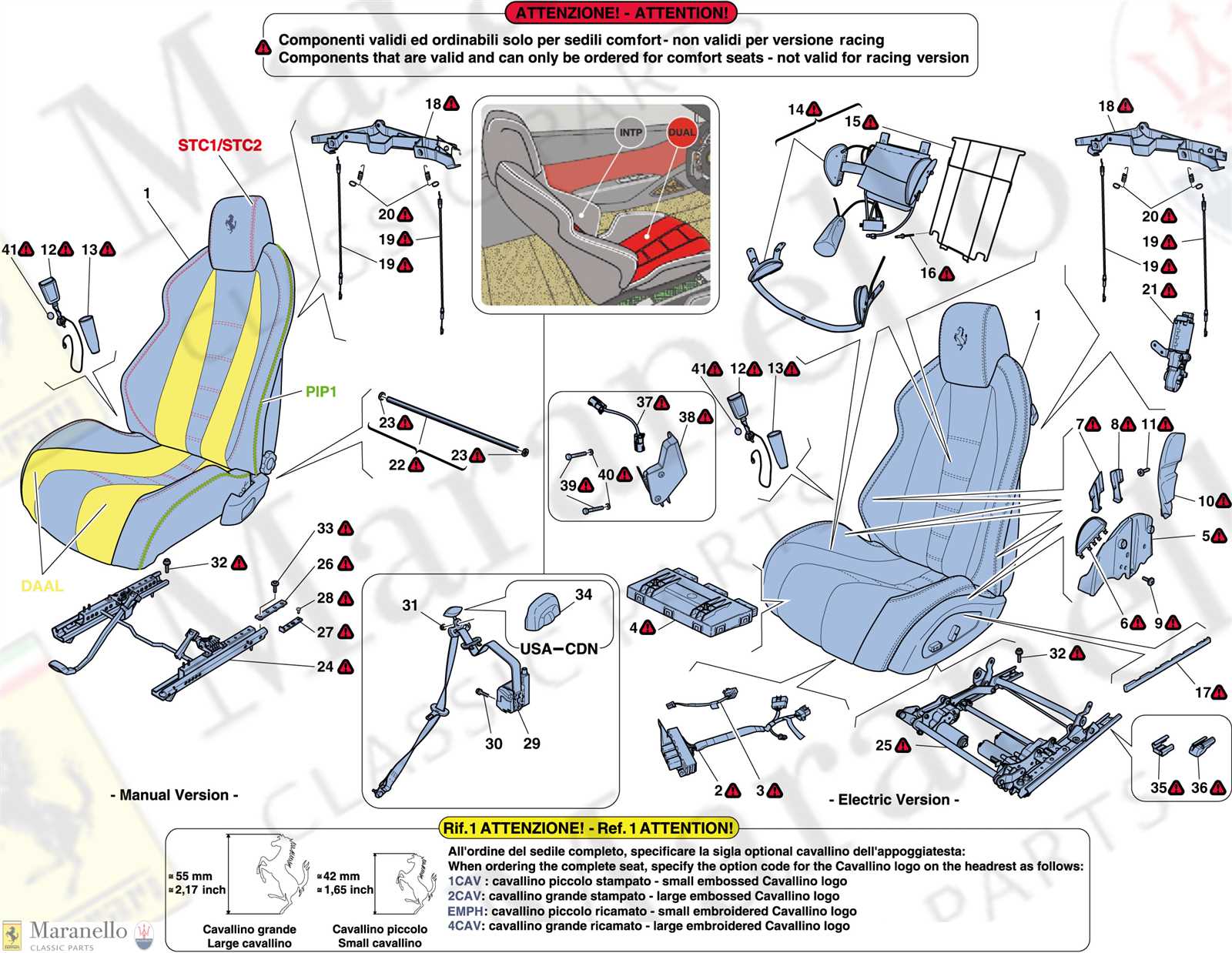
When it comes to automotive safety, the various elements that contribute to the effective functioning of restraint systems play a crucial role. These components work together to ensure that occupants are protected in the event of an unexpected incident. By examining each element, we can gain a deeper appreciation of how they enhance safety on the road.
