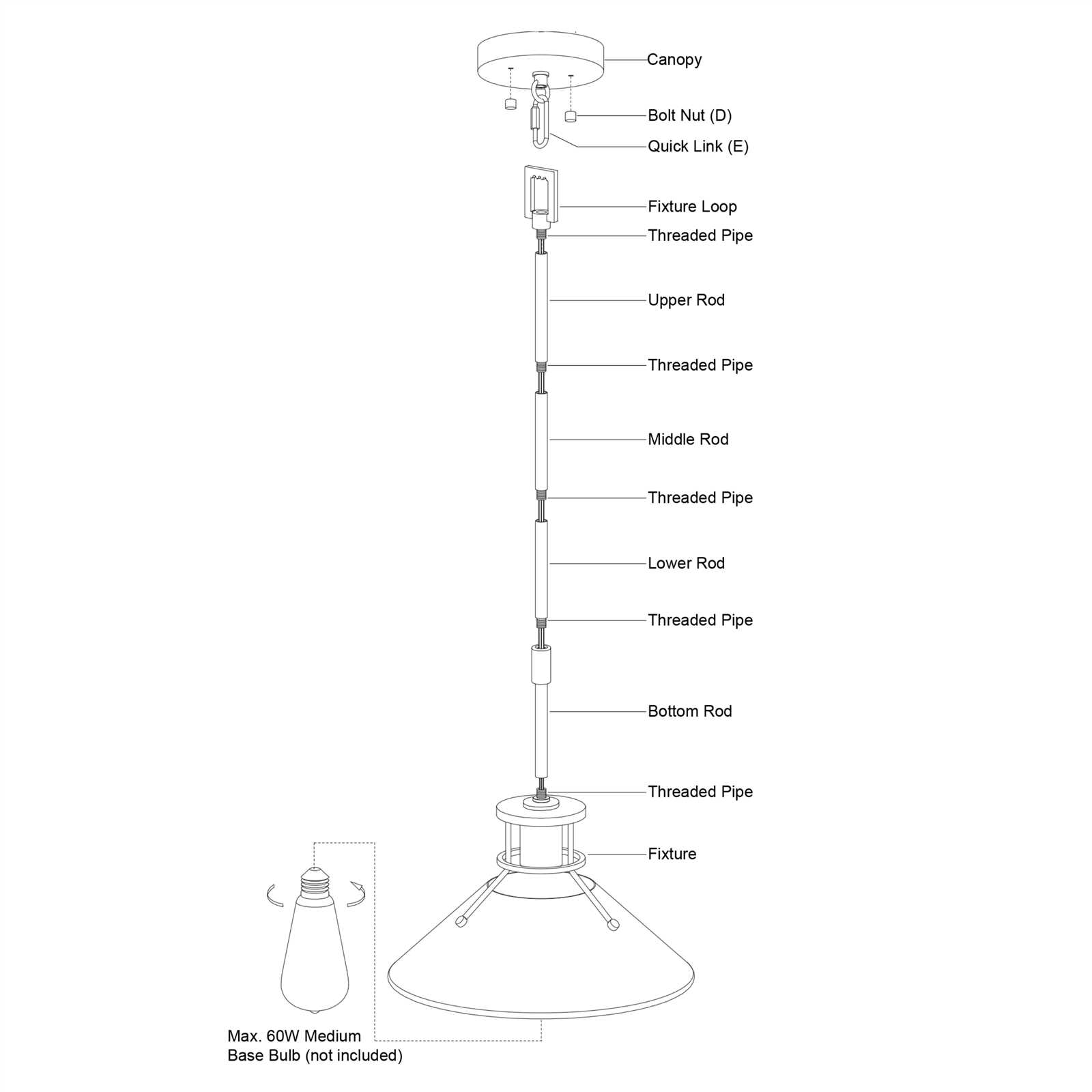
When it comes to enhancing the ambiance of a room, overhead systems play a crucial role in delivering both functionality and aesthetics. The components that make up these systems work together to provide efficient illumination while adding a decorative touch to the overall design. By exploring the individual elements, one can gain a better understanding of how these systems operate and how they contribute to the look and feel of an interior space.
The arrangement of components in such a system may seem complex, but with a closer look, each element serves a specific purpose in ensuring optimal performance. From the connectors that hold everything together to the electrical mechanisms that enable proper functioning, each piece is designed to interact seamlessly with the others. Understanding these connections is essential for both installation and maintenance.
In this section, we will delve into the key elements that form the basis of overhead illumination systems. By examining the role of each part, we aim to provide clarity on their functionality and how they contribute to the overall performance of the setup. This guide will serve as a helpful reference for those looking to familiarize themselves with the intricate details of these systems.
Understanding the Structure of Ceiling Light Fixtures
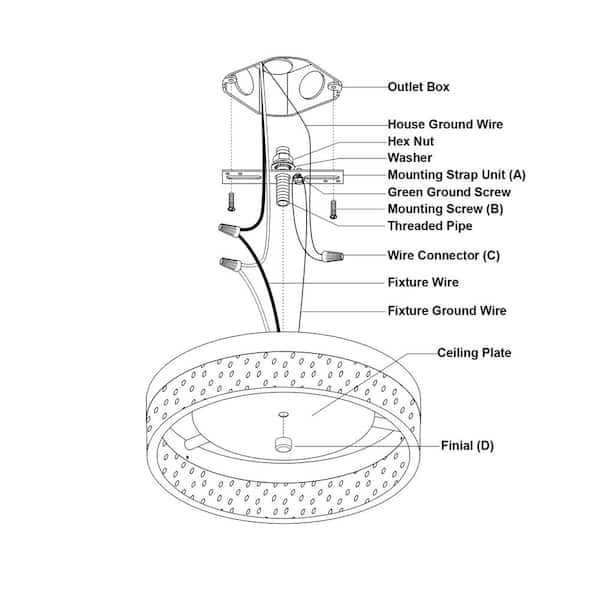
Examining the design and internal framework of overhead illumination units allows one to appreciate how various components work together to produce effective lighting. By understanding the key elements that make up these units, users can better manage maintenance and potential upgrades.
