Understanding the layout of mechanical and electrical systems is crucial for maintaining any vehicle. Whether you’re performing a repair or simply exploring how different elements are connected, a detailed guide to component organization will be invaluable. This allows for precise troubleshooting and enhances the overall efficiency of maintenance tasks.
In this guide, you will explore the interconnected systems and assemblies found within a popular mid-sized truck model. From its engine configuration to the electrical wiring, every element plays a vital role in ensuring the vehicle’s performance and longevity. Identifying these components will help you better understand the inner workings of this well-known model, contributing to more informed maintenance and repair decisions.
Additionally, gaining insight into how different parts align within the vehicle’s frame will make it easier to detect issues early on and prevent costly repairs. This knowledge is not only beneficial for enthusiasts but also for professionals looking to improve their mechanical skills.
Overview of Key Components in the 2000 Ford Ranger
Understanding the essential systems and mechanisms within this model is crucial for efficient maintenance and repair. This section covers the primary elements that ensure optimal performance, safety, and functionality of the vehicle. We will look into the vital systems that work together to provide a smooth driving experience and reliable operation over time.
Powertrain and Drivetrain Elements
The core of any vehicle lies in its power and motion systems. The engine, transmission, and drive mechanisms form the backbone of its functionality. These elements are responsible for generating power, transferring it to the wheels, and ensuring proper control under various conditions. Regular upkeep of these components is essential for maintaining vehicle longevity and efficiency.
Suspension and Braking Systems
Safety and comfort on the road are heavily dependent on suspension and braking mechanisms. The suspension system stabilizes the vehicle, absorbing shocks and providing a smoother ride, while the braking system ensures quick, reliable stopping power. Both of these aspects are integral to the overall
Engine Layout and Essential Parts
The structure of the engine is a complex system, where various components work in unison to ensure optimal performance. This section explores the fundamental elements that form the core of this machinery, describing how each piece contributes to the overall functionality.
Key Components of the Engine
- Block: The foundation of the engine, housing many vital systems and providing support for other mechanisms.
- Cylinder Head: Positioned on top of the block, it contains the passages for fuel and air intake, as well as the exhaust system.
- Transmission System Components Breakdown
The transmission system plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transfer between the engine and the vehicle’s wheels. Understanding the various elements that make up this system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Each component works in tandem to facilitate smooth transitions between gears and manage the overall drive experience.
Gearbox: The gearbox is responsible for modulating the engine’s output, allowing the driver to change speeds and manage acceleration effectively. It consists of multiple gears that help in controlling the power delivered to the wheels.
Clutch Assembly: This mechanism enables the engagement and disengagement of the engine from the transmission system. When the clutch is pressed, it interrupts the power flow, allowing smooth gear shifts without damaging the internal components.
Torque Converter: In automatic transmissions, the torque converter serves to transmit and multiply engine torque to the transmission. It ensures that the engine operates
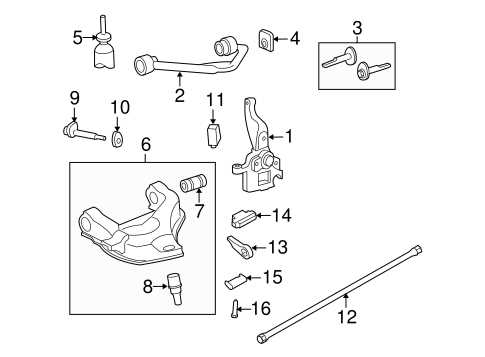
Suspension Structure and Critical Elements
The suspension system is a complex arrangement designed to ensure optimal vehicle stability, comfort, and handling across various terrains. This configuration harmonizes multiple interconnected elements, which work together to absorb shocks, maintain alignment, and provide seamless motion control.
Key components include shock absorbers, springs, and control arms, each playing a distinct role in balancing the weight distribution and minimizing vibrations. The alignment and proper function of these elements are essential for maintaining the overall performance, reducing wear on tires, and enhancing driving safety.
Additionally, structural elements like sway bars and bushings contribute to reducing body roll during cornering and stabilizing the frame. Regular inspections and timely maintenance of these elements are critical to ensure that the system continues to function efficiently under varying conditions.
Exhaust System Overview for Efficient Performance
The exhaust system plays a critical role in enhancing the overall performance of any vehicle. By efficiently managing the removal of combustion gases, this system ensures that the engine runs smoothly, reducing harmful emissions and improving fuel efficiency. An optimized exhaust setup can significantly impact the longevity and functionality of the engine, providing better airflow and maintaining ideal operating conditions.