Identifying the individual components of these systems reveals a complex interplay of technology and design. Each element has a specific function, designed to optimize performance and reliability. Understanding these components can empower users to make informed decisions about vehicle safety and maintenance.
Furthermore, exploring the intricacies of these systems highlights advancements in engineering that continuously improve protection features. The evolution of these components reflects a commitment to enhancing passenger safety, making vehicles increasingly secure.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the various elements that constitute a safety harness system within vehicles. Understanding these components is crucial for appreciating how they function together to ensure occupant protection during travel. Each element plays a specific role, contributing to the overall effectiveness and reliability of the safety mechanism.
Essential Components of a Safety Harness
Safety harnesses consist of several key elements that work in unison. The main components include the restraining mechanism, the anchoring system, and the adjustment features that enhance comfort and effectiveness. These parts are engineered to withstand significant forces during a collision, ensuring that occupants remain securely in place.
Functionality of Each Element
Each component of the safety harness serves a distinct purpose, enhancing the overall performance of the system. Below is a table detailing the primary elements, their functions, and typical materials used in their construction.
| Component | Function | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Retractor | Automatically retracts the webbing | Plastic, metal springs |
| Anchor Points | Secure the harness to the vehicle frame | Steel, high-strength alloys |
| Webbing | Resists stretching and supports occupant | Nylon, polyester |
| Adjusters | Facilitate a snug fit for occupants | Plastic, metal |
Key Functions of Safety Belts
Safety harnesses play a crucial role in ensuring the protection of vehicle occupants during travel. Their primary objective is to minimize the risk of injury by restraining individuals in the event of sudden stops or collisions. Understanding their essential functions highlights their importance in automotive safety.
Primary Functions
- Injury Prevention: By keeping occupants securely in place, safety harnesses significantly reduce the likelihood of serious injuries during accidents.
- Energy Distribution: They spread the forces experienced during a crash across stronger parts of the body, such as the chest and pelvis, reducing the chance of localized injuries.
- Posture Support: Safety harnesses help maintain an upright position, preventing occupants from being thrown forward, which can lead to additional injuries.
Additional Benefits
- Legal Compliance: Most regions mandate the use of safety harnesses in vehicles, ensuring adherence to safety regulations.
- Enhanced Protection: Advanced designs incorporate features such as pretensioners and load limiters, further increasing the effectiveness of safety harnesses in mitigating harm.
Types of Seat Belt Mechanisms
Various systems are employed in safety harnesses to ensure the protection of passengers in vehicles. These mechanisms serve crucial roles in securing occupants during travel, contributing significantly to overall safety. Understanding the different types of these systems is essential for recognizing their functionality and benefits.
The mechanisms can be classified into several categories based on their design and operation. Here are the primary types:
| Mechanism Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Automatic Retractor | This system retracts the harness automatically when not in use, ensuring it is ready for the next occupant. |