- Base Unit: The foundational component that holds everything together and is mounted onto the surface.
- Wiring Mechanism: A crucial part that facilitates the flow of electricity, connecting the unit to the power supply.
- Cover or Enclosure: Protects the inner components while also diffusing light for a balanced effect in the room.
- Bulb Holder: The section designed to securely hold and position the bulb in place, ensuring proper function.
- Fastening Elements: These include screws or clips, which ensure that all parts are securely connected and safe for operation.
By recognizing these essential elements, one gains a better understanding of how these units operate and what is needed to maintain them effectively over time.
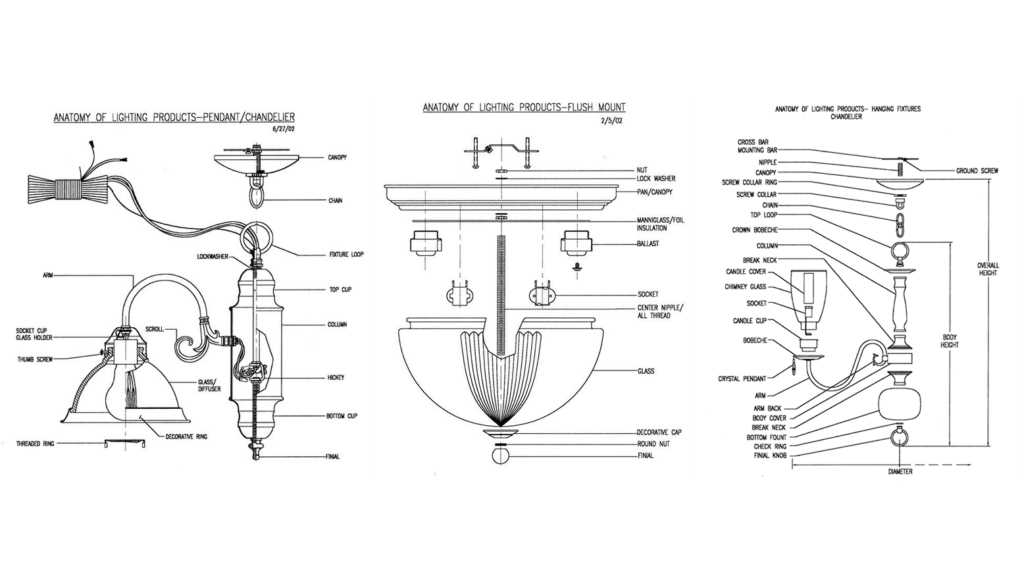
Main Components of a Ceiling Light
Understanding the key elements that make up an overhead illumination device is crucial for its proper installation and maintenance. These components work together to provide functional and aesthetic lighting in any room, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Core Elements
- Mounting Base: This component serves as the foundation, securing the lighting device to the surface and providing structural support.
- Electrical Wires: These carry the current necessary for powering the illumination source, connecting it to the building’s electrical system.
- Fasteners: Screws, brackets, or other hardware that hold various pieces together, ensuring stability and durability.
Light Source Holder
This part houses the bulb or another type of light source, ensuring it is positioned correctly for optimal performance. It also serves to connect the electrical current to the light, allowing it to function safely.
- Socket: Holds the light source in place and connects it to the electrical wiring.
- Reflector: Positioned behind the bulb, it helps to direct the light output efficiently into the room.
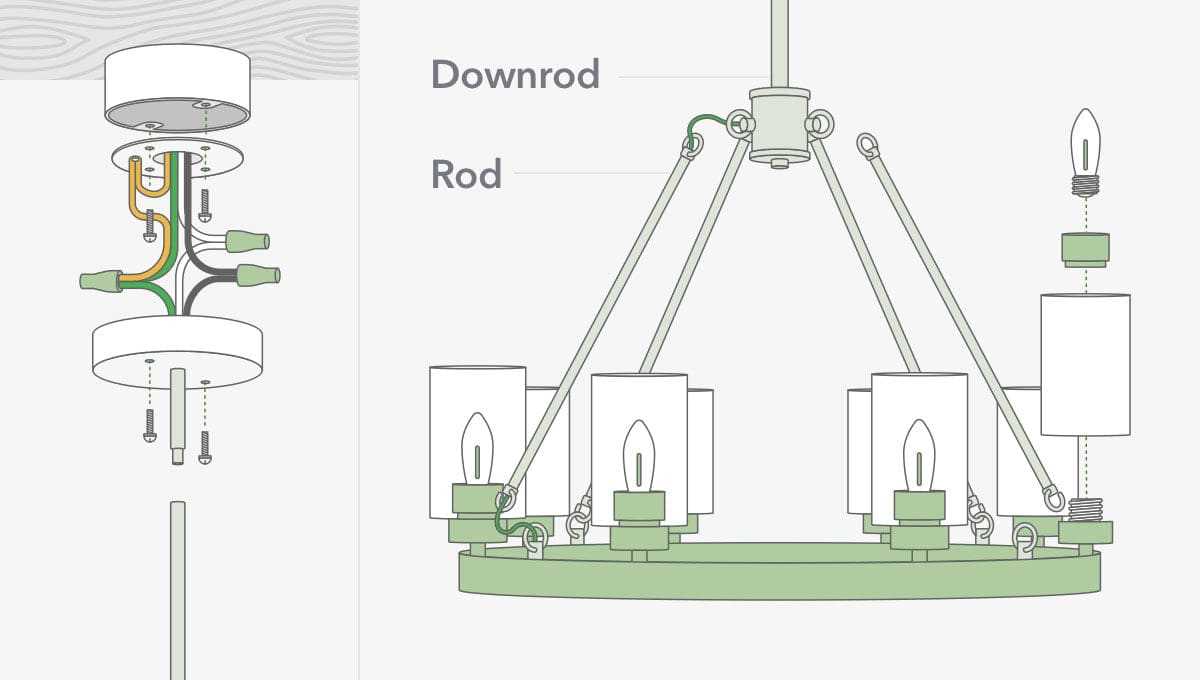
