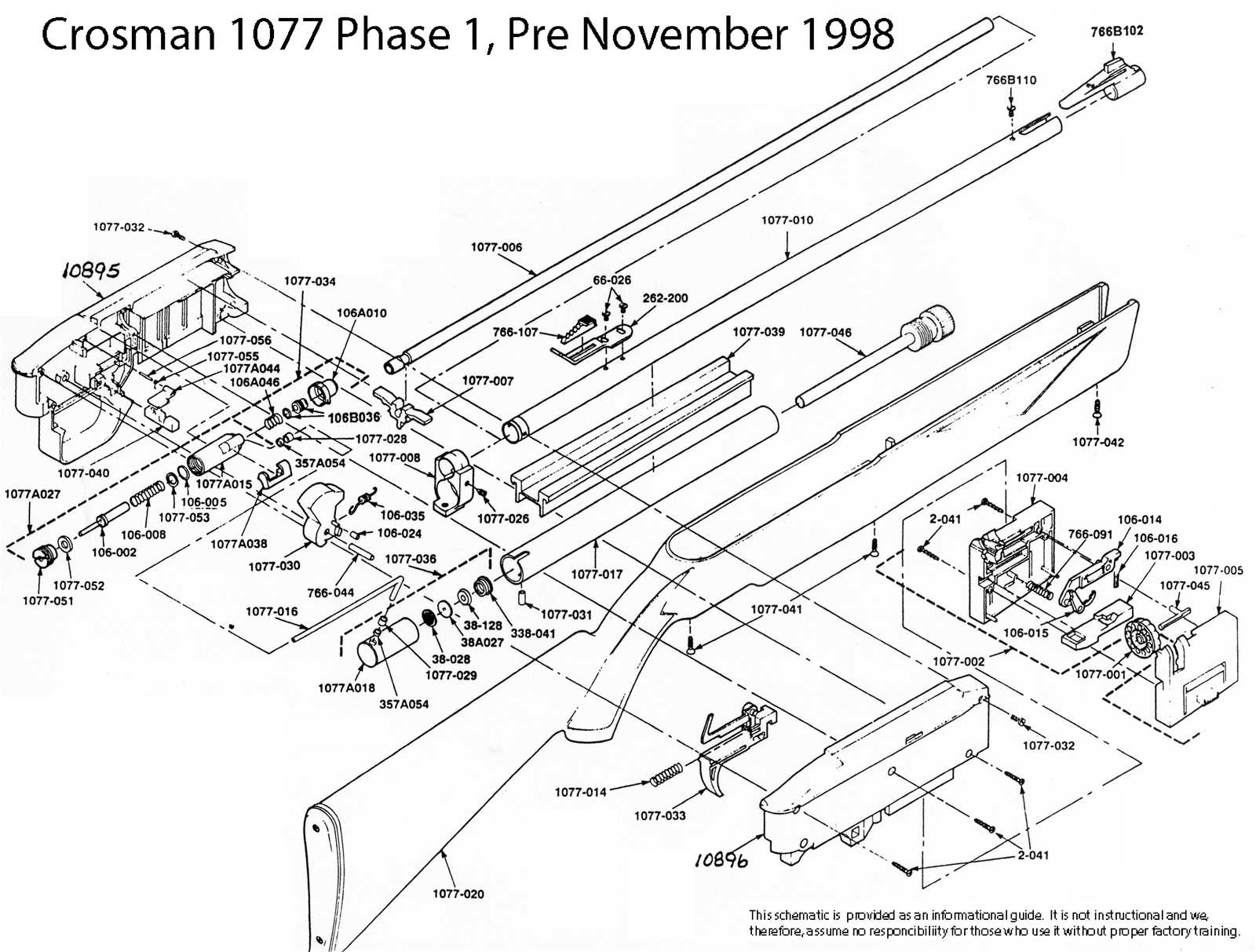
When it comes to maintaining and repairing air-powered tools, knowing how each individual piece fits into the overall mechanism is essential. This section provides a comprehensive look at the internal workings, focusing on the essential elements that ensure smooth operation and reliability over time.