| Manual Adjustment | Occupants can adjust the harness manually for a snug fit, allowing for personal comfort and security. |
| Emergency Locking | This type locks the harness in place during sudden stops or impacts, providing additional security. |
| Dynamic Tensioning | This mechanism automatically tightens the harness during a collision, reducing movement and potential injury. |
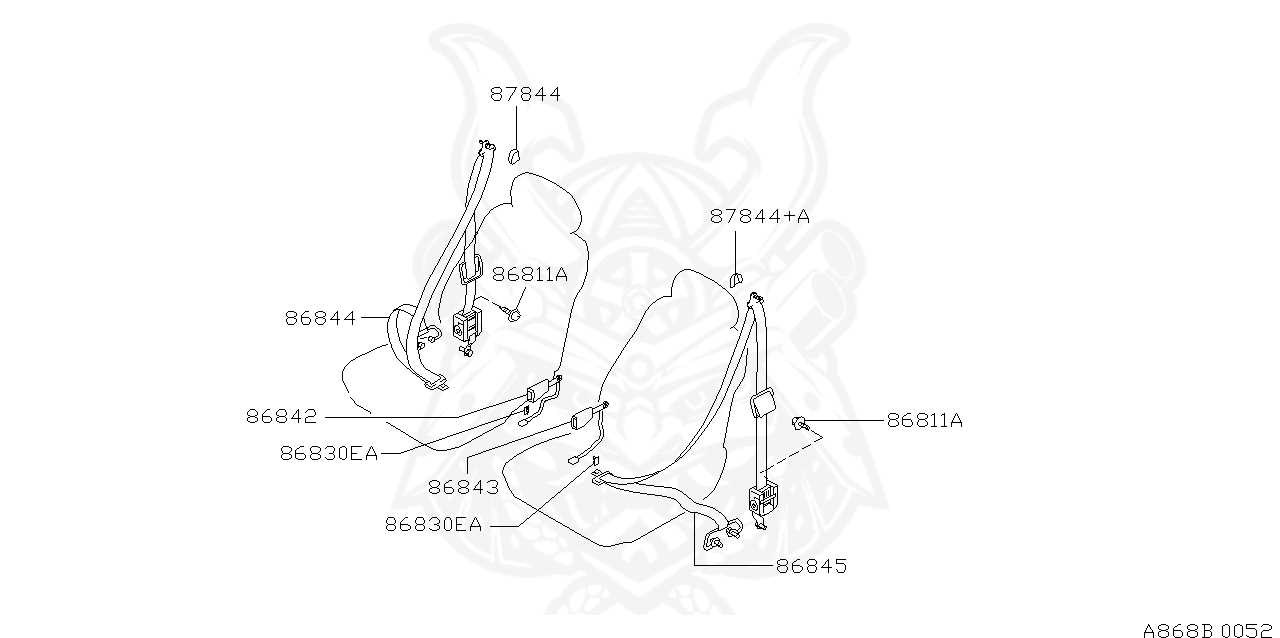
Identifying Common Seat Belt Parts
Understanding the essential components of a safety restraint system is crucial for ensuring proper functionality and safety. Each element plays a significant role in protecting occupants during a collision. Recognizing these elements can help in maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key components include:
- Webbing: The fabric strap that extends and retracts to secure occupants.
- Retractor: The mechanism that manages the webbing’s tension and allows it to retract.
- Anchor: The fixed point where the webbing is attached to the vehicle.
- Latch Plate: The metal piece that locks into the buckle to secure the occupant.
- Buckle: The device that allows the user to fasten and unfasten the restraint.
By familiarizing oneself with these components, individuals can better understand how to ensure the safety mechanisms are functioning effectively.
Importance of Buckle Design
The design of the fastening mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and functionality in restraint systems. A well-engineered buckle not only secures occupants but also enhances the user experience by providing ease of use and reliability in various scenarios.
Key Factors in Buckle Design
- Safety: A robust buckle must withstand high forces during an impact, preventing accidental release.
- User-Friendliness: The mechanism should allow for quick engagement and disengagement, accommodating users of all ages.
- Durability: Materials used must resist wear and corrosion to ensure longevity and consistent performance.
Impact on Overall System Performance
A well-designed fastening mechanism contributes significantly to the overall efficacy of restraint systems. Key benefits include:
- Enhancement of passenger protection during collisions.
- Reduction of the risk of misuse or improper fastening.
- Improvement of user confidence and compliance with safety practices.
Role of the Retractor System
The retraction mechanism serves a crucial function in the safety apparatus of vehicles, ensuring that the harness remains snug and secure during travel. This component is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of the protective system by allowing the webbing to extend and retract seamlessly, adapting to the movement of the occupant.
In the event of a collision, the retractor’s primary responsibility is to lock the webbing in place, preventing excessive forward movement and minimizing the risk of injury. The system typically employs a spring-loaded mechanism that quickly engages when sudden deceleration is detected. Proper functioning of this component is vital, as it directly impacts the overall safety performance of the protective equipment.
Additionally, the retraction system enhances user comfort and usability, allowing for easy adjustments when securing individuals in the vehicle. This balance of safety and convenience makes the retractor a fundamental aspect of any modern automotive safety setup.
Impact of Anchor Points on Safety
The location and design of attachment points play a crucial role in the effectiveness of restraint systems during collisions. Properly positioned anchor points enhance the overall stability of these systems, significantly contributing to passenger safety. Understanding their importance can help in the design of more secure vehicles.