Electrical Wiring in Ceiling Fixtures
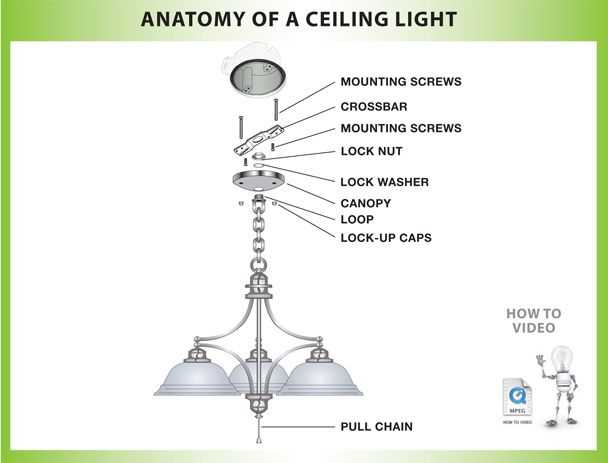
The electrical connections involved in overhead lighting setups are crucial for ensuring proper functionality and safety. Understanding the wiring components and their arrangement can help with both installation and troubleshooting. This section outlines the basic principles of connecting the electrical elements in overhead installations, focusing on safe practices and efficient setups.
To successfully manage the wiring, it’s important to identify the key elements that contribute to a functional setup. Below are the essential components typically involved:
- Power Supply Wires: These are the wires that carry the current from the main source to the device. Proper identification of the hot and neutral lines is necessary for safe operation.
- Ground Wire: This serves as a protective measure against electric shock. It’s usually connected to a grounding point within the electrical system, preventing potential hazards.
- Connection Points: These are the areas where the wires from the power source connect to the unit’s wires, typically using wire nuts or other secure connectors.
- Wire Color Codes: Most systems use standardized color codes to differentiate between various lines, such as live, neutral, and ground. Understanding these colors helps ensure correct connections.
When working with electrical setups, it is essential to follow local regulations and safety standards to prevent potential risks. Proper insulation, tight connecti
Mounting Bracket Functions and Types
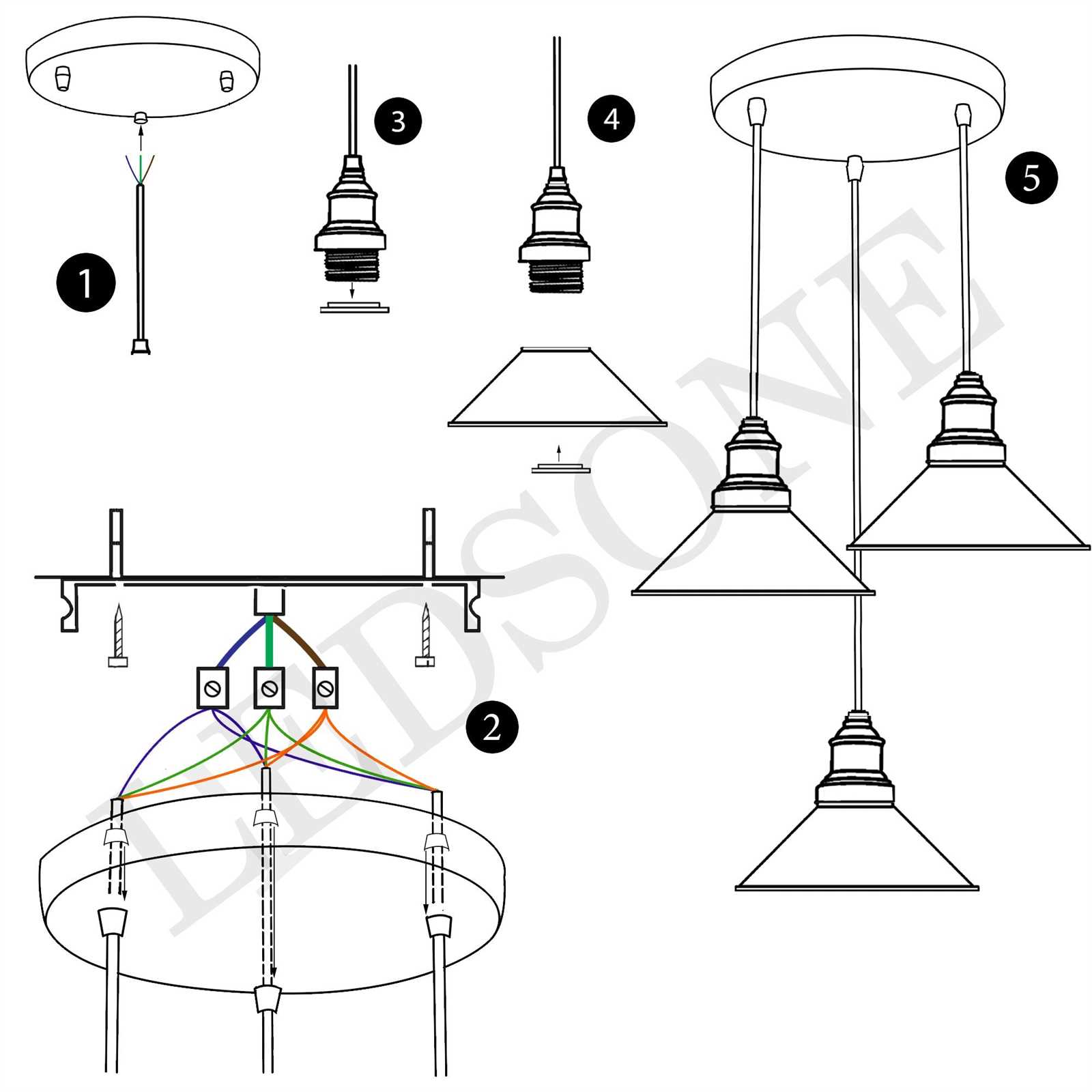
Mounting brackets play a crucial role in securing and supporting various components during installation. They ensure stability, proper alignment, and contribute to the overall durability of the setup. These brackets come in different designs, each serving a specific purpose to accommodate different installation environments and structural needs.
