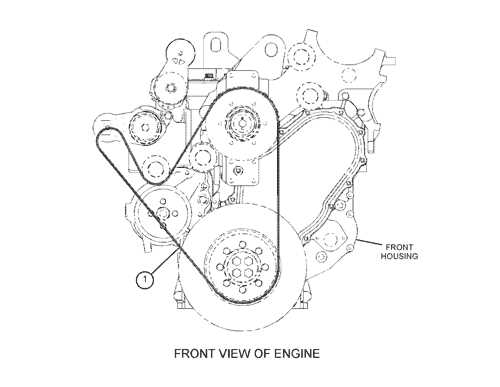
When delving into the intricacies of heavy-duty vehicles, a comprehensive understanding of their structural layouts is essential. These layouts serve as visual representations, guiding technicians and enthusiasts alike in identifying and locating various elements within the machinery. Analyzing these layouts enhances the ability to troubleshoot, repair, and maintain vehicles effectively.
In the context of commercial transportation, familiarity with the configurations of specific models is particularly valuable. Each vehicle possesses unique characteristics, and recognizing these distinctions can significantly influence performance and longevity. This knowledge is vital for ensuring that maintenance tasks are executed accurately and efficiently.
Moreover, grasping the arrangement of various components fosters a deeper appreciation of the engineering involved in vehicle design. It allows individuals to comprehend how different systems interact, leading to improved functionality. By mastering these layouts, one can approach mechanical challenges with confidence and precision, contributing to safer and more reliable operation.
Understanding the International 4300 Model
This section explores a specific model known for its robustness and versatility in various commercial applications. Often utilized in the transportation and logistics sectors, this vehicle combines strength with efficiency, making it a preferred choice among fleet operators. Understanding its key features and functionalities can greatly enhance operational performance.
Key Features
The vehicle is designed with a strong chassis, ensuring durability under heavy loads. It typically includes a powerful engine option, which contributes to its reliability and performance on the road. Additionally, the spacious cabin provides comfort for the driver, making long hauls more manageable.
Common Applications
This model is frequently employed in diverse sectors, including construction, delivery services, and waste management. Its adaptability allows it to be configured for various tasks, ranging from hauling cargo to serving as a base for specialized equipment. Such versatility makes it an asset in numerous industries.
Key Components of the Vehicle
The functionality and efficiency of a heavy-duty truck rely on several critical elements that work together seamlessly. Understanding these essential components is vital for both maintenance and performance optimization.
One of the primary features is the chassis, which provides the structural foundation for the entire vehicle. This robust framework supports all other elements, including the engine, which is crucial for generating the power needed for movement. The transmission system plays a vital role by transferring that power to the wheels, ensuring smooth operation across various terrains.
Another significant aspect is the braking system, which guarantees safe stopping and control during driving. Additionally, the suspension system enhances ride quality by absorbing shocks and vibrations, making long hauls more comfortable for the driver.
Moreover, the electrical system powers critical features such as lighting, instrumentation, and communication devices, contributing to overall safety and functionality. Each of these components is integral to the vehicle’s operation, highlighting the importance of proper maintenance and understanding for optimal performance.