Key factors influencing the effectiveness of attachment points include:
- Placement: The position of the anchor points affects how well the restraint system restrains the occupants during a sudden stop or crash.
- Strength: Anchor points must be robust enough to withstand the forces exerted during an accident.
- Accessibility: Easy access to anchor points facilitates proper installation and adjustment of the restraint system.
- Design: The design of anchor points should accommodate various body types and sizes for maximum effectiveness.
Ensuring that these components are well-engineered and strategically placed can greatly minimize injury risks. Properly designed anchor points not only enhance restraint effectiveness but also contribute to a safer overall vehicle environment.
Analyzing Seat Belt Webbing Types
Understanding the different types of webbing used in restraint systems is crucial for assessing their effectiveness and safety. Various materials and weaving techniques contribute to the overall performance and durability of these components. The choice of webbing not only affects comfort but also plays a significant role in the ability to absorb energy during a collision.
Polyester is one of the most commonly used materials, known for its strength and resistance to stretching. This fabric provides a reliable balance between flexibility and durability, making it suitable for various applications. In contrast, nylon offers excellent elasticity, allowing for greater comfort and adaptability to different body shapes. However, it may be less durable under prolonged exposure to UV light.
The weaving technique also influences the performance of the webbing. Common methods include plain weave and twill weave, each providing distinct advantages in terms of flexibility and resistance to fraying. Analyzing these aspects helps manufacturers enhance safety features while ensuring user comfort during transportation.
Understanding the Role of Pretensioners
Pretensioners are critical components within the restraint systems of vehicles, designed to enhance safety during sudden deceleration or collision events. Their primary function is to reduce the amount of slack in the safety restraints, thereby securing occupants more effectively and minimizing the risk of injury.
Functionality and Mechanism
The operational mechanism of pretensioners is quite sophisticated. Upon detecting an impact, these devices activate rapidly to pull the restraint system snug against the occupant’s body. This immediate action serves several purposes:
- Reduces forward movement during a collision
- Enhances the effectiveness of the restraint system
- Prevents the occupant from being ejected from their seating position
Types of Pretensioners
There are various types of pretensioners employed in modern vehicles, each with unique characteristics:
- Pyrotechnic Pretensioners: These utilize a small explosive charge to activate the mechanism swiftly.
- Mechanical Pretensioners: These rely on springs and levers to achieve rapid tightening of the restraint system.
- Electromechanical Pretensioners: These utilize electric motors for precise control and activation.
Maintaining and Inspecting Seat Belts
Regular upkeep and examination of safety harnesses are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and passenger protection. A thorough inspection can help identify any wear or damage that might compromise their effectiveness in an emergency situation. Understanding the key elements to check and the recommended maintenance practices is essential for any vehicle owner.
Key Areas of Focus: It is important to routinely assess various components for signs of fraying, tearing, or other forms of degradation. Ensure that all mechanisms function smoothly and that any locking systems engage properly. Pay attention to the attachment points, making sure they are secure and free from corrosion.
Maintenance Tips: Keeping harnesses clean is vital. Use mild soap and water to remove dirt and debris, avoiding harsh chemicals that could weaken the fabric. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance recommendations to preserve their integrity and safety.
Conclusion: Consistent care and attention to detail in examining these crucial safety devices can significantly enhance vehicle safety and provide peace of mind for all passengers. Make it a habit to incorporate these inspections into your routine vehicle maintenance schedule.
Advancements in Seat Belt Technology
Over the years, significant innovations have transformed how restraint systems function, enhancing safety and comfort for vehicle occupants. These advancements have been driven by a combination of engineering improvements, materials science, and evolving safety regulations aimed at reducing injuries during collisions.
Key Developments in Restraint Systems
- Increased use of high-strength materials for improved durability.
- Integration of sensors that adapt tension based on the severity of an impact.
- Development of pretensioners that tighten the harness upon collision.
- Incorporation of load limiters that manage forces during an accident.
Future Trends in Safety Innovations
- Expansion of smart technologies for automatic adjustments.
- Research into alternative designs that provide greater protection.
- Focus on enhanced compatibility with various body types and sizes.