Primary Functions of Mounting Brackets
The main function of a mounting bracket is to provide a reliable connection between the installed element and the surface it attaches to. They are designed to hold objects securely, ensuring they remain in place under various conditions. Weight distribution is another key aspect, as brackets help distribute the load evenly, reducing stress on individual points.
Common Types of Mounting Brackets
There are several common types of mounting brackets, each suited for specific applications. Flat brackets are often used in straightforward installations where minimal complexity is required. Adjustable brackets, on the other hand, offer flexibility, allowing the installer to modify the position and angle to suit different setups. Additionally, corner brackets provide reinforcement in areas where stability is critical.
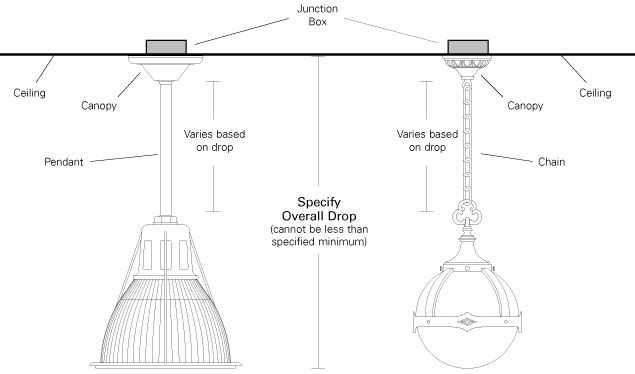
Ceiling Canopy: Purpose and Installation
The canopy serves as an essential component in securing decorative installations, offering a clean and finished look while concealing connection points. It plays a key role in stabilizing the setup and maintaining aesthetic harmony with the surrounding décor. Its design ensures both practicality and visual appeal, blending into various design styles seamlessly.
Primary Function of the Canopy
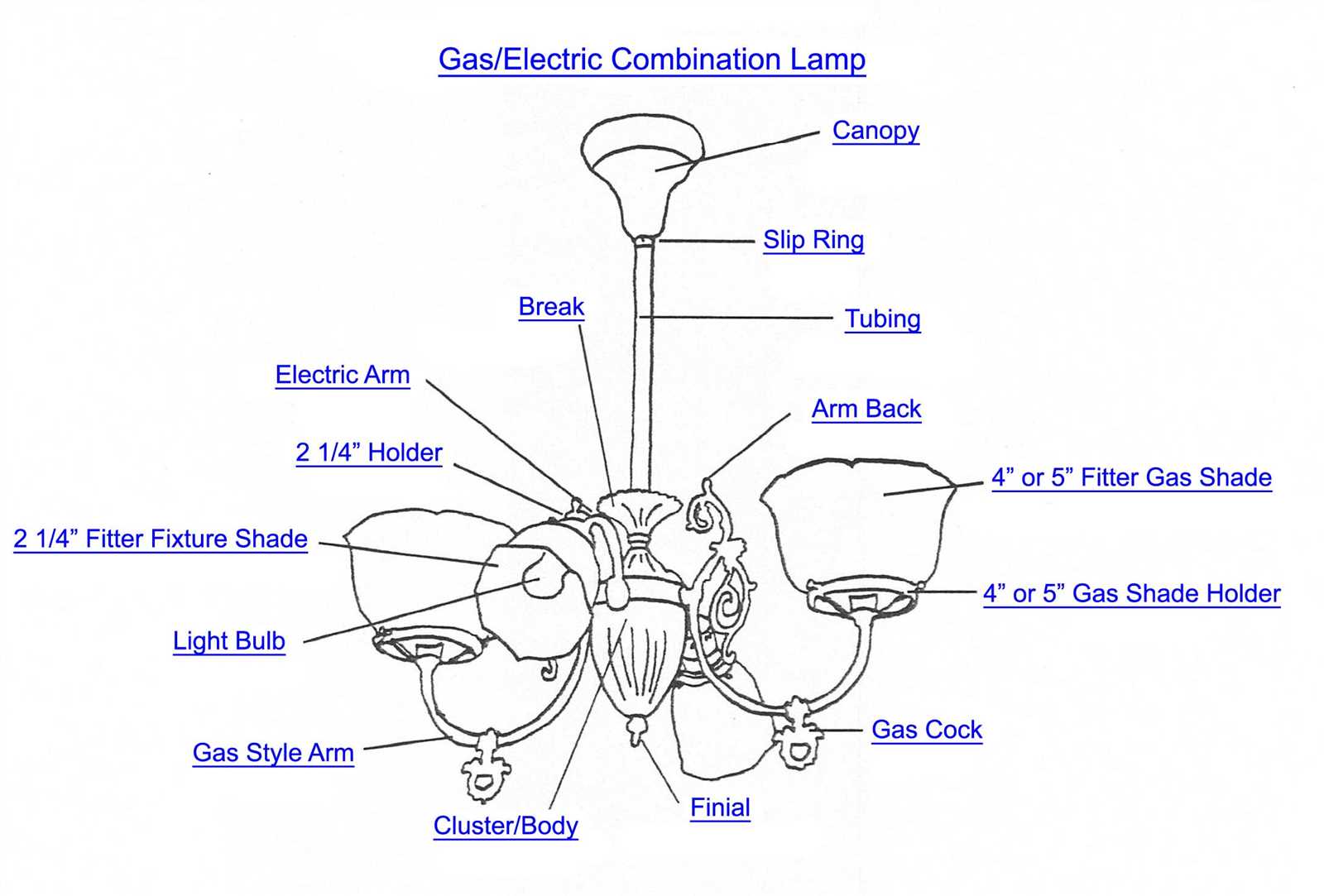
At its core, the canopy is designed to cover mounting elements and provide structural support for overhead setups. By masking wires and other technical components, it ensures that only the desired features are visible. This results in a polished and tidy appearance, which is crucial for both modern and traditional interiors.
