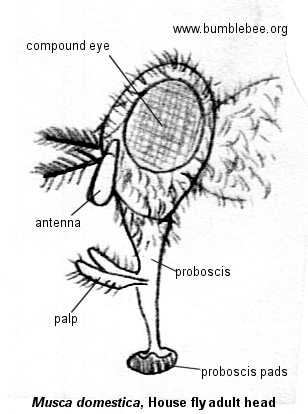
Understanding the intricate structures that facilitate feeding in various insects reveals a fascinating world of adaptation and survival. These specialized organs enable creatures to efficiently process a range of food sources, from liquids to solids, showcasing nature’s ingenuity. The examination of these mechanisms not only highlights their functional significance but also provides insights into the ecological roles these insects play in their environments.
In particular, one common species exhibits a unique arrangement that allows for effective consumption of diverse nutrients. Through a detailed look at its anatomical features, we can appreciate how evolution has shaped these structures to meet specific dietary needs. The interplay of form and function becomes evident as we delve into the various elements involved in the feeding process.
Visual representations of these structures serve as valuable tools for comprehension. They offer a clear understanding of how each component works in harmony to facilitate feeding. By analyzing these illustrations, we can deepen our knowledge of insect biology and their remarkable adaptations that have enabled them to thrive in various habitats.
Mouthparts of Housefly Explained
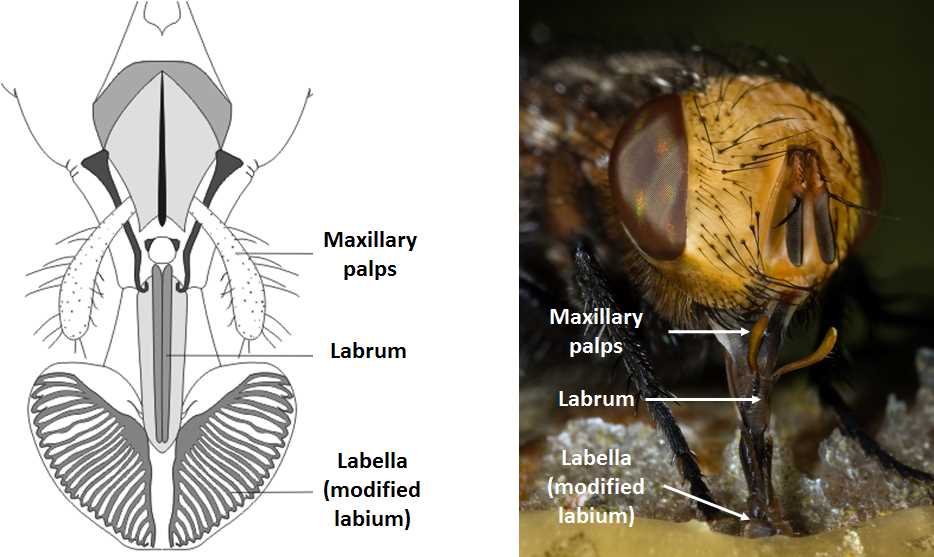
This section explores the intricate feeding structures of a common insect, highlighting their functions and adaptations that enable survival and interaction with the environment.
- Lapping Structure: Specialized for liquid consumption, allowing for effective feeding on various substances.
- Stylet Function: Thin appendages that assist in piercing surfaces to access nutrients.
- Palps: Sensory organs that enhance taste and texture perception during feeding.
Understanding these adaptations provides insight into the insect’s ecological role and behavioral patterns.
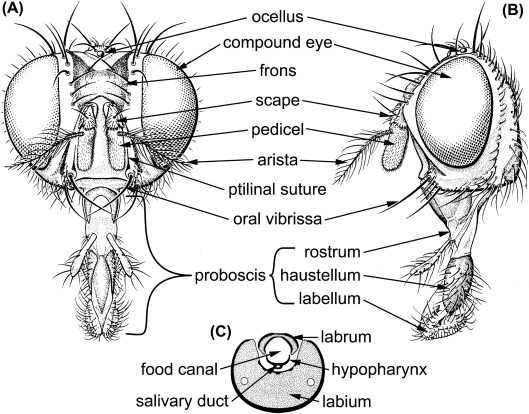
Anatomy of a Housefly’s Mouth
This section explores the intricate structures involved in feeding and sensory perception of a common insect. These elements are adapted for specific functions, allowing the creature to thrive in various environments.
Feeding Mechanism: The primary tool for nourishment consists of specialized appendages that assist in liquid extraction. These adaptations enable the insect to consume a wide range of substances efficiently.
Sensory Functions: Alongside feeding, certain features are equipped with sensory receptors. These enhance the ability to detect food sources, contributing to survival.
Evolutionary Adaptations: Over time, these structures have evolved to optimize feeding efficiency and sensory input, highlighting the organism’s adaptability to diverse ecological niches.
Function of Housefly Mouthparts