The mechanical system is composed of various interconnected units, each playing a critical role in the device’s overall function. By understanding these elements, you can enhance your ability to perform regular maintenance, troubleshoot issues, and even carry out necessary repairs with greater precision.
Whether you’re an experienced user or a novice, familiarizing yourself with the structure and its key sections will improve your overall experience and efficiency. Delving deeper into this layout will reveal the vital links between all moving parts, allowing for better upkeep and longevity.
Component Breakdown
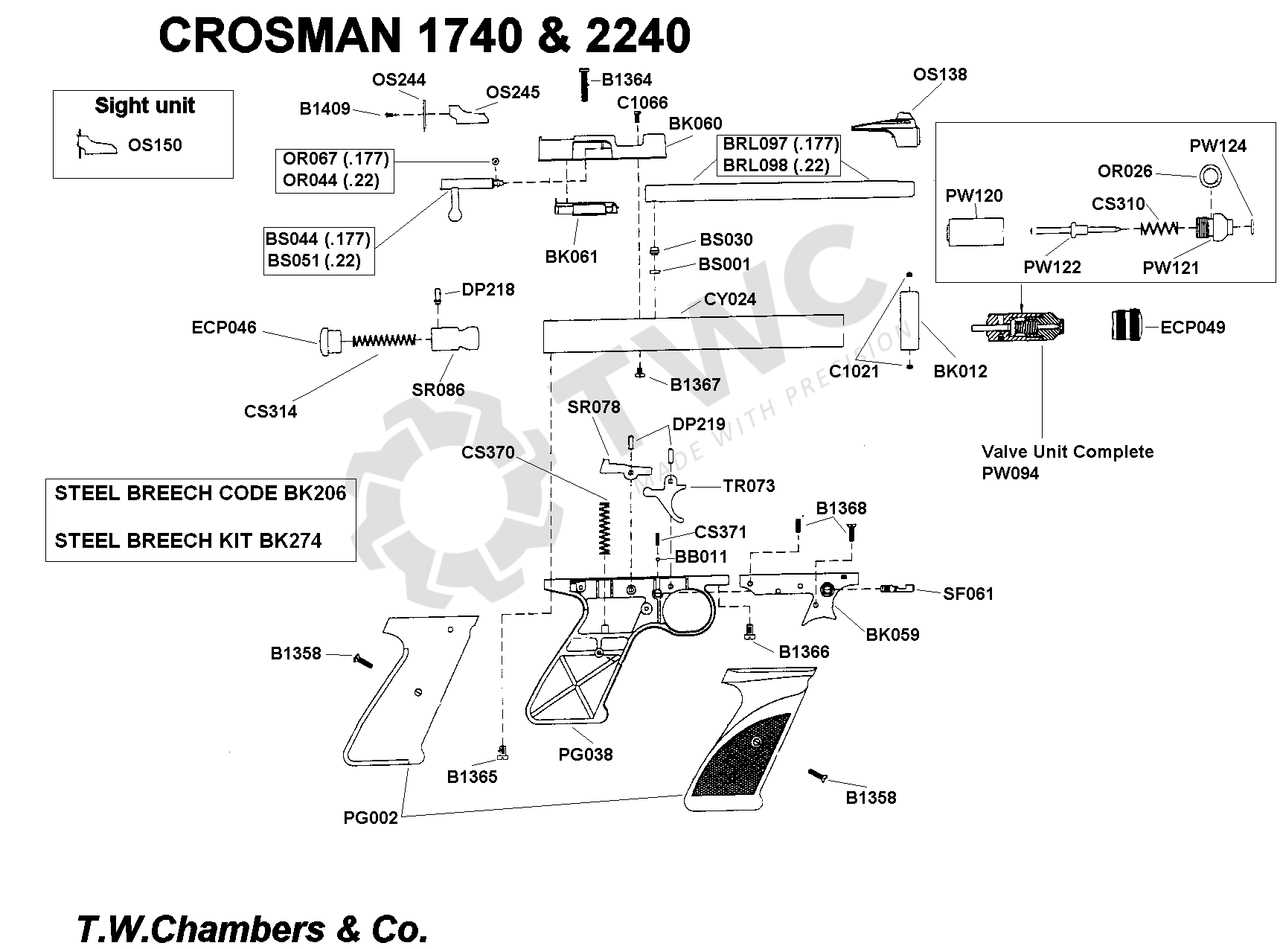
Understanding the structure of this air-powered device requires a closer look at its internal and external elements. Each part plays a critical role in the overall functionality, ensuring precise operation and long-term durability. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key sections and their individual components.
