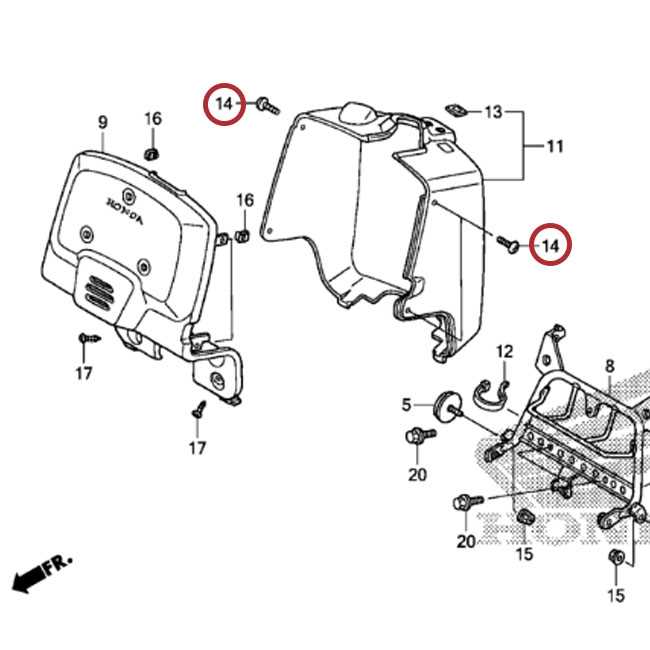
Understanding the structural arrangement and essential elements of a motorized two-wheeler is key to ensuring smooth maintenance and customization. Whether you’re looking to enhance performance or replace existing components, knowing the placement and function of each element within the vehicle is crucial.
The intricate framework consists of various interconnected pieces, all playing a role in the overall functionality. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you can confidently approach upgrades or repairs, ensuring your ride remains reliable and efficient.
This guide offers a detailed breakdown of all essential pieces, making it easier for enthusiasts and professionals alike to navigate through complex arrangements. With a focus on clarity and simplicity, you’ll gain valuable insight into the inner workings of your vehicle.
Honda Ruckus Parts Diagram Overview
When analyzing the structural layout of this popular two-wheeler, it’s essential to focus on the composition and interaction of its core elements. Each component is meticulously designed to contribute to the overall performance, ensuring durability and reliability in various conditions.
Main Structural Components
The foundation of the vehicle is built upon a sturdy frame that supports both the engine and the rider. Various mechanical pieces, including the suspension and braking systems, are intricately connected to ensure a smooth and safe ride.
Essential Mechanical Elements
Key functional parts, such as the power system and transmission, are designed to work seamlessly together, delivering optimal power output and control. These elements are complemented by a sophisticated electrical system that regulates the vehicle’s operation.
Key Components of Honda Ruckus
Understanding the core elements of this model is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The structure includes a variety of interconnected mechanisms that work in harmony to provide stability, efficiency, and ease of handling. Below, we’ll explore the most essential segments of this popular vehicle, detailing their function and importance in the overall design.
Frame and Suspension
The frame serves as the foundation, supporting the entire structure. It is designed to offer a balance between weight and durability, ensuring smooth rides on various terrains. The suspension system complements the frame by absorbing shocks, providing a comfortable and stable experience even on uneven roads.
Engine and Transmission
The heart of the machine is its motor, which drives the vehicle forward. Coupled with a transmission system, it ensures the efficient transfer of power, allowing for smooth acceleration and control. These components are designed for reliability and easy maintenance, ensuring long-term usage with minimal issues.
- Engine block
- Transmission gears
- Cooling system
Understanding the Engine Layout
The structure of the motor in this model is designed to provide both reliability and efficiency. At its core, the setup is optimized for smooth power delivery while maintaining a compact and durable configuration. Each component is carefully placed to enhance performance without sacrificing space, making the overall layout practical for everyday use.
The engine operates using an air-cooled system, ensuring temperature regulation during long rides. Key elements include a compact cylinder, a lightweight crankshaft, and an efficient transmission system. The focus is on creating an easy-to-maintain setup that simplifies regular upkeep.
With proper maintenance, this layout ensures longevity and consistent performance, making it ideal for those seeking a balance between power and practicality. Its design prioritizes user-friendly maintenance, allowing for quick inspections and adjustments.