The specialized structures found in certain insects play a crucial role in their feeding behavior and interaction with the environment. These adaptations allow them to efficiently extract nutrients from various sources, showcasing a remarkable evolutionary trait that supports their survival and ecological niche.
Feeding Mechanism

The unique configuration enables these insects to engage in a variety of feeding techniques. By utilizing their specialized features, they can effectively consume liquids, which is essential for their nutritional intake. This method of feeding also facilitates the transfer of pathogens, highlighting their impact on ecosystems and human health.
Adaptations for Nutrient Extraction
Different feeding strategies among insects can be observed based on their evolutionary adaptations. The structures allow for both mechanical and enzymatic breakdown of food, maximizing nutrient absorption. This versatility is vital for thriving in diverse environments.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Liquid Consumption | Allows for the ingestion of liquids, crucial for hydration and nutrient uptake. |
| Pathogen Transfer | Facilitates the spread of microorganisms, impacting both ecology and human health. |
| Nutrient Breakdown | Enables mechanical and enzymatic processing of food for optimal nutrient absorption. |
Types of Feeding Mechanisms
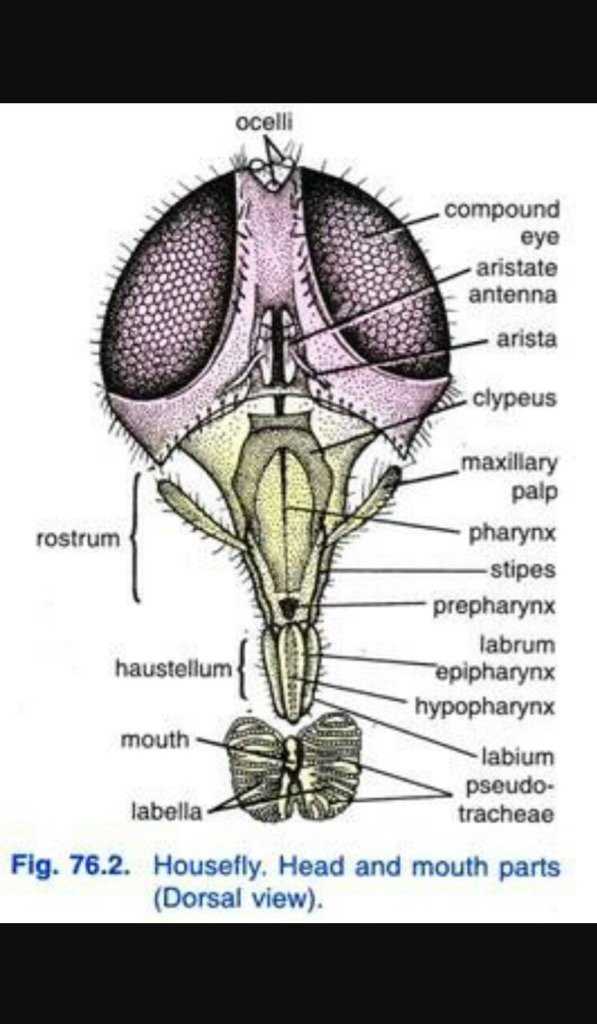
The various strategies for obtaining nourishment among insects reveal the incredible adaptability of these creatures. Different approaches not only dictate their diet but also influence their ecological roles and interactions with the environment. Understanding these methods provides insights into their survival and evolutionary success.
Liquid Feeding

One prominent technique involves the extraction of fluids, allowing access to nutrients dissolved in liquids. Insects employing this mechanism often have specialized structures to facilitate efficient intake. This method is vital for survival, especially in environments where solid food sources are scarce.
Solid Food Processing
Another approach focuses on the consumption and breakdown of solid materials. Insects utilizing this strategy typically possess robust features for grinding or tearing their food. Such mechanisms enable them to exploit a wide range of organic matter, showcasing their versatility in different habitats.
Comparative Anatomy with Other Insects
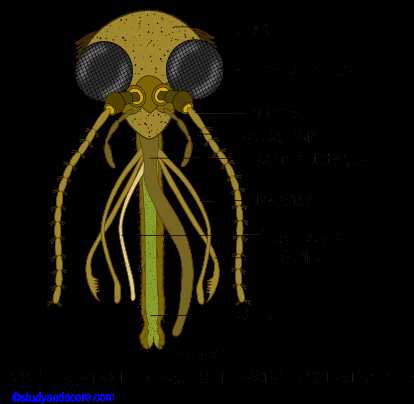

This section delves into the anatomical variations observed among various insect species, particularly focusing on feeding structures. By examining these differences, we can gain insights into the ecological niches that different insects occupy and their adaptations for survival.
Functional Adaptations