Steps for Proper Installation
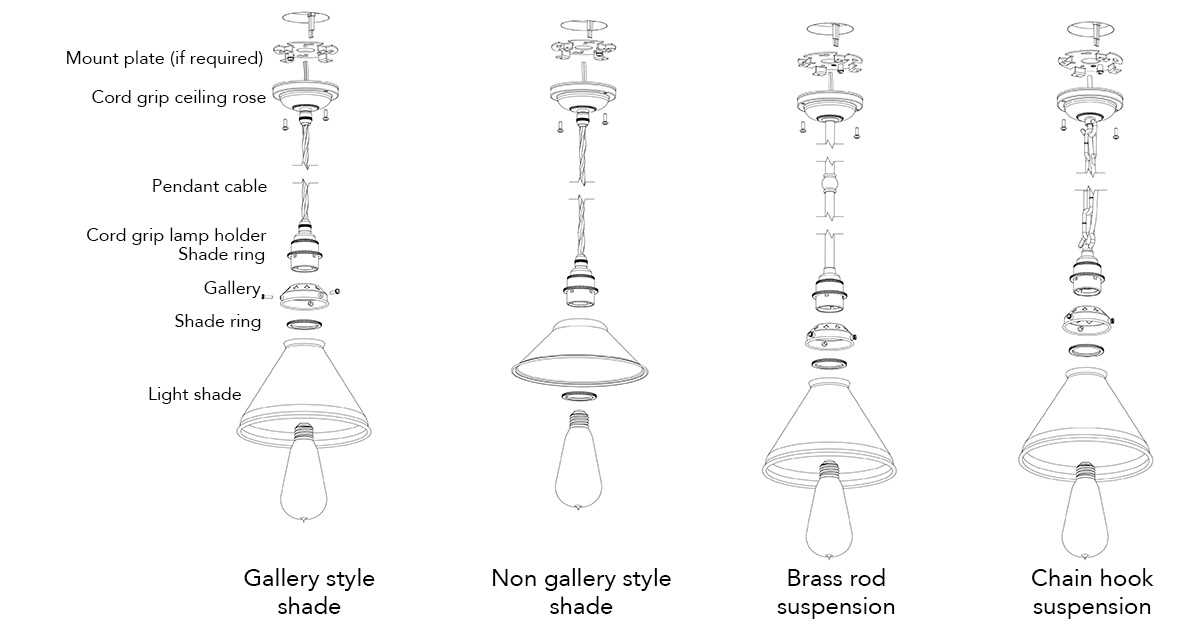
Installing the canopy requires attention to detail to ensure a secure and level attachment. First, position the mounting bracket, aligning it with the attachment point. After securing the bracket, the canopy is carefully placed over it, ensuring it aligns properly with the supporting hardware. This step guarantees a stable hold, minimizing any movement or shifting over time.
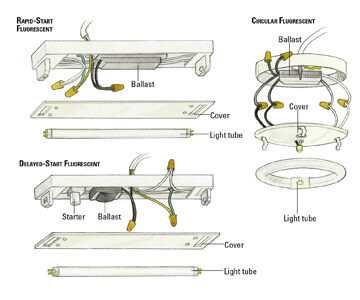
Light Socket Variations in Fixtures
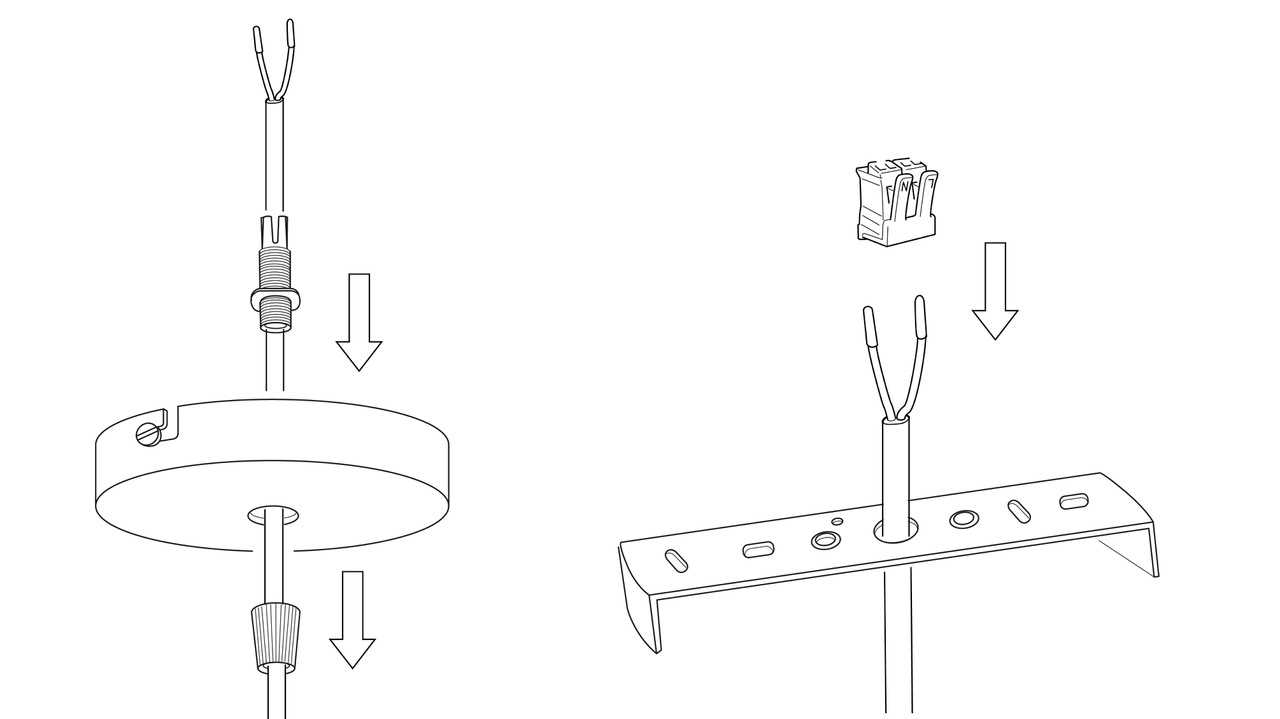
In the realm of illumination installations, the components that hold the bulbs play a crucial role in both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the different types of these components is essential for selecting the right option for any setting, whether it be residential or commercial. Variations in these elements can influence the type of bulbs used, their efficiency, and the overall design of the installation.
Below are some common variations found in these essential elements:
- Edison Socket: This classic design is prevalent in many traditional and contemporary settings. It typically accommodates a wide range of incandescent and LED bulbs.
- Bayonet Socket: Known for its easy installation and removal, this type uses a twist-and-lock mechanism, often seen in automotive and outdoor applications.
- GU10 Socket: Commonly used in halogen and LED applications, this variation features a two-pin design and is ideal for spotlights and downlights.