Electrical System Overview
The electrical architecture of a vehicle is fundamental to its operation, providing the necessary energy to various components. This system ensures that all electrical devices function harmoniously, enabling essential functions like starting the engine, powering lights, and facilitating communication between different parts of the vehicle. Understanding this framework is crucial for troubleshooting issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Key Components
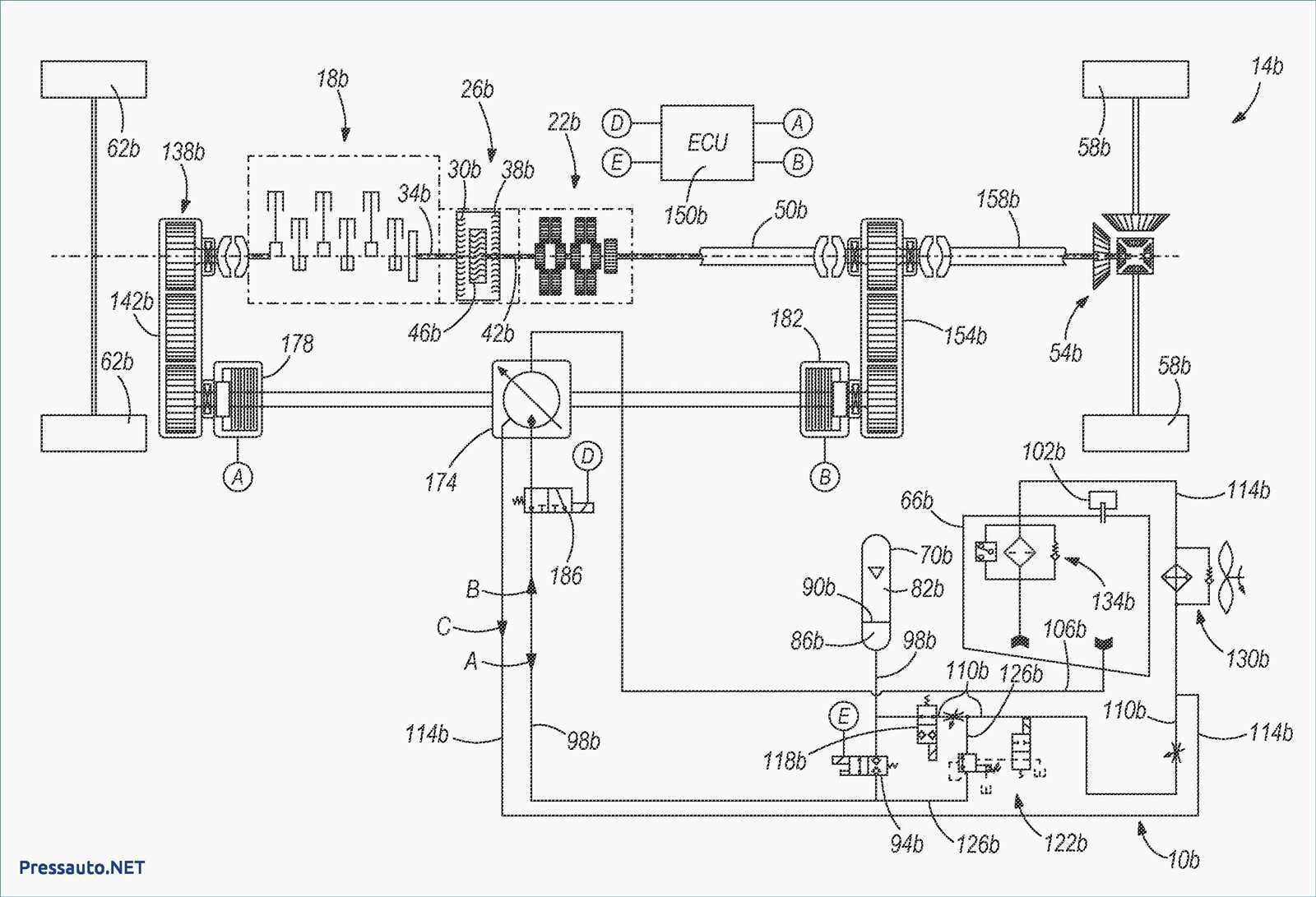
Several integral elements make up the electrical system, each serving a specific purpose. Below is a table summarizing these components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine and operate electrical devices. |
| Alternator | Generates electricity while the engine is running, recharging the battery and powering electrical systems. |
| Starter Motor | Engages the engine to initiate the combustion process. |
| Fuses | Protect electrical circuits by preventing overloads and short circuits. |
| Wiring Harness | Connects all electrical components, allowing the flow of electricity throughout the vehicle. |
System Functionality
The electrical framework operates through a complex network of connections that allow for efficient energy distribution. It ensures that power reaches the necessary devices at the right time, enhancing overall functionality. Proper maintenance of this system is vital to prevent failures and ensure the longevity of the vehicle.
