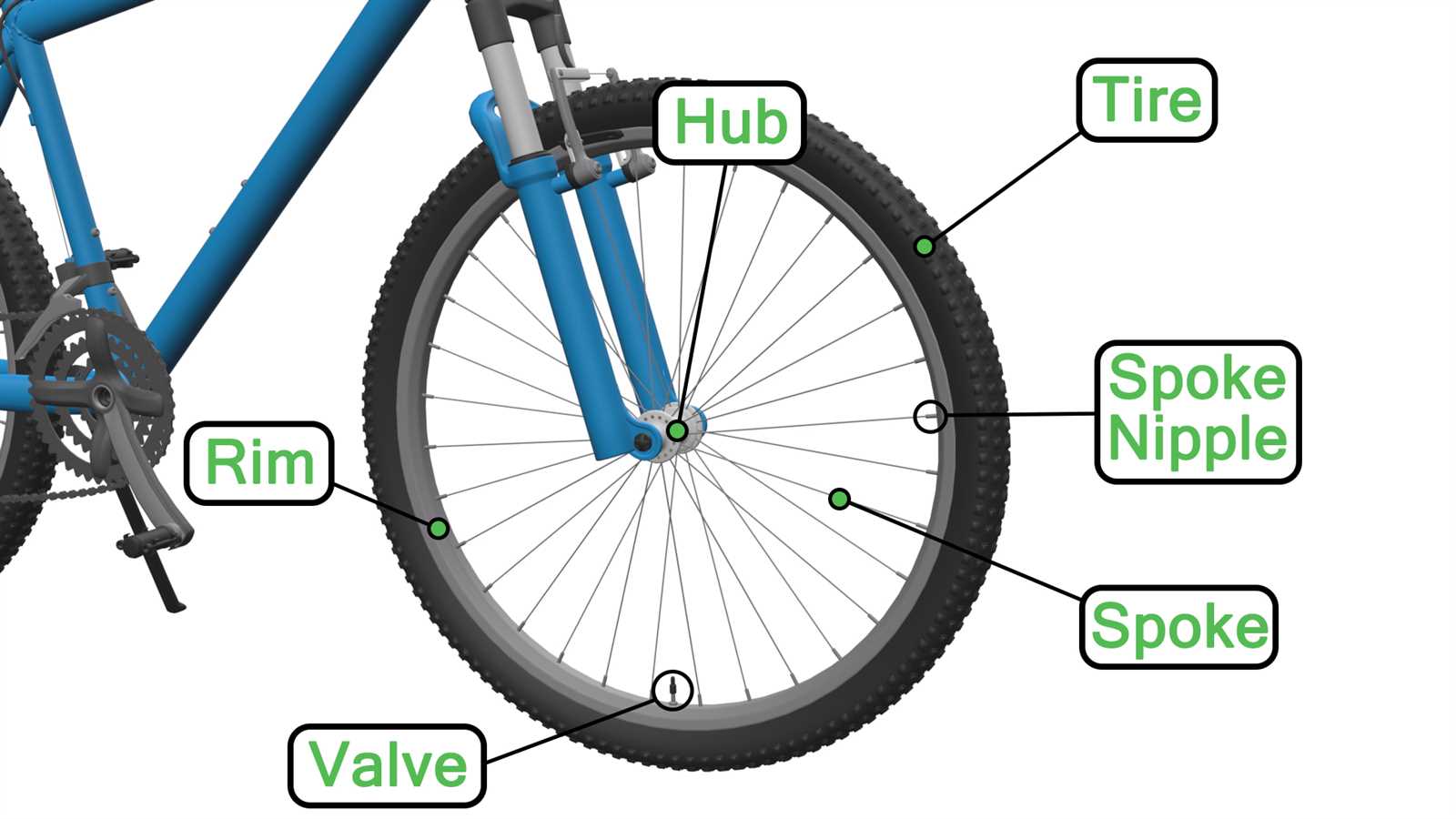
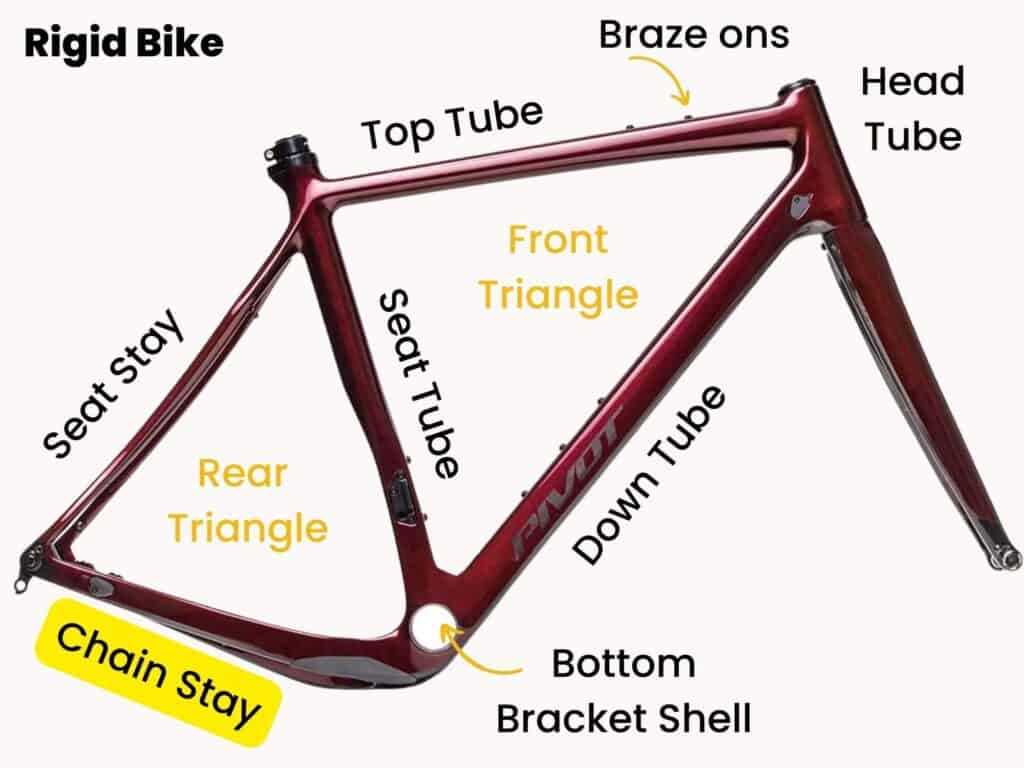
Exploring the intricacies of a two-wheeled vehicle’s propulsion system reveals a fascinating interplay of elements that work harmoniously to ensure efficient movement. Each component serves a specific function, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the system.
Visual representations can significantly enhance comprehension, allowing enthusiasts and mechanics alike to grasp the layout and functionality of these essential mechanisms. By dissecting the individual elements, one can appreciate the engineering that enables smooth operation.