- GU5.3 Socket: Designed primarily for low-voltage bulbs, this type is often used in accent lighting and landscape applications.
- Socket with Dimmer Functionality: These components allow for adjustable brightness levels, providing flexibility in creating various atmospheres.
When choosing the right component, it is vital to consider not only compatibility with the bulb type but also the desired ambiance and functionality of the installation. The right choice can significantly enhance both the efficiency and aesthetic value of the overall design.
Types of Bulb Holders for Ceiling Lights
When it comes to illuminating spaces, the design and functionality of the components play a crucial role. Among these components, the holders for bulbs are essential for ensuring compatibility with various lighting sources. Understanding the different types available can greatly enhance the overall lighting experience and provide options for both aesthetics and practicality.
Below are some common types of bulb holders that are widely used:
- E26/E27 Base: This is one of the most common sizes, often used in residential settings. Its widespread adoption makes it easy to find replacement bulbs.
- B22 Bayonet Base: Featuring a unique twist and lock mechanism, this type provides a secure fit and is popular in many regions.
- GU10 Base: Typically used for spotlighting, this holder allows for easy installation and removal of halogen or LED bulbs.
- MR16 Base: Commonly used in track lighting and recessed applications, this holder is ideal for low-voltage setups.
- G9 Base: Often found in decorative lighting, this type allows for compact designs and is compatible with both halogen and LED bulbs.
Choosing the appropriate holder is essential for achieving the desired illumination effect while ensuring compatibility with various bulb types. Each design serves unique functions and caters to different preferences, making them crucial components in any lighting setup.
The Role of the Grounding Wire
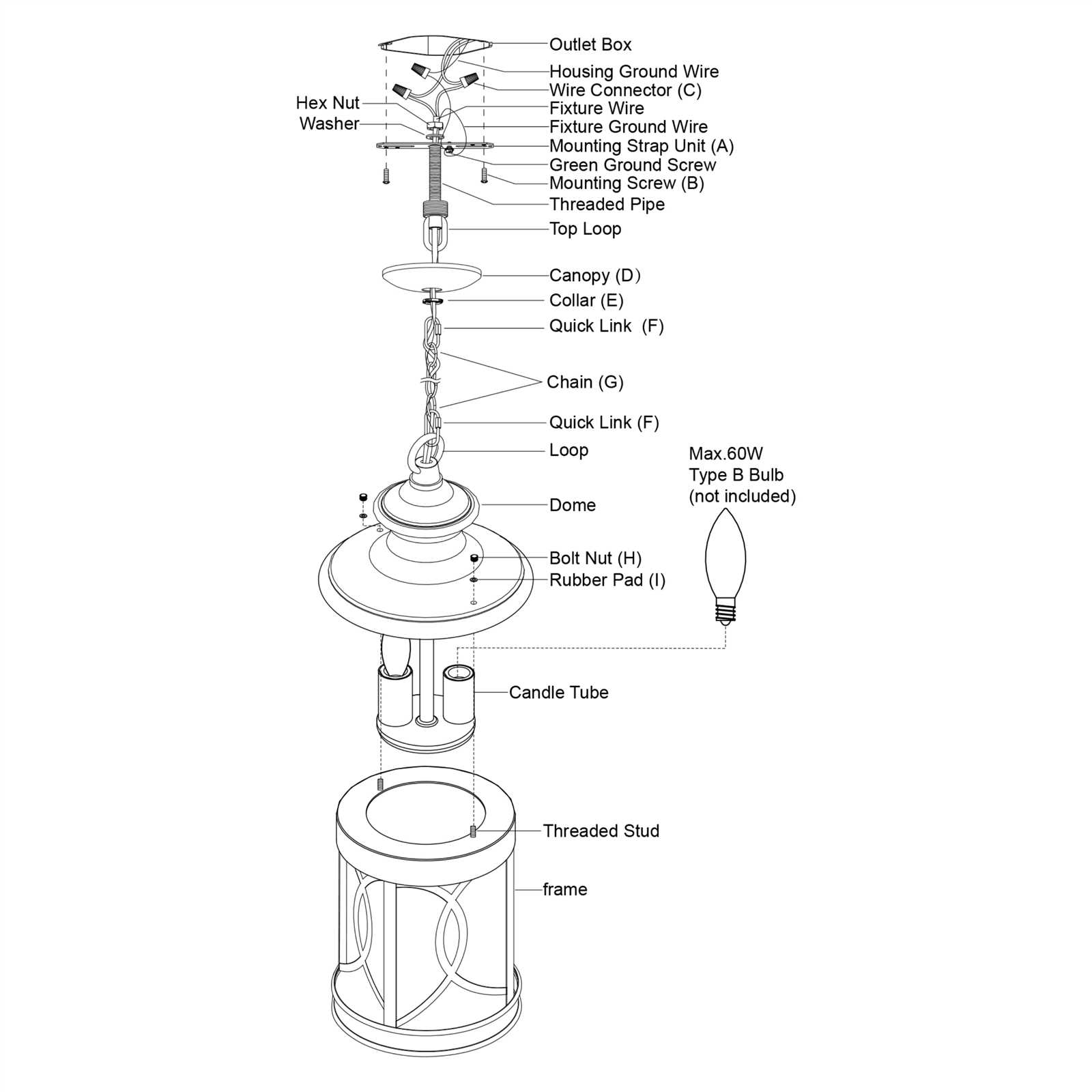
The grounding wire is an essential component in electrical systems, providing a pathway for electrical currents to safely dissipate. Its primary function is to protect both people and equipment from potential electrical faults, ensuring a reliable and secure operation of electrical installations.
Safety and Protection
By directing stray currents away from users and devices, the grounding wire significantly reduces the risk of electric shock and fire hazards. In the event of a fault, such as a short circuit, this wire offers an alternative route for electricity to flow, minimizing damage and enhancing safety.
Ensuring Proper Functionality
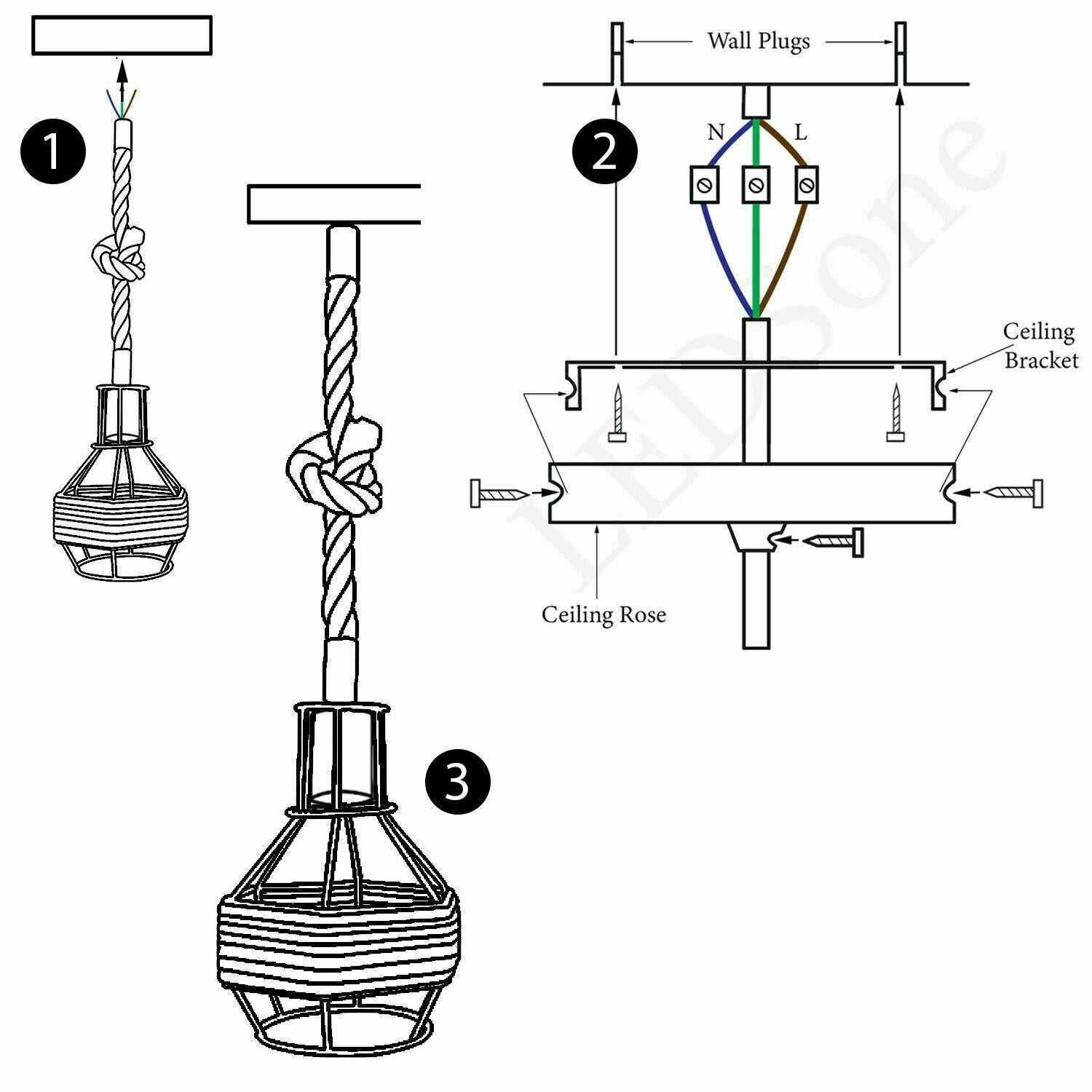
Moreover, a properly installed grounding wire contributes to the effective performance of electrical equipment. It helps maintain voltage stability and reduces interference, promoting a more efficient energy usage. Ensuring that the grounding system is in place is crucial for the longevity and reliability of any electrical setup.