Engine Specifications and Parts
This section provides an overview of the essential components and characteristics of the engine, highlighting its significance in vehicle performance and efficiency. Understanding these features is crucial for proper maintenance and optimal functioning.
Key specifications include:
- Engine Type: A description of the design and configuration, such as inline or V-type.
- Displacement: The total volume of all the cylinders, typically measured in liters or cubic inches.
- Power Output: The maximum horsepower produced, which influences the vehicle’s acceleration and towing capacity.
- Torque: The rotational force generated at the engine’s output, essential for effective hauling and climbing.
- Fuel Type: The recommended fuel grade that ensures efficient combustion and engine longevity.
Important components of the engine include:
- Cylinder Block: The core structure housing the cylinders and supporting the internal components.
- Pistons: Movable parts within the cylinders that convert fuel energy into mechanical work.
- Cylinder Head: The top section of the engine, containing intake and exhaust valves that regulate airflow.
- Crankshaft: The shaft that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Timing Belt/Chain: A crucial component ensuring proper synchronization of the engine’s moving parts.
Understanding these specifications and components will assist in making informed decisions regarding maintenance, repairs, and upgrades to enhance the overall performance of the vehicle.
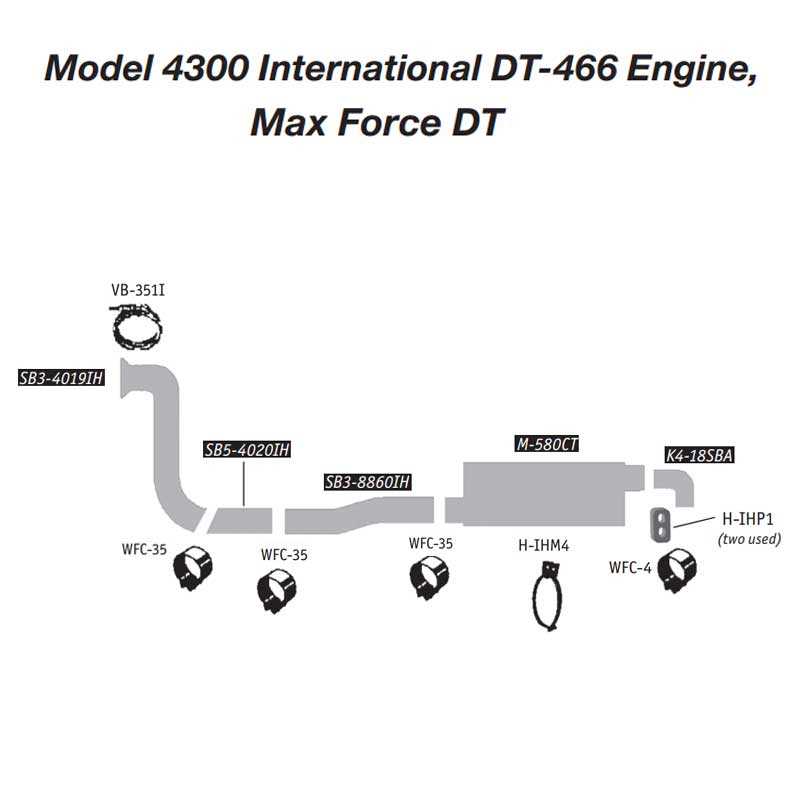
Transmission Details and Diagrams
This section provides an overview of the components and configurations associated with the gear-shifting mechanism found in heavy-duty vehicles. Understanding these elements is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
The transmission system consists of various parts that work together to facilitate smooth gear changes. Below are the key components:
- Gear Sets: These sets are designed to provide different gear ratios, allowing for efficient power transfer and speed regulation.
