Every motorcycle consists of numerous intricate elements that work together to create a functional and efficient vehicle. Proper understanding of these individual parts is essential for maintenance, repair, and optimization. By exploring the structure of these machines, one can gain insight into how each piece contributes to overall performance and reliability.
In order to maintain or upgrade a vehicle, it’s important to have a clear understanding of how each component interacts with others. This not only helps in troubleshooting issues but also in making informed decisions about modifications. A well-detailed overview of these parts offers clarity on their roles, ensuring that any adjustments or replacements can be done with confidence.
Whether you are looking to repair an aging model or restore a classic, being familiar with the layout and specifications of each component can save time and prevent mistakes. This knowledge allows you to navigate the technical aspects of motorcycle repair more effectively, ensuring longevity and improved performance for your vehicle.
Understanding Honda ST90 Components
The intricate design of a classic two-wheeled vehicle involves a wide range of elements, each playing a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation. By examining the various parts that contribute to its functionality, one can gain a deeper understanding of how this vehicle maintains its performance and reliability over time. From the engine to the frame, each component is engineered for a specific task, working together harmoniously to provide a superior riding experience.
Key Elements of the Vehicle’s Engine and Transmission
The core of any two-wheeled machine is the engine, which serves as the powerhouse. This section includes the combustion chamber, crankshaft, and other essential parts that generate and transfer power to the wheels. The transmission system, with its gears and linkages, ensures that the power from the engine is smoothly transmitted to the driving wheels. Proper functioning of these elements is critical to maintain the speed and control of the vehicle.
Chassis and Suspension System

The chassis provides the structural support for the entire vehicle, ensuring that all other components remain securely attached and aligned. The suspension system, including the front forks and rear shocks, absorbs bumps and ensures a smooth ride over various terrains. Together, these elements help in maintaining stability and comfort, especially during off-road use.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Crankshaft | Converts linear motion into rotary motion to drive the wheels |
| Transmission | Transfers power from the engine to the wheels |
| Chassis | Provides the main frame for all other components |
| Suspension | Absorbs shocks and provides stability during riding |
Key Parts for Efficient Bike Maintenance
Regular upkeep of a motorcycle is essential for ensuring smooth performance and longevity. Understanding the critical components that require frequent attention allows riders to maintain their machine in optimal condition. Proper care of these key elements will prevent unexpected failures and enhance overall riding experience.
Engine Components
- Spark Plugs: Regular inspection and replacement ensure optimal combustion and smooth engine operation.
- Air Filter: Keeps the engine clean by preventing debris and dirt from entering, improving air-fuel mixture and efficiency.
- Fuel System: Clean fuel injectors and fuel lines are crucial for maintaining proper fuel flow and engine performance.
Suspension and Brakes
- Forks: The front suspension absorbs shocks and ensures stability during rides.
- Brake Pads: Regularly checking and replacing worn-out pads prevents accidents and ensures stopping power.
- Rear Shock Absorber: Essential for a smooth ride, it absorbs impact and stabilizes the rear of the vehicle.
Exploring the Engine Assembly of Honda ST90
The heart of any vehicle is its engine, and understanding how the components fit together is crucial for efficient performance. The engine assembly consists of several key elements that work in harmony to deliver power. By examining each section, it becomes clear how these components contribute to the overall functioning of the machine. This section breaks down the core components and their roles in driving the system forward.
Main Engine Components
- Crankshaft: The central shaft that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion.
- Piston: A key part that moves up and down within the cylinder, helping to generate power.
- Camshaft: Responsible for opening and closing the valves at the right moments during the engine cycle.
- Cylinder Head: Houses the valves and the combustion chamber, playing a critical role in the power generation process.
Fuel and Exhaust System
- Carburetor: Mixes air and fuel in the right proportions before combustion.
- Exhaust Valve: Allows the gases from combustion to exit the engine after power is produced.
- Air Filter: Keeps impurities out of the engine by filtering the incoming air supply.
Each of these components must be properly maintained and aligned to ensure smooth operation and longevity. Regular inspection and care can prevent issues and extend the lifespan of the engine.