Ceiling Fixture Trim and Aesthetic Options
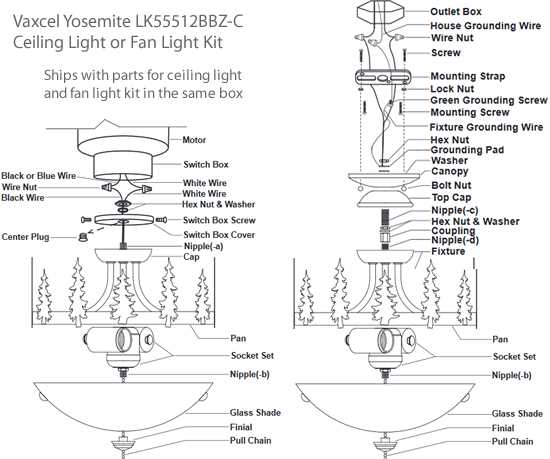
When it comes to enhancing the ambiance of a space, the selection of finishing elements and decorative styles plays a crucial role. These components not only contribute to the overall look but also set the mood, making it essential to choose wisely to complement the room’s theme.
Various trims and designs are available, each offering unique characteristics:
- Traditional Styles: Classic designs often feature ornate details, providing a timeless elegance.
- Modern Finishes: Sleek lines and minimalistic approaches offer a contemporary feel, perfect for modern interiors.
- Rustic Touches: Natural materials and rough finishes bring warmth and a cozy vibe, ideal for farmhouse or vintage aesthetics.
- Industrial Looks: Utilitarian designs with exposed elements add a trendy, urban edge to any space.
Choosing the right aesthetic options involves considering not only personal taste but also the existing decor. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Color Coordination: Ensure that the color of the trim harmonizes with the surrounding environment.
- Material Selection: Different materials can affect the overall appearance and feel; options range from metals to wood to glass.
- Scale and Proportion: The size of the finishing elements should be proportionate to the room to maintain balance.
By thoughtfully selecting trims and aesthetic elements, one can create a cohesive and inviting atmosphere that enhances the overall appeal of the space.
How to Replace Ceiling Light Parts Safely
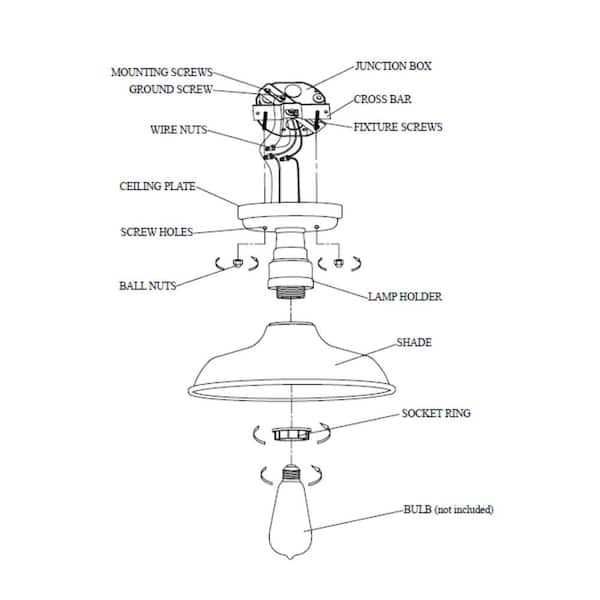
When it comes to updating or fixing overhead lighting solutions, safety is paramount. Ensuring that you approach this task with caution can prevent accidents and damage. This guide provides essential steps and tips to help you effectively change components while prioritizing your well-being.
Preparation Steps
- Turn off the electricity at the circuit breaker to avoid any electrical hazards.
- Gather necessary tools, including a screwdriver, voltage tester, and safety goggles.
- Ensure you have replacement components that match the specifications of the original setup.
Replacement Process
- Carefully remove the cover or shade from the overhead installation.
- Use a voltage tester to confirm that no electricity is flowing to the existing setup.
- Disconnect the wiring by loosening the screws that hold the wires in place.
- Replace the old component with the new one, making sure to connect wires securely.
- Reattach the cover or shade once everything is in place.
- Restore power at the circuit breaker and test the new installation.
By following these guidelines, you can safely update your overhead lighting solutions, ensuring they function correctly and efficiently.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Ceiling Lights
Addressing issues related to overhead illumination can often be straightforward with a systematic approach. Various factors may contribute to unexpected behavior or malfunctions, ranging from power supply problems to component failures. Understanding common symptoms and their potential causes can facilitate effective resolution and restore functionality.
Frequent Problems and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No illumination | Power outage or blown fuse | Check circuit breakers or replace fuses as needed. |
| Flickering | Loose connections | Inspect and tighten all wiring connections. |
| Dim illumination | Old or incompatible bulbs | Replace bulbs with suitable wattage and type. |
| Unpleasant odor | Overheating or damaged components | Turn off power and examine for signs of damage. |
Preventative Measures
Regular maintenance can significantly reduce the occurrence of issues. Periodically inspect for any signs of wear and tear, ensuring all components are functioning correctly. Keeping the area free of dust and debris will also enhance performance and longevity.