- Main Housing: The central frame that holds all other elements together, providing a sturdy base for the entire mechanism.
- Pneumatic Pump: This component is essential for generating air pressure, allowing the device to operate efficiently.
- Barrel Assembly: Responsible for guiding the projectile, this section ensures accuracy and precision in every shot.
- Trigger Mechanism: A key part that controls the firing process, it ensures that the device responds smoothly to user input.
- Safety Features: Built-in mechanisms designed to prevent accidental firing, enhancing overall safety during use.
- Optical Sight Mount: An attachment point for scopes or sights, aiding in better aim and precision.
Each of these components contributes to the performance, making the overall system reliable and efficient for various purposes.
Exploring the Internal Mechanisms

The internal mechanisms of air-powered devices are composed of intricate components working together to ensure smooth operation. Understanding the relationship between these parts is essential for anyone looking to maintain or enhance the performance of their equipment. This section delves into the various elements that contribute to the functionality, providing insights into how these components interact and function as a cohesive system.
Main Operating Components

At the heart of the mechanism lies a complex assembly of valves, springs, and chambers. Each of these plays a crucial role in managing the air pressure, ensuring the necessary force for propelling the projectile. The compression system, typically powered by either manual effort or an air pump, creates the required buildup of pressure, which is then released in a controlled manner to generate consistent propulsion.
Trigger and Firing System
The firing system is another vital part of the internal structure. It consists of a trigger mechanism that, when engaged, releases the stored pressure to fire the projectile. The precision of this system is paramount to achieving accuracy, as even slight misalignments can affect the overall performance. The careful synchronization of these elements ensures that the device operates efficiently and reliably.
Key Parts of the Firing System
The firing mechanism in air-powered devices consists of several essential components that work together to deliver precise and reliable performance. Understanding the function of each element is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of the system. Below is a breakdown of the core elements involved in this process.
- Barrel: The barrel serves as the channel through which the projectile is directed. Its alignment and quality are essential for maintaining accuracy.
- Trigger Assembly: This part controls the firing sequence, ensuring that the device only releases a shot when desired. It includes levers and springs that interact to provide a controlled firing action.
- Piston: The piston is responsible for compressing air or gas, which generates the pressure needed to propel the projectile forward. It works in conjunction with the air chamber to create the necessary force.
- Air Chamber: This compartment stores the compressed air or gas, which is released during firing to push the projectile through the barrel.
- Spring or Gas Ram: The spring or gas ram powers the piston. When compressed and released, it provides the energy to push the piston, initiating the firing process.
- Breech Seal: The breech seal ensures that the air or gas pressure remains contained within the chamber until the projectile is fired, maximizing efficiency and power.
Understanding the Pumping Mechanism
The pumping system in air-powered devices operates through a manual process that increases internal pressure. This buildup of compressed air is key to powering the device effectively. To better understand how this system works, it’s essential to explore the components and the role each plays in creating the necessary force.
- Pump Lever – This is the primary part responsible for generating air pressure by moving a piston within the chamber.