- Torque Converter: This component transmits power from the engine to the transmission, enhancing acceleration while preventing stalling.
- Clutch Mechanism: Engages and disengages the power flow, enabling smooth transitions between gears.
- Shifter Linkage: Connects the gear shifter to the transmission, allowing the driver to select the desired gear.
Understanding the layout of these components is essential for effective repair and servicing. The following illustrations depict the arrangement and interaction of the transmission parts:
- Overview of the Gear System: This illustration highlights the primary gear sets and their arrangement.
- Torque Converter Functionality: A diagram explaining how the torque converter operates within the transmission.
- Clutch Operation: A detailed look at the clutch mechanism and its role in gear changes.
Familiarity with these elements will aid in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the vehicle’s drivetrain.
Chassis and Frame Components
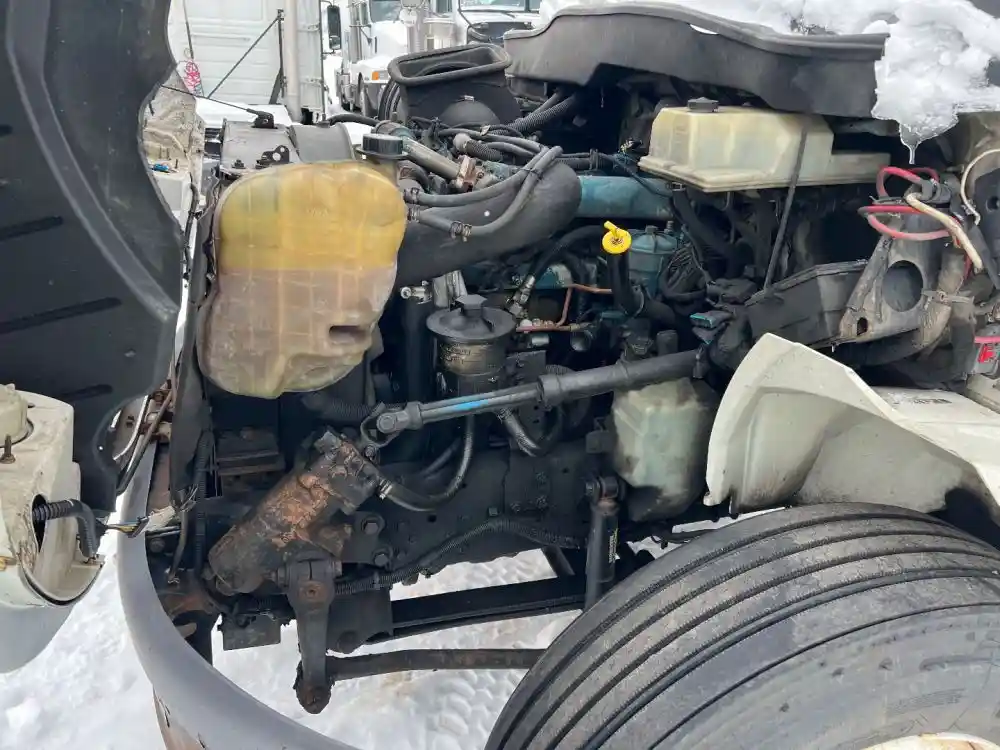

The structural foundation of any vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall performance and stability. This section delves into the essential elements that make up the undercarriage and framework, ensuring durability and support for various components. Understanding these elements is vital for both maintenance and enhancement of the vehicle’s capabilities.
Frame: The frame serves as the backbone of the vehicle, providing the necessary support for the body and other mechanical systems. It is designed to withstand various loads and stresses while maintaining structural integrity. Typically made from high-strength steel, the frame is engineered to offer both flexibility and rigidity.
Crossmembers: These horizontal members are integral to the frame, connecting the side rails and enhancing torsional stiffness. They provide mounting points for critical components such as the suspension system and drivetrain, ensuring proper alignment and functionality.