Frame and Chassis Breakdown
The structure and bodywork of a two-wheeled vehicle play a crucial role in ensuring stability, comfort, and overall performance. These components are designed to withstand external forces while providing a solid foundation for other key systems. Understanding the various parts that make up the frame and chassis is essential for both maintenance and upgrades, as each element contributes to the overall integrity and functionality of the machine.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frame | The central skeleton that supports all other components, providing the base for the motor, suspension, and wheels. |
| Fork | Part of the front suspension system, responsible for steering and absorbing shocks from the road or terrain. |
| Swingarm | Suspension element that connects the rear wheel to the frame, allowing for controlled movement and stability. |
| Foot Pegs | Mounted on the frame, these provide a place for the rider’s feet, offering stability and control during operation. |
| Subframe | A secondary frame that supports additional components such as the seat and rear suspension, reinforcing the overall structure. |
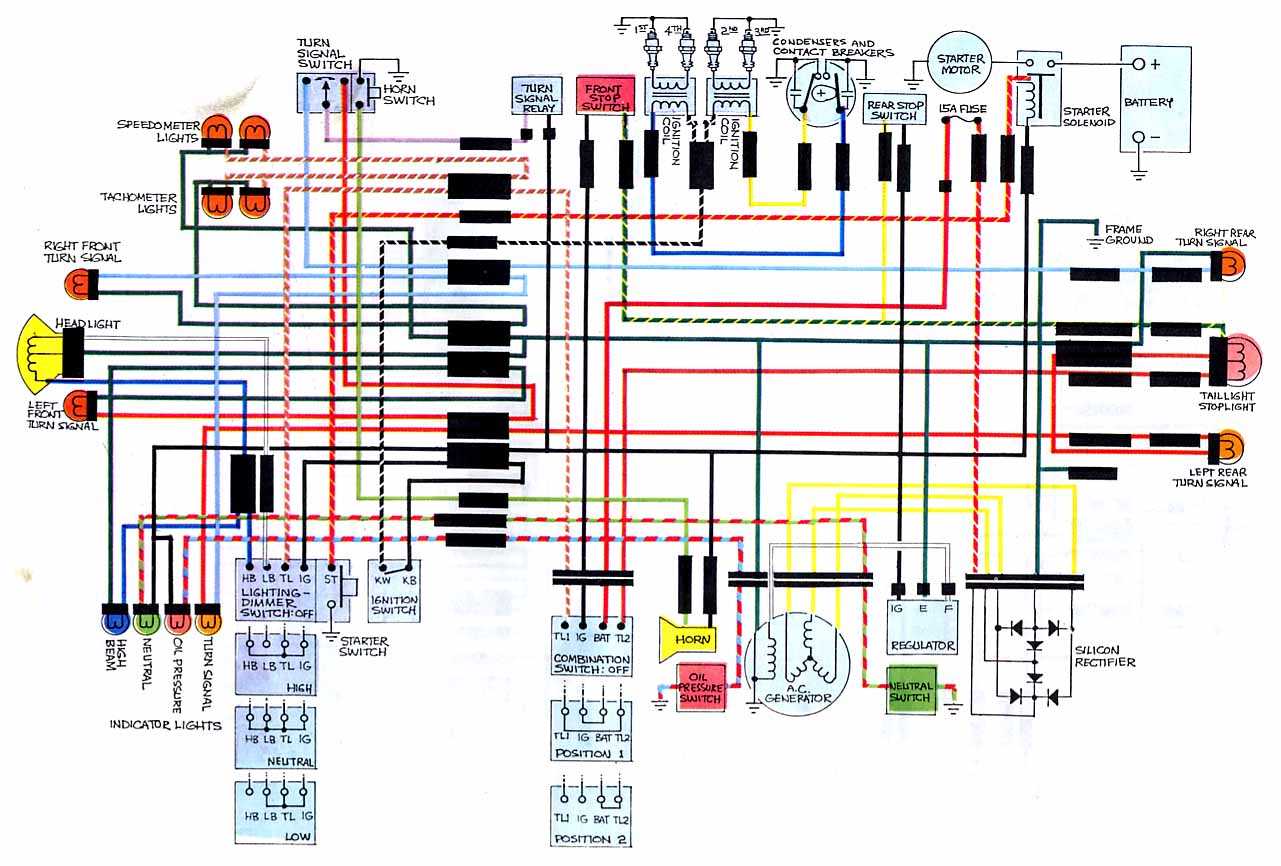
Electrical System Overview
The electrical setup in a two-wheeled vehicle is a vital component that ensures proper functioning of key systems such as lighting, ignition, and battery charging. It serves as the backbone for managing power distribution throughout the vehicle, connecting various electrical components in a seamless manner. Understanding the layout and function of the electrical system helps maintain optimal performance and address potential issues efficiently.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores and supplies electrical energy for starting the engine and powering accessories. |
| Ignition System | Ignites the fuel mixture in the engine, enabling it to start and run smoothly. |
| Headlight | Provides visibility during nighttime or low-light conditions for safe riding. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity to recharge the battery and power electrical systems while the engine runs. |
| Fuse Box | Protects electrical circuits by interrupting power in case of overloads or shorts. |
Suspension Parts and Their Functionality
The suspension system of a vehicle is essential for ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It plays a critical role in absorbing shocks and maintaining control, especially on uneven surfaces. This system consists of various components that work together to provide comfort, safety, and optimal handling. Each element of the suspension contributes to minimizing the impact of rough terrain and keeping the vehicle’s wheels in proper contact with the ground.