Component Function Exhaust Manifold Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe. Catalytic Converter Reduces harmful pollutants by converting toxic gases into less harmful emissions. Electrical Wiring and Connections Guide
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the electrical systems within a compact truck. Understanding the wiring layout and connection points is crucial for maintenance and repair tasks. Proper knowledge of these components ensures reliable vehicle operation and helps prevent electrical issues.
The electrical system consists of various elements that work together to provide power and functionality. Below are some key components you should be familiar with:
- Battery
- Alternator
- Fuses and relays
- Wiring harnesses
- Ground connections
To effectively manage electrical repairs or upgrades, consider the following steps:
- Review the wiring layout to identify the position of each component.
- Inspect connections for corrosion or damage.
- Test the continuity of wires to ensure proper conductivity.
- Replace any faulty fuses or relays as needed.
- Secure all ground connections to prevent electrical malfunctions.
By familiarizing yourself with these essential aspects, you can confidently tackle electrical tasks and maintain the functionality of your vehicle’s systems.
Fuel System Diagram and Components
The fuel system is crucial for the efficient operation of any vehicle, ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for combustion. Understanding the layout and various elements involved in this system is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. This section will explore the key components and their functions within the fuel delivery mechanism.
Fuel Tank: This is the reservoir where fuel is stored before being delivered to the engine. It is designed to withstand various pressures and environmental conditions.
Fuel Pump: Positioned either inside the fuel tank or along the fuel line, this component is responsible for moving fuel from the tank to the engine. It is vital for maintaining the correct pressure within the system.
Fuel Filter: This element serves to remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine, protecting critical components from damage.
Fuel Lines: These are the pathways through which fuel travels from the tank to the engine. They must be durable and resistant to corrosion to ensure longevity and performance.
Fuel Injectors: These devices spray a precise amount of fuel into the engine’s combustion chambers, facilitating the ignition process. Proper functioning of fuel injectors is critical for optimal engine performance.
Pressure Regulator: This component maintains the appropriate fuel pressure within the system, ensuring that the injectors receive the correct amount of fuel regardless of engine demand.
By familiarizing oneself with these essential elements, vehicle owners and technicians can effectively manage the fuel system’s maintenance and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
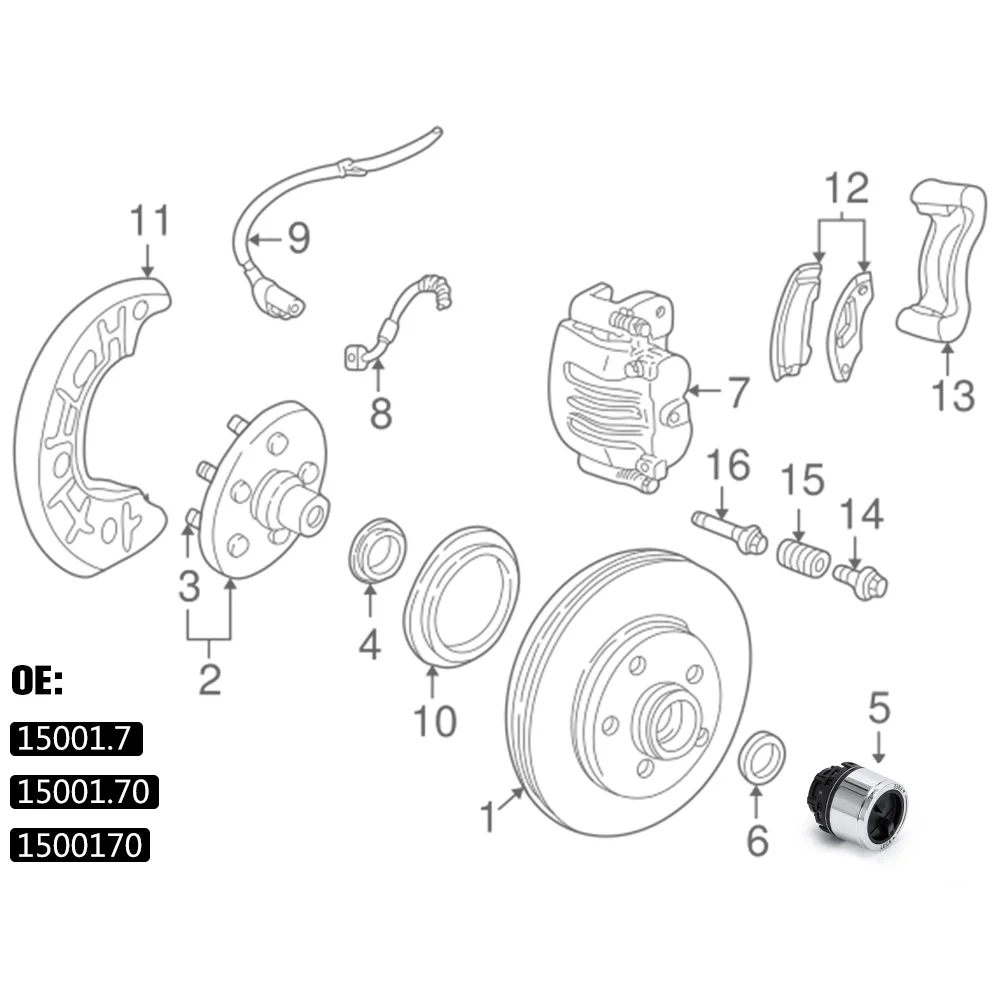
Brake Mechanism Overview for Safety
The braking system is a crucial component in any vehicle, ensuring safe stopping and control. Understanding its functioning helps in recognizing the importance of maintenance and timely inspections. An effective braking mechanism significantly enhances overall driving safety, reducing the risk of accidents.
