Understanding various types of blooming vegetation enhances appreciation for nature’s beauty and diversity. Here, we explore some popular species that are essential for both enthusiasts and gardeners alike.
| Plant Name | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Rosa | Known for its stunning petals and fragrance, this perennial is a favorite in many gardens. |
| Tulipa | These bulbous plants offer vibrant colors and are often associated with springtime celebrations. |
| Hibiscus | This tropical plant showcases large, colorful blooms and thrives in warm climates. |
| Lilium | Featuring striking, trumpet-shaped blossoms, this species is a staple in floral arrangements. |
| Chrysanthemum | These hardy blooms come in various forms and are cherished for their late-season display. |
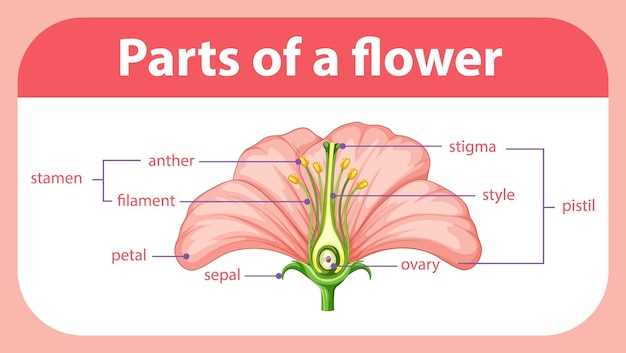
Understanding Flower Anatomy Terms
The intricate structure of a bloom plays a crucial role in its life cycle and reproductive success. Familiarizing oneself with the terminology associated with these botanical features can enhance appreciation and comprehension of their functions. This section delves into essential vocabulary, providing clarity on various components and their roles within the reproductive system.
Key Components
- Stamen: The male reproductive organ, composed of an anther and filament, responsible for pollen production.
- Carpel: The female reproductive unit, typically consisting of the ovary, style, and stigma, essential for seed development.
- Petals: Often colorful structures that attract pollinators and facilitate reproduction.
- Sepals: The outer protective layer that encases the developing bloom.
Function and Importance
Each component has a specific role that contributes to the overall reproductive process:
- The stamen releases pollen, which is vital for fertilization.
- The carpel nurtures ovules, leading to seed formation.
- Petals enhance visibility and accessibility for pollinators.
- Sepals safeguard the reproductive structures during development.
Understanding these terms allows for a deeper insight into the fascinating world of plant reproduction and ecology.
Significance of Flower Symmetry
The arrangement and balance of floral structures play a crucial role in the overall aesthetics and functionality of plants. Symmetry not only enhances visual appeal but also influences various ecological interactions. Understanding this phenomenon can provide insights into plant evolution and reproductive strategies.
Attraction and Pollination
Symmetrical forms often attract pollinators more effectively than asymmetrical ones. Visual harmony allows pollinators to identify flowers quickly, ensuring successful visits. This attraction is vital for reproductive success, as it increases the chances of cross-pollination and genetic diversity.
Adaptation and Survival
In addition to attracting pollinators, symmetrical structures can aid in environmental adaptation. Uniform distribution of floral components can enhance resilience against wind and rain, ensuring that the reproductive parts remain functional. This adaptability contributes to the long-term survival of species in diverse habitats.
Ecological Impact of Flowers
The role of these vibrant entities in ecosystems extends far beyond their aesthetic appeal. They serve as vital components within various habitats, supporting a multitude of interactions among organisms. Through their intricate relationships with pollinators, they contribute significantly to biodiversity and the stability of ecological networks.
One of the most notable effects is their involvement in the reproductive processes of many plants, which ultimately sustains food webs. The presence of these organisms can influence population dynamics and promote genetic diversity, thereby enhancing resilience against environmental changes.
| Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
|---|---|
| Support pollinator species | Can attract invasive pests |
| Promote biodiversity | May lead to competition with native species |
| Enhance soil health | Can cause localized resource depletion |
| Provide habitat for various organisms | Potential allergenic effects on humans |
In summary, the significance of these organisms in ecosystems is multifaceted. While they are essential for supporting life and maintaining ecological balance, they can also introduce challenges that need to be managed for the health of the environment.