Shocks and Springs: These are the primary components responsible for cushioning the vehicle. Shocks help control the up-and-down motion of the vehicle after encountering bumps or dips, while springs absorb the energy from the road, preventing the vehicle from bouncing excessively.
Control Arms and Linkages: These parts connect the suspension to the vehicle’s frame and allow for the controlled movement of the wheels. They ensure that the wheels remain aligned during turns and straight driving, contributing to better handling and stability.
Bushings and Mounts: These are used to reduce vibrations and noise while improving the durability of the suspension system. Bushings absorb the stress between moving parts, while mounts secure components to the vehicle’s frame or body.
Fuel and Carburetor Components
The fuel system and carburetor are essential for ensuring smooth operation and efficient power delivery. These components work together to regulate the amount of fuel mixed with air, allowing the engine to perform at its best under various conditions. Understanding how these parts interact is key to maintaining proper functionality and resolving common performance issues.
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank is the starting point for the fuel delivery system. It stores and supplies fuel to the engine, ensuring a steady flow for combustion. Proper maintenance, such as cleaning and checking for leaks, is vital for optimal performance.
Carburetor: The carburetor is responsible for mixing fuel with air in the correct proportions before it enters the engine. It controls the engine’s speed and power output based on the air-fuel ratio. Regular cleaning and adjustment of the carburetor can prevent stalling and poor acceleration.
Throttle Valve: The throttle valve controls the amount of air entering the carburetor. By adjusting the throttle, the rider can regulate the engine’s power. A well-functioning throttle ensures smooth acceleration and deceleration.
Fuel Lines: Fuel lines transport gasoline from the tank to the carburetor. These lines must be checked periodically for cracks or leaks that could compromise fuel delivery. Ensuring these lines are clear and unobstructed is crucial for proper engine operation.
Choke: The choke enriches the air-fuel mixture during cold starts, helping the engine warm up more quickly. It should be used correctly to avoid flooding the engine or causing hard starts. Regular inspection and proper use of the choke are important for efficient starting in cold weather.
Air Filter: The air filter prevents dirt and debris from entering the carburetor, ensuring clean air mixes with fuel. A clogged air filter can reduce engine efficiency, so it should be cleaned or replaced regularly to maintain optimal airflow.
Brakes and Wheel Mechanisms Explained
Understanding the braking and wheel systems is essential for maintaining the overall performance and safety of any vehicle. These mechanisms work together to ensure smooth movement and controlled stopping power. Each component plays a crucial role in the interaction between the wheels and the road, providing stability and control during operation.
Key components of the braking system include:
- Brake pads: These provide the necessary friction to stop the vehicle when pressure is applied to the brake lever.
- Brake discs: Attached to the wheels, these discs help in dissipating the heat generated during braking.
- Brake calipers: These house the brake pads and apply pressure to the brake discs, helping to reduce speed.
In addition to braking, the wheel assembly also plays a pivotal role in handling and maneuvering. Essential parts of the wheel mechanism include:
- Rims: The outer part of the wheel, which holds the tire and connects to the axle.
- Hubs: These are central components that allow the wheels to rotate smoothly around the axle.
- Bearings: Located within the hubs, these reduce friction and ensure smooth wheel movement.