Cab Mounts: These mounts are essential for securing the driver’s compartment to the chassis. They help absorb vibrations and impacts, contributing to a smoother ride. Proper installation and maintenance of cab mounts are vital for ensuring driver comfort and safety.
Suspension System: The suspension system, while part of the overall framework, deserves special attention. It is designed to support the vehicle’s weight, absorb shocks, and maintain contact with the road surface. A well-functioning suspension contributes to handling, stability, and overall ride quality.
Axle Assemblies: These components connect the wheels to the frame and are crucial for transferring power from the engine to the road. They play a significant role in determining the vehicle’s load capacity and handling characteristics, making their design and maintenance vital for optimal performance.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the framework and its components is essential for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance or enhancement. Each part plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall functionality and safety of the vehicle.
Suspension System Breakdown
The suspension system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It consists of various components that work together to absorb shocks from the road, maintain tire contact, and enhance overall driving comfort. Understanding the elements that comprise this system is essential for diagnosing issues and performing effective maintenance.
Key Components
Several vital parts contribute to the functionality of the suspension mechanism. Shock absorbers are responsible for damping the oscillations of the springs, preventing excessive bouncing. Leaf springs, commonly found in heavier vehicles, provide support and stability by distributing weight evenly across the chassis. Control arms connect the suspension to the vehicle frame, allowing for controlled wheel movement.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection and maintenance of the suspension components are essential for ensuring optimal performance. Worn-out bushings and damaged shock absorbers can lead to compromised handling and increased wear on tires. Keeping the suspension system in good condition not only enhances ride quality but also contributes to overall vehicle safety.
Braking System Overview
The braking mechanism is a critical component of any vehicle, ensuring safe and controlled deceleration. This system plays a vital role in vehicle dynamics, contributing to overall safety by allowing the driver to effectively manage speed and halt motion when necessary. Understanding the functionality and components of the braking system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
Key Components
At the heart of the braking system are several essential elements that work in concert to facilitate effective stopping power. These include:
- Brake Pads: These components create friction against the rotor to slow down or stop the wheels.
- Rotors: The discs that the brake pads clamp down on, converting kinetic energy into heat.
- Calipers: These house the brake pads and pistons, applying pressure to the pads against the rotors.
- Brake Lines: These transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, enabling the braking action.
Operating Principle
The operation of the braking mechanism relies on the principles of hydraulics. When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic fluid is forced from the master cylinder through the brake lines. This pressure activates the calipers, which in turn push the brake pads against the rotors. The resulting friction generates heat and slows the vehicle down. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential for ensuring efficient operation and preventing potential failures.
Fuel System and Components
The fuel mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in its performance and efficiency. This system is responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal combustion and operation. Understanding the components involved in this mechanism is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Fuel System
The fuel system comprises several integral parts that work together to facilitate the proper flow and distribution of fuel. Each component has a specific function that contributes to the overall efficiency of the engine.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel before it is sent to the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Moves fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel to protect the engine. |
| Fuel Injector | Delivers the precise amount of fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and engine. |
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel system components are vital for preventing potential issues. This includes checking for leaks, ensuring proper fuel flow, and replacing filters as needed. Proper upkeep of this system enhances the overall efficiency and longevity of the vehicle.