Components of the Braking System
Each part of the braking system plays a vital role in its performance. From the pedal to the calipers, each element must work in harmony to provide optimal braking efficiency. Below is a summary of the key components:
Component Function Brake Pedal Transmits force from the driver’s foot to the braking system. Master Cylinder Converts pedal force into hydraulic pressure. Brake Lines Carry hydraulic fluid to the brake calipers. Brake Calipers Clamp the brake pads against the rotors to create friction. Brake Pads Friction material that grips the rotors to slow down the vehicle. Rotors Discs that rotate with the wheels, providing a surface for the pads to clamp onto. Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine checks of the braking system are essential for ensuring safety on the road. Worn-out pads, low fluid levels, or air in the brake lines can severely compromise braking performance. Regular inspections help in identifying potential issues before they lead to failure, thereby enhancing vehicle reliability and safety.
Cooling System Parts and Their Functions
The cooling system in a vehicle plays a critical role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring overall engine efficiency. Understanding the various components within this system helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key Components
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant that flows through it, helping to cool the engine fluids before they circulate back.
- Water Pump: Essential for circulating coolant throughout the system, ensuring that hot fluid is moved away from the engine and cooled in the radiator.
- Thermostat: A temperature-regulating valve that opens and closes to maintain the correct coolant temperature, allowing for efficient engine operation.
- Coolant Reservoir: This container holds excess coolant and allows for expansion and contraction as temperatures change, preventing system pressure from becoming too high.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components, ensuring a continuous flow of fluid throughout the system.
Functions of the Cooling Components
- Regulate engine temperature to prevent overheating.
- Facilitate heat exchange through the radiator to maintain fluid temperature.
- Ensure consistent circulation of coolant for optimal heat dissipation.
- Allow for thermal expansion and contraction without compromising system integrity.
- Provide a pathway for coolant movement, maintaining efficiency throughout the cooling system.
By understanding these vital elements and their roles, vehicle owners can better appreciate the importance of the cooling system in maintaining engine health and performance.
Steering Mechanism and Its Key Elements
The steering mechanism plays a crucial role in vehicle control, allowing drivers to navigate safely and accurately. This system comprises various components that work in unison to facilitate smooth turning and stability on the road.
Understanding the primary elements of the steering system is essential for both maintenance and performance enhancement. Below are the key components:
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface between the driver and the vehicle, allowing for directional control.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the gearbox and provides support for the wheel’s movement.
- Steering Gearbox: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, directing the vehicle’s wheels.
- Linkage: Transfers movement from the steering gearbox to the wheels, ensuring coordinated motion.
- Wheel Assembly: Includes various components such as tie rods and knuckles, which connect to the wheels for responsive steering.
Each part contributes to the overall functionality of the steering mechanism, affecting handling, response time, and safety. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can enhance driving experience and prolong vehicle lifespan.
Body and Frame Parts Layout
The configuration of structural components in a vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall performance and safety. Understanding the arrangement of these elements provides insight into the engineering that ensures durability and functionality. This section delves into the key components that constitute the exterior and structural integrity of the vehicle, highlighting their significance and interrelationships.
Key Structural Elements
The essential components forming the framework include the chassis, body panels, and reinforcements. Each element is designed to serve specific functions, contributing to the vehicle’s rigidity and protection. Below is a summary of the main elements:
Component Description Chassis The base frame that supports the entire vehicle structure and mechanical systems. Body Panels Outer surfaces that form the shape and aesthetic appeal of the vehicle, providing protection and insulation. Reinforcements Additional structural elements that enhance strength and stability, particularly in areas prone to stress. Importance of Proper Layout
A well-thought-out arrangement of the aforementioned components is vital for optimal performance. Proper alignment ensures that the vehicle can withstand impacts, maintain stability during operation, and provide safety for occupants. Regular inspections and maintenance of these elements can prevent wear and tear, extending the vehicle’s lifespan.