Moreover, delving into the specifics of each segment not only fosters a deeper understanding but also empowers users to identify potential issues and maintain their vehicle effectively. The ultimate goal is to create a seamless riding experience, backed by knowledge and skill.
Bicycle Chain Parts Overview
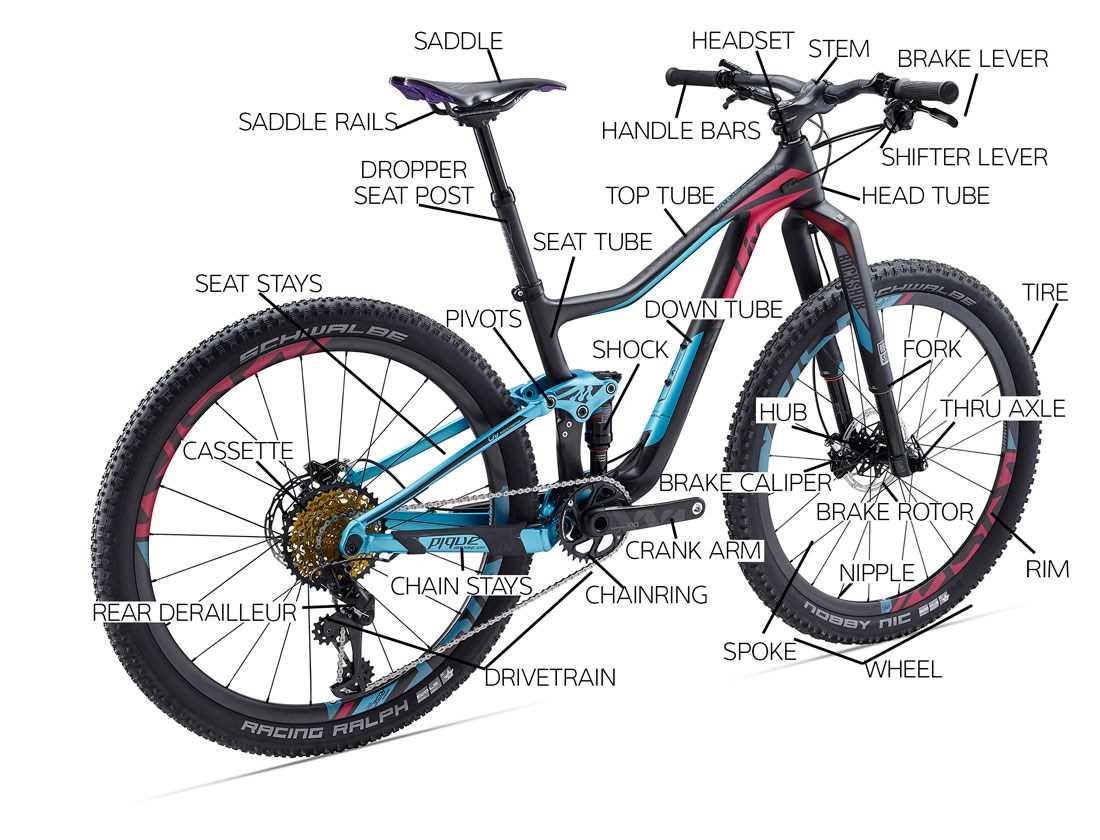

This section provides an insight into the essential components that contribute to the smooth functioning of a two-wheeled vehicle’s propulsion system. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and performance optimization.