Transmission and Gear System Insights
The heart of any two-wheeled vehicle’s performance lies in its ability to efficiently transfer power from the engine to the wheels. This process involves a complex interaction of mechanical components that manage speed and torque. Understanding how the transmission and gear system function together is essential for optimizing riding experience and maintaining smooth operation.
Shifting gears allows the rider to adapt to different riding conditions, whether it’s climbing a steep incline or cruising at high speeds. Each gear has a specific purpose, influencing the overall acceleration and top speed. The system is designed to provide a balance between power and control, ensuring the rider can tackle various terrains with ease.
The quality of the gear engagement directly impacts the vehicle’s responsiveness. Proper lubrication and maintenance are critical to prevent wear and tear, ensuring longevity and smooth transitions between gears. By understanding how the transmission operates, riders can better anticipate the performance of their vehicle in various conditions, contributing to a safer and more enjoyable ride.
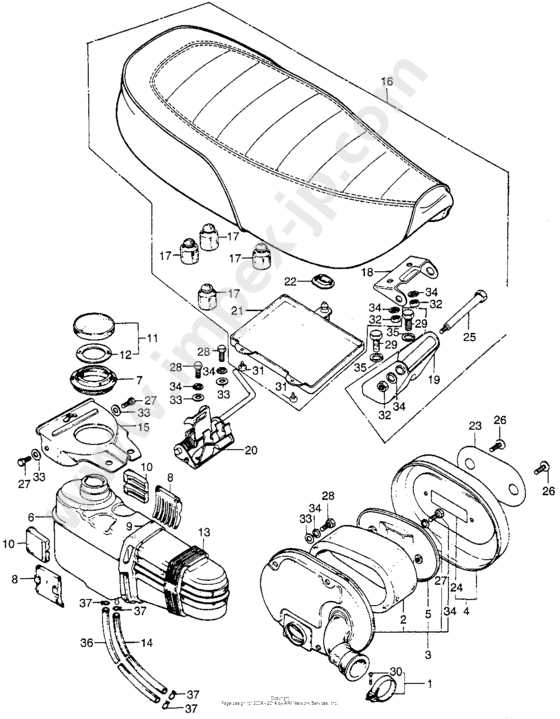
Identifying Exhaust and Muffler Parts

The exhaust system is a critical component that ensures smooth engine operation and reduces noise. Proper identification of the key components within this system is essential for maintenance and performance optimization. The primary parts responsible for controlling emissions and sound are the exhaust pipe and muffler. Understanding their structure and function helps in recognizing when replacements or repairs are needed.
Here are the main components commonly associated with the exhaust and muffler system:
- Exhaust Pipe: A metal tube that directs the gases away from the engine and through the system.
- Muffler: A device that reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Gasket: A sealing element that prevents leaks between the pipe and the engine head.
- Mounting Brackets: Components used to secure the exhaust and muffler to the frame or body.
- Heat Shield: A protective layer that prevents excessive heat from damaging nearby components.
By properly identifying and maintaining these elements, you ensure a quiet, efficient, and safe riding experience.
Choosing Replacement Parts for Longevity
When it comes to maintaining your vehicle, selecting the right components for replacement is essential for ensuring long-term performance and durability. Opting for high-quality replacements not only enhances the efficiency of the system but also reduces the risk of frequent repairs. The key to making the best choice lies in understanding the factors that contribute to the longevity of these components, such as material quality, design compatibility, and the environment in which the vehicle operates.
Material Quality
The longevity of any replacement component largely depends on the materials used in its construction. Choosing items made from durable, corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or high-grade alloys ensures that they can withstand wear and tear, harsh weather conditions, and mechanical stress. While cost-effective options may seem appealing initially, investing in more robust materials can save money in the long run by reducing the frequency of replacements.
Compatibility with Your Vehicle
It’s crucial to ensure that the replacements you choose are perfectly suited for your vehicle’s specifications. Using components designed to work seamlessly with your vehicle’s original design can prevent premature damage and improve overall performance. Even minor mismatches in size, shape, or functionality can cause strain on the system, leading to further issues down the line.
| Component | Material | Longevity Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Chain | Stainless Steel | High resistance to rust and wear |
| Brake Pads | High-Quality Carbon Composite | Improved friction and heat tolerance |
| Wheels | Alloy | Better durability under pressure |