Exploring the Electrical System of Ruckus
The electrical setup of this model is a key component that powers various essential functions, ensuring smooth operation. Understanding how the wiring is structured and how different elements interact with the power source is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Main Components of the System
This system includes various elements responsible for powering lights, ignition, and other features. Each component has a specific role, and their proper functioning ensures that the vehicle operates smoothly. Below is a table outlining key elements of the setup and their purposes:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Supplies energy to all electrical parts |
| Ignition Coil | Generates the spark needed for combustion |
| Regulator/Rectifier | Controls voltage levels and ensures stable energy flow |
| Wiring Harness | Connects various components and allows energy transmission |
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular checks on the electrical system can prevent malfunctions. Key areas to inspect include the condition of the battery, connections, and potential wear on wiring. Addressing
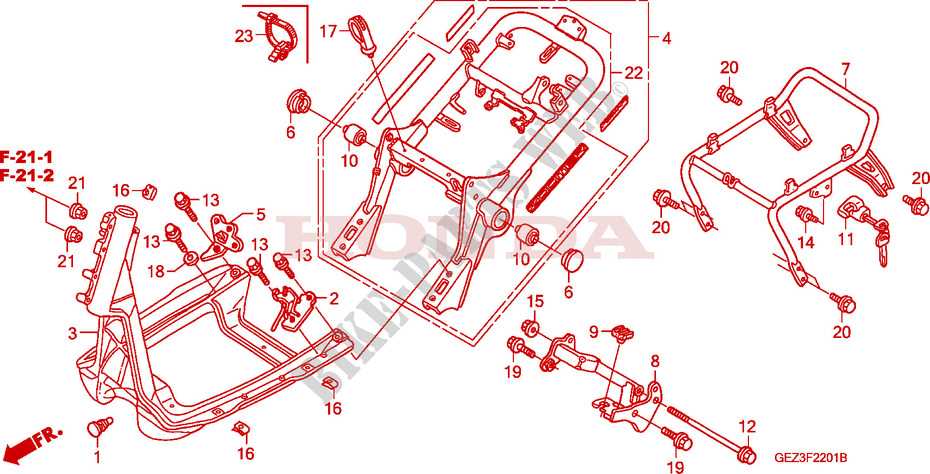
Frame and Body Structure Breakdown
The structural composition of a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for its overall stability and performance. Understanding the frame and body configuration helps to maintain balance, durability, and a smooth ride. The foundation holds everything in place, while the external shell provides protection and aerodynamics.
Main Frame
The core of the vehicle’s design, the main frame, serves as the backbone supporting various components. It ensures a sturdy connection between the engine, suspension, and other critical elements. Built for strength, it helps absorb shocks and vibrations while riding on uneven surfaces.
Exterior Panels
The exterior shell not only adds to the vehicle’s appearance but also plays a key role in protecting vital internal parts from environmental factors. These panels are typically lightweight, providing coverage without compromising the vehicle’s speed and efficiency.
Suspension System and Shocks Overview
The suspension framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth ride and maintaining stability. It absorbs shocks from the road and enhances comfort for the rider. This system is composed of various components that work in harmony to manage the vehicle’s response to uneven surfaces and obstacles.
Key elements of the suspension system include:
- Shocks Absorbers: These devices dampen the impact of road irregularities, improving control and comfort.
- Springs: They support the weight of the vehicle and allow for vertical movement, contributing to ride quality.
- Linkages: Various arms and bars connect components, ensuring proper alignment and function.
- Struts: Combining shock absorption and structural support, struts enhance stability and handling.
Understanding the functionality of these components is essential for maintenance and upgrades. Regular inspections can identify wear and tear, which may lead to diminished performance. Maintaining the integrity of the suspension system is vital for ensuring safety and enhancing the overall riding experience.
Wheels and Tires Configuration Explained
The configuration of wheels and tires plays a crucial role in the overall performance and handling of any two-wheeled vehicle. Understanding how different sizes, types, and specifications of these components interact can greatly enhance stability, maneuverability, and comfort during operation. A well-thought-out wheel and tire setup is essential for optimizing traction, braking efficiency, and ride quality.
Typically, the front and rear wheels differ in width and diameter, which affects the distribution of weight and balance of the vehicle. The front tire is usually narrower, allowing for easier steering and better response to directional changes, while the rear tire is wider for improved grip and stability. Choosing the right tire pressure is also vital, as it influences handling characteristics and tread wear.
Moreover, tire tread patterns are designed for specific conditions, whether for dry pavement or wet surfaces. A suitable tread design can enhance grip and minimize the risk of skidding. Additionally, the material composition of tires can vary, affecting durability and performance under various environmental conditions. By carefully considering these elements, riders can ensure a more enjoyable and safer experience.