- Links: The individual segments that connect to form the entire mechanism.
- Rollers: Cylindrical elements that facilitate smooth movement as they engage with the gear teeth.
- Pin: A crucial piece that secures the links together, ensuring structural integrity.
- Plates: Flat surfaces that help maintain alignment and support the overall configuration.
- Master Link: A specialized link that allows for easy assembly and disassembly of the entire system.
Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient energy transfer from the pedals to the wheels, enhancing the riding experience.
- Regular inspection of each element can prevent premature wear.
- Proper lubrication is vital for maintaining optimal function.
- Replacement of worn-out components can significantly improve overall performance.
By familiarizing oneself with these integral segments, riders can make informed decisions regarding care and upgrades.
Key Components of Bicycle Chains
Understanding the essential elements of a cycling propulsion system is crucial for optimal performance and maintenance. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and durability.
- Links: These are the individual segments that connect together, forming the flexible mechanism.
- Rollers: Positioned between links, they facilitate movement and reduce friction.
- Pins: These connect the links, providing structural integrity and flexibility.
- Inner and Outer Plates: They sandwich the rollers, contributing to strength and durability.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can significantly enhance the overall efficiency and longevity of the system.
Understanding Chain Links Functionality
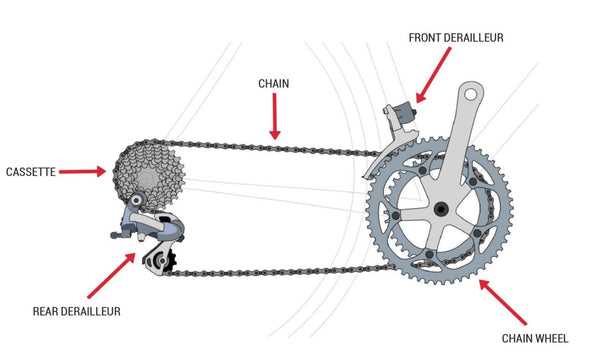
At the heart of every cycling mechanism lies a crucial element that facilitates movement and power transfer. This intricate system allows for efficient energy transmission, ensuring a seamless ride. Each individual segment plays a significant role in achieving optimal performance and longevity, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the equipment.
Role of Each Link
Each segment functions as a connector, allowing for flexibility and adaptability while maintaining strength. The design of these components ensures they can withstand tension and pressure, making them vital for achieving smooth operation. Their interplay ensures that energy generated by the rider is effectively converted into forward motion.
Maintenance and Longevity
Importance of Chain Rollers
Rollers play a crucial role in the smooth operation of a cycling system, ensuring efficient energy transfer and minimizing friction. Their design and functionality significantly affect the overall performance and longevity of the entire mechanism.
Efficiency and Performance

High-quality rollers enhance the overall efficiency, allowing for a seamless transition of energy from the pedals to the wheels. This results in a smoother ride and improved speed, essential for both casual and competitive riders.
Maintenance and Durability
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for preventing wear and tear. Proper care not only extends the lifespan of the system but also ensures safety and reliability during use. Investing in durable rollers can ultimately lead to a more enjoyable cycling experience.