- Air Chamber – The space where air is stored and compressed as the user operates the lever.
- Piston – This moves back and forth within the chamber, pushing air into a confined space, leading to an increase in pressure.
- Valve System – Once the desired pressure is achieved, this component ensures the controlled release of the stored energy.
By manipulating these elements, users can efficiently build the force needed for optimal performance. Understanding the individual components allows for better use and maintenance of the system.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep is essential to ensure the durability and consistent performance of any air-powered device. By following simple yet effective care techniques, you can extend its operational life, ensuring reliable use over time. This section provides key maintenance recommendations that are easy to implement and vital for long-term reliability.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Regular cleaning is crucial to prevent debris buildup that could hinder performance. After each use, wipe down all accessible surfaces and ensure that no dirt has entered moving parts. Applying a light coat of appropriate lubricant to metal components reduces friction and protects against corrosion.
Component Check and Replacement
Frequent inspection of wear-prone elements is necessary. Pay attention to seals, springs, and other vital pieces that may degrade over time. If any show signs of wear, timely replacement is key to maintaining peak efficiency and preventing future damage.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Surface cleaning | After each use |
| Lubrication of metal parts | Every 500 shots |
| Component inspection | Monthly |
Trigger Assembly: How It Works

The trigger assembly is a crucial component of any firing mechanism, responsible for initiating the discharge process. This system operates through a series of interconnected parts that work harmoniously to ensure precise and safe firing. Understanding how each element functions can enhance both the performance and maintenance of the device.
Components of the Trigger Mechanism

- Trigger: The part that the user pulls to activate the firing sequence.
- Sear: Engages with the hammer and holds it in place until the trigger is pulled.
- Hammer: The component that strikes the firing pin or pellet when released.
- Spring: Provides the necessary tension to return the hammer or trigger to its resting position.
Operation of the Trigger Assembly
When the user pulls the trigger, the following sequence occurs:
- The trigger moves backward, which releases the sear.
- The sear disengages from the hammer, allowing it to move forward.
- The hammer strikes the firing pin, creating the necessary force to propel the projectile.
- After the shot, the spring returns the trigger and hammer to their original positions, ready for the next cycle.
Regular maintenance of the trigger assembly is essential for reliable operation. Proper lubrication and periodic inspections can prevent malfunctions and enhance overall performance.
Replacing Worn-Out Seals and O-Rings

Regular maintenance of pneumatic devices often includes the replacement of deteriorated seals and O-rings. These components play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the system, preventing air leaks, and ensuring optimal performance. Over time, exposure to various environmental factors can lead to wear and tear, compromising their functionality.
To begin the replacement process, gather the necessary tools, including a suitable lubricant, replacement seals, and a precise measuring device to ensure proper fit. Start by disassembling the device according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, taking care to keep track of each component.
Once disassembled, carefully remove the old seals and O-rings. Inspect the surrounding areas for any signs of damage that could affect the new components’ performance. Clean the surfaces thoroughly to eliminate any debris or remnants of the old seals.
Before installing the new seals and O-rings, apply a small amount of lubricant to facilitate a smooth fit. This step helps prevent tearing during installation and ensures a proper seal once reassembled. Place the new components in their designated grooves, ensuring they sit evenly and securely.
After replacing the seals and O-rings, reassemble the device meticulously, following the reverse order of disassembly. Conduct a thorough inspection to confirm that everything is in place and functioning correctly. Finally, perform a test run to verify that the new components have restored the device’s efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Malfunctions
When using air-powered devices, it’s not uncommon to encounter various issues that can affect performance. Understanding the typical problems and their solutions can enhance your experience and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
1. Loss of Power: If you notice a significant drop in power, check for air leaks. Ensure all connections are secure and inspect seals for wear. Additionally, verify that the air source is functioning properly.