Fuel System and Tank Diagram
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the operation of any two-wheeled vehicle. It is responsible for delivering the necessary fuel to the engine for efficient combustion. Understanding the layout and components of this system can significantly enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. This section provides an overview of the key elements involved in the fuel delivery process.
The primary component of the fuel assembly is the fuel tank, which stores the liquid until needed by the engine. Fuel is drawn from this tank through a series of lines and filters that ensure it reaches the engine free from impurities. The fuel pump is integral to this system, as it generates the pressure required to move fuel through the various components. Additionally, the fuel filter serves to trap contaminants, protecting the engine from damage and ensuring optimal performance.
In conjunction with these elements, the fuel injector delivers the precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber, facilitating efficient mixing with air for optimal ignition. The overall arrangement of these parts can vary, but their collective function remains the same: to supply the engine with the right amount of fuel for seamless operation. A thorough understanding of this configuration is essential for any enthusiast or technician looking to maintain or modify their vehicle effectively.
Brake System Components of Ruckus
The braking system is essential for ensuring safety and control in any two-wheeled vehicle. It comprises various components that work in harmony to provide effective stopping power. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components
The primary elements of the braking mechanism include the brake lever, master cylinder, brake lines, and calipers. The brake lever, located on the handlebar, allows the rider to engage the braking system. The master cylinder converts the lever’s movement into hydraulic pressure, which is transmitted through the brake lines to the calipers.
Additional Elements
Other significant components are the brake pads, rotors, and various mounting brackets. The brake pads grip the rotor when pressure is applied, slowing down the wheel’s rotation. Regular inspection and timely replacement of these parts are vital for optimal performance and safety.
Exhaust System Structure and Layout
The exhaust assembly of a compact two-wheeler plays a crucial role in both performance and efficiency. This system is designed to channel exhaust gases away from the engine, minimizing back pressure while maximizing output. An efficient layout not only enhances power delivery but also contributes to the overall riding experience.
Typically, the exhaust system consists of several key components, including the header, muffler, and intermediate pipes. The header collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them through the piping. The muffler then reduces noise levels and may also influence the flow characteristics, ensuring that emissions are managed effectively.
Proper configuration of the exhaust system is essential for optimizing engine performance. Factors such as pipe diameter, length, and bends can significantly affect gas flow and pressure. Additionally, the positioning of components is vital to prevent heat buildup and ensure durability. Regular maintenance and inspection of this system are recommended to avoid potential issues that may arise from wear or damage.
Lights and Indicators Configuration
This section explores the arrangement and functionality of lighting elements and signaling devices on a compact vehicle. Properly configured illumination is essential for ensuring visibility and safety while enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the vehicle.
Illumination Features
The vehicle is equipped with various lighting options, including headlamps, taillights, and turn signals. Each component plays a crucial role in providing clear visibility during nighttime or adverse weather conditions. The alignment and intensity of these lights must be carefully calibrated to meet safety standards.
Signaling and Alert Systems
In addition to standard lighting, this vehicle includes an array of indicators that communicate operational status to the rider and other road users. These indicators include warning lights for engine malfunctions, fuel levels, and turn signal activation. Understanding the configuration of these signals is vital for effective vehicle management.
Maintenance Tips Using Parts Diagrams
Understanding the layout and components of your vehicle is crucial for effective upkeep and repair. Visual representations of these elements can significantly enhance your ability to identify issues, replace worn parts, and ensure optimal performance. By utilizing these illustrations, you can streamline your maintenance processes and avoid common pitfalls associated with vehicle care.
Regular Inspection: Make it a habit to frequently examine the different sections outlined in the visuals. This practice helps in spotting signs of wear or damage early on, allowing for timely interventions.
Component Familiarization: Take time to familiarize yourself with each component illustrated. Understanding the function and location of each part can make troubleshooting and repairs much more straightforward.
Utilize Reference Materials: Always have a copy of the visual guides on hand while performing maintenance tasks. These resources serve as a valuable reference, ensuring that you don’t overlook any critical elements during repairs.
Step-by-Step Approach: When undertaking repairs, follow a systematic approach as depicted in the illustrations. This method can help prevent confusion and ensure that each step is executed correctly.
Record Keeping: Maintain a log of the maintenance activities performed. Note which parts were replaced and any observations made during the process. This documentation can be beneficial for future reference and ongoing care.