Chain Pin: Role and Purpose
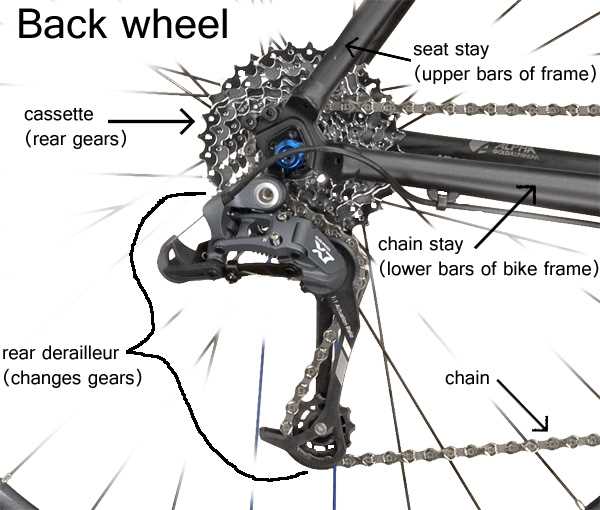
The fundamental element in the movement of mechanical systems serves a crucial function in linking various components together. Its design and placement are vital for seamless operation and durability.
Key roles of this component include:
- Ensuring secure connections between links.
- Facilitating smooth rotation and movement.
- Minimizing wear and tear through effective load distribution.
Understanding the significance of this component helps in:
- Enhancing overall efficiency.
- Improving longevity of the system.
- Reducing maintenance requirements.
How Chain Plates Work
The functioning of these essential components is pivotal in the overall efficiency of any mechanical system. They play a crucial role in the transmission of energy and motion, ensuring seamless operation.
Understanding their design is fundamental to grasping how they interact with other elements. Each piece is crafted to fit precisely, allowing for smooth engagement and disengagement during movement. This intricate connection is vital for maintaining performance and durability.
The materials used in their construction often include durable alloys, providing strength and resistance to wear. This selection is significant, as it directly impacts the longevity and reliability of the entire mechanism.
In essence, these components serve as the backbone of the system, enabling power transfer with minimal friction and maximum efficiency. Recognizing their importance can enhance one’s appreciation for the complexities involved in mechanical design.
Impact of Chain Wear on Performance
Wear and tear of critical components can significantly affect overall functionality and efficiency. As these elements degrade over time, they may lead to diminished responsiveness and increased energy loss during operation.
Performance decline is often linked to increased friction and misalignment, which can result in a less smooth experience. When components are not functioning optimally, users may notice a reduction in speed and power transfer, ultimately hindering performance.
Additionally, excessive wear can lead to further mechanical issues, potentially requiring more frequent maintenance or replacement. Addressing these concerns promptly can ensure longevity and maintain the ultimate effectiveness of the system.
Maintenance Tips for Chain Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your vehicle’s drive system requires consistent attention and care. By following specific maintenance practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of the components involved. Regular upkeep not only enhances performance but also prevents unnecessary wear and tear.
Regular Cleaning
Keeping the system clean is crucial for optimal functioning. Dirt and grime can accumulate, leading to increased friction and damage. Here are some effective cleaning steps:
- Use a soft brush to remove loose debris.
- Apply a suitable degreaser to break down stubborn grime.
- Rinse thoroughly and allow it to dry completely before re-lubricating.
Proper Lubrication
Lubrication plays a vital role in maintaining smooth operation. A well-lubricated system reduces friction and enhances efficiency. Follow these tips:
- Choose high-quality lubricant designed for your specific needs.
- Apply the lubricant evenly, ensuring complete coverage of the contact surfaces.
- Wipe off any excess to avoid attracting more dirt.
By incorporating these practices into your routine, you can promote the longevity of your drive system and enjoy a smoother experience overall.
Types of Bicycle Chains Available
When it comes to enhancing performance and durability, understanding the various options in the world of link systems is essential. Each variation is designed to cater to specific riding styles, terrain types, and overall functionality, making the right choice critical for achieving optimal results.
Single-Speed Systems
These configurations are straightforward and ideal for urban commuting or leisurely rides. With a simplified design, they offer ease of maintenance and efficient power transfer, making them a popular choice for riders who prefer minimalism and reliability.
Multi-Speed Variations
Engineered for versatility, these setups accommodate a range of gears, allowing for smooth transitions across different terrains. They are particularly favored by those who enjoy varied landscapes, from steep hills to flat roads, providing an adaptable solution for diverse cycling experiences.
Choosing the Right Chain for Your Bike
Selecting the appropriate linking mechanism for your two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the specifications and requirements can significantly enhance your riding experience, ensuring smooth operation and reliability on various terrains.
Factors to Consider
When making your choice, consider the size, compatibility with your gear system, and the material. Each element plays a vital role in how efficiently your machine operates. Additionally, pay attention to the number of speeds and the intended use, whether it’s for commuting or off-road adventures.