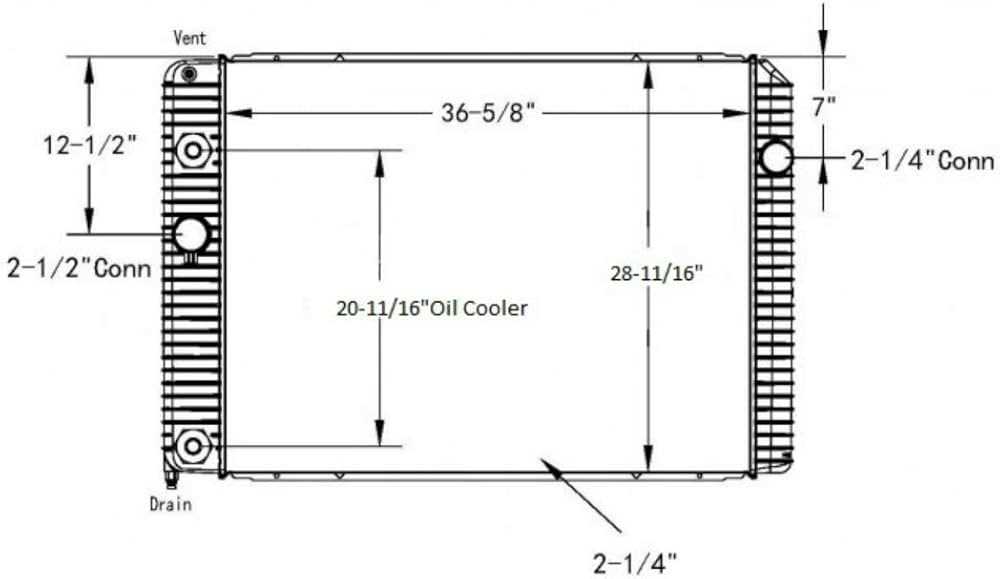
Cooling System Essentials
A well-functioning cooling mechanism is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and longevity. This system is responsible for regulating the temperature of the engine, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient operation. Understanding the components and their roles can significantly enhance maintenance efforts and performance efficiency.
Key Components of the Cooling Mechanism
The cooling assembly typically includes a radiator, water pump, thermostat, and coolant. Each part plays a vital role in heat dissipation and temperature control. The radiator acts as a heat exchanger, dissipating heat from the coolant that circulates through the engine. The water pump is essential for maintaining fluid flow, while the thermostat regulates the coolant temperature to ensure it operates within a specific range.
Maintenance and Common Issues
Regular inspection and maintenance of the cooling system are vital to prevent common problems such as leaks, clogs, or component failure. Checking the coolant level and quality, as well as inspecting hoses and connections, can help identify potential issues early. Addressing these concerns promptly can prevent severe engine damage and ensure the system functions effectively.
Interior Layout and Features
The interior design of this vehicle emphasizes functionality and comfort, ensuring that the driver and passengers enjoy a user-friendly experience. A well-thought-out arrangement of elements enhances both accessibility and efficiency, making it ideal for various tasks and journeys.
Cockpit Design
The cockpit is meticulously crafted to offer an intuitive control layout. Key elements include:
- Ergonomically positioned controls for ease of access
- High visibility dashboard with clear instrumentation
- Comfortable seating designed for long hours of operation
- Ample storage compartments for tools and personal items
Seating and Comfort
Comfort plays a vital role in the overall experience, with a focus on providing a pleasant atmosphere for both the driver and passengers. Key features include:
- Adjustable seats to accommodate different body types
- Climate control options for year-round comfort
- Sound insulation to minimize external noise
- Spacious legroom for enhanced comfort during travel
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and optimal performance of your vehicle requires consistent upkeep and attention to various components. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of essential systems but also enhances overall reliability, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures. Following a structured maintenance routine can significantly contribute to the vehicle’s efficiency and safety.
| Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 5,000 miles | Replace engine oil and filter to ensure proper lubrication and reduce wear. |
| Fluid Levels Check | Monthly | Inspect and top off fluids, including coolant, brake fluid, and transmission fluid. |
| Tire Inspection | Every 6,000 miles | Examine tire pressure, tread depth, and alignment to promote even wear and handling. |
| Brake System Check | Every 10,000 miles | Inspect brake pads, rotors, and fluid for optimal stopping power. |
| Battery Maintenance | Annually | Clean terminals and check charge levels to prevent starting issues. |
By adhering to these guidelines, you can significantly enhance the lifespan of your vehicle while ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Regular attention to these areas will help prevent costly repairs and maintain peak performance.