2. Inconsistent Accuracy: Inconsistent shots may result from a dirty barrel or improper ammunition. Regularly clean the barrel and use high-quality projectiles to maintain precision.
3. Jamming Issues: If the mechanism jams, it may be due to debris in the loading area. Carefully disassemble the unit and clean any obstructions. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance.
4. Difficulty in Cocking: If the cocking mechanism feels stiff, it could indicate a lack of lubrication. Apply a suitable lubricant to moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
By addressing these common issues proactively, users can enjoy a more reliable and enjoyable experience with their air-powered devices.
Cleaning and Lubrication Best Practices
Maintaining the performance and longevity of your equipment requires regular cleaning and appropriate lubrication. These practices not only enhance the efficiency of moving parts but also prevent wear and tear caused by dust and grime accumulation. Following proper procedures can significantly improve the lifespan and reliability of your device.
Cleaning Procedures
Begin by ensuring the device is unloaded and safe to handle. Use a soft cloth or brush to remove any dust, dirt, or debris from the exterior and accessible internal components. For stubborn residues, consider using a mild cleaning solution. Avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage sensitive parts. After cleaning, ensure that all surfaces are completely dry before proceeding to lubrication.
Lubrication Techniques
Select an appropriate lubricant designed for your device’s specifications. Apply the lubricant sparingly to moving parts, ensuring that it penetrates joints and bearings without creating excess buildup. It is essential to avoid over-lubrication, as this can attract dirt and lead to premature wear. Regularly check lubrication levels and reapply as necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Stock and Barrel: Structural Overview
The stock and barrel of a firearm play crucial roles in its overall performance and handling. These components not only contribute to the aesthetic appeal but also affect accuracy, stability, and user experience. Understanding their structure and function is essential for maintenance and enhancement.
Stock Features
The stock serves as the primary interface between the shooter and the firearm. Key characteristics include:
- Material: Stocks can be made from wood, synthetic materials, or composite substances, each offering different benefits in terms of weight, durability, and recoil absorption.
- Design: The design of the stock influences the shooter’s comfort and stability. Options may include adjustable cheek rests and length-of-pull adjustments.
- Ergonomics: A well-designed stock enhances grip and control, allowing for better handling during operation.
Barrel Considerations
The barrel is integral to the firearm’s accuracy and range. Important aspects include:
- Length: Longer barrels generally provide increased accuracy and velocity, while shorter barrels may enhance maneuverability.
- Caliber: The diameter of the barrel must match the ammunition used, impacting performance and safety.
- Rifling: The internal grooves of the barrel impart spin to the projectile, stabilizing it for improved trajectory.
Reassembling After Disassembly: A Guide
Reassembling a disassembled device can be a meticulous yet rewarding task. Understanding the various components and their proper arrangement is essential for restoring functionality. This guide provides step-by-step instructions to aid you in the reassembly process.
Follow these general steps for a successful reassembly:
- Gather Tools and Components:
Ensure you have all necessary tools and components within reach. This may include screwdrivers, pliers, and any small parts that were removed during disassembly.
- Review Documentation:
Before starting, refer to any diagrams or guides you may have saved. This will help you visualize the assembly process and ensure accuracy.
- Start with the Base Assembly:
Begin by reassembling the base components. This often includes larger parts that provide the structure for the entire unit.
- Install Internal Mechanisms:
Next, focus on internal mechanisms. Pay attention to the orientation and placement of each piece, as they may need to fit together in a specific way.
- Secure Connections:
Use screws and fasteners to secure connections. Make sure each component is firmly in place to avoid issues during operation.
- Final Assembly:
Once all internal parts are in place, complete the assembly by attaching any outer casing or covers. Double-check that everything aligns properly.
- Testing:
After reassembly, conduct a thorough test to ensure that the device operates as intended. If any issues arise, revisit the assembly steps to troubleshoot.
By following these steps, you can successfully reassemble your device, ensuring its continued functionality and longevity.