Compatibility Table
| Type | Speed Compatibility | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 1-6 speeds | Casual riding |
| Multi-speed | 7-11 speeds | Urban commuting |
| High-performance | 12+ speeds | Competitive cycling |
Common Issues with Bicycle Chains
Every cycling enthusiast may encounter various challenges related to the mechanism that transfers power from the pedals to the wheels. Understanding these common problems can enhance the overall performance and longevity of your two-wheeled companion.
Wear and Tear: Over time, components may experience degradation due to friction and environmental factors. Regular inspections are essential to identify signs of wear early.
Misalignment: Improper alignment can lead to inefficient power transfer and increased resistance. Ensuring that the setup is correctly adjusted can improve overall efficiency.
Rust and Corrosion: Exposure to moisture can lead to rust, affecting movement and performance. Keeping the mechanism clean and properly lubricated is crucial for preventing this issue.
Stiff Links: Occasionally, links may become stiff due to debris or lack of lubrication. Regular maintenance can help keep these connections smooth and functional.
Skipping: If the mechanism skips under load, it may indicate compatibility issues or damage. Identifying and addressing the root cause is vital for a seamless ride.
Tools for Chain Inspection and Repair
Maintaining optimal functionality of your ride requires specific implements designed for thorough examination and restoration of the crucial elements involved. Regular check-ups help prevent issues and enhance overall performance, making it essential to have the right tools on hand.
Essential Inspection Tools
Utilize a wear indicator to assess the condition of the links and ensure they remain within acceptable limits. A ruler or caliper can also be invaluable for measuring elongation and detecting any deviations that may require attention.
Repair Implements
For repairs, a link remover is indispensable for quick adjustments or replacements. Pair it with a replacement kit that includes connectors and pins to ensure you’re prepared for any unexpected issues.
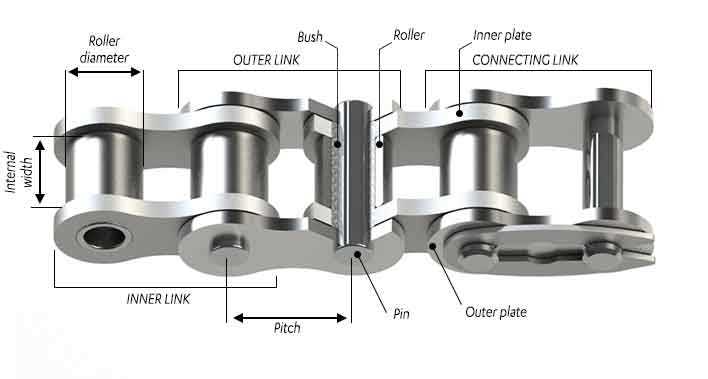
Visual Guide to Chain Diagrams
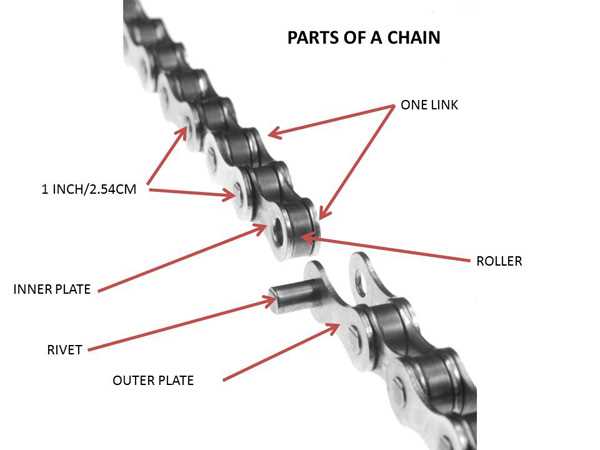
This section provides an insightful overview of the components involved in the mechanical linkage of a cycling system. Understanding the visual representation of these elements enhances one’s comprehension of their functions and interrelations.
Key components often illustrated include:
- Links: The individual units that form the entire structure.
- Connecting Pins: Essential for joining the links together.
- Rollers: Facilitate smooth movement along the gear mechanisms.
- Outer Plates: Provide stability and protection to the internal elements.
- Inner Plates: Help secure the rollers and maintain overall integrity.
By analyzing these visuals, enthusiasts can better appreciate the mechanics at play and the importance of maintenance and adjustments. The following points outline how to effectively interpret these illustrations:
- Identify each component and its role within the system.
- Note the arrangement and how it affects performance.
- Understand the impact of wear and tear on functionality.
- Recognize how modifications can enhance efficiency.
Ultimately, a well-rounded grasp of these visuals is crucial for anyone looking to delve deeper into the mechanics of cycling systems.