Insects exhibit a wide range of functional adaptations related to their feeding mechanisms. For example, while some species possess elongated structures suited for piercing and sucking, others have evolved robust components for grinding and chewing. These distinctions not only highlight the diversity within the insect world but also reflect their dietary preferences, whether herbivorous, carnivorous, or omnivorous.
Evolutionary Implications
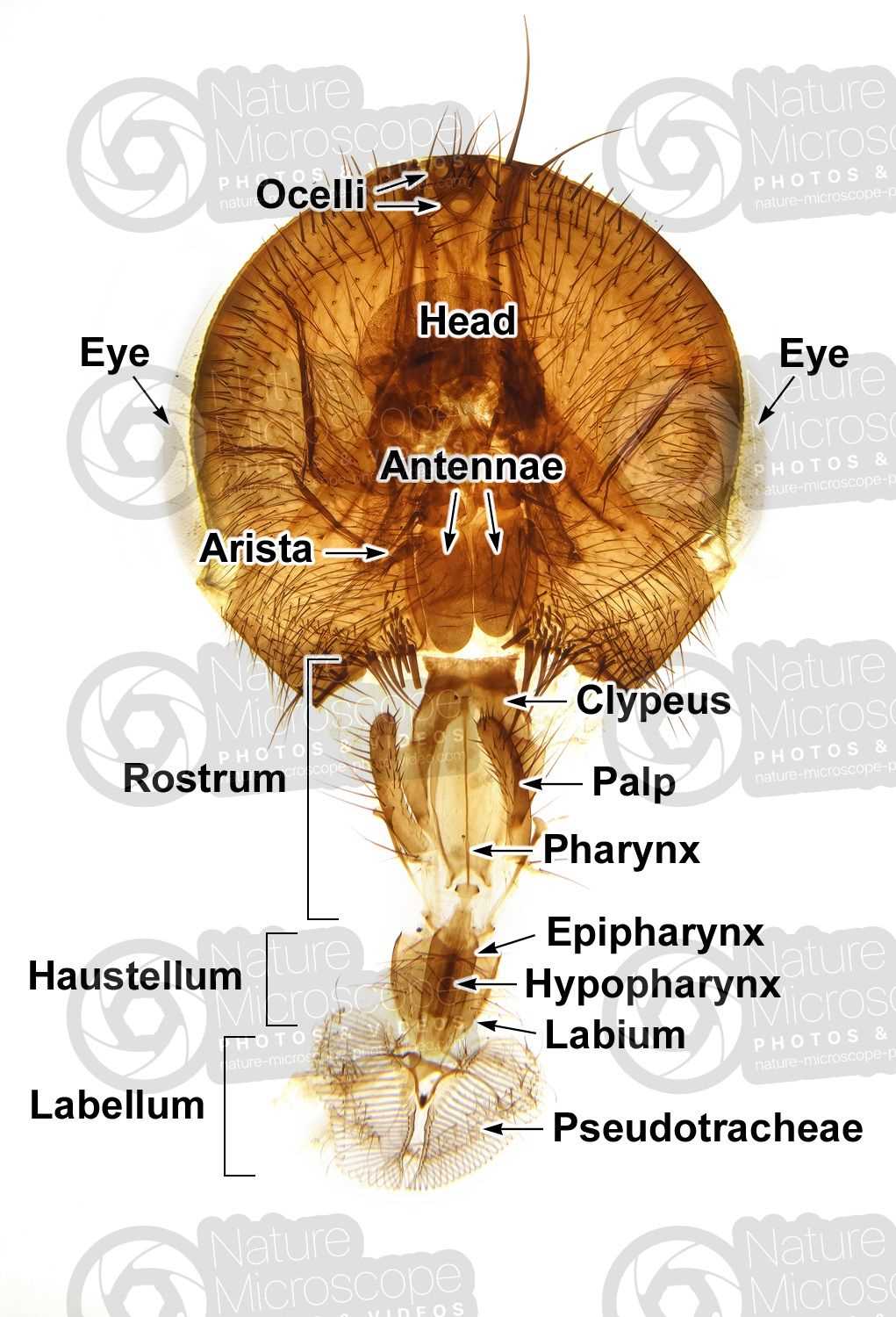
The evolutionary trajectories of these creatures have significantly influenced their anatomical designs. Structures that facilitate specialized feeding strategies often evolve in response to environmental pressures and resource availability. For instance, the unique modifications seen in pollinators compared to scavengers demonstrate how anatomical features can enhance efficiency in accessing specific food sources.
In summary, understanding the anatomical variations among different insects provides valuable insights into their evolutionary history and ecological roles.
Role in Ecosystem and Pollination
The significance of these insects extends far beyond their presence in human habitats. They play a vital role in various ecological processes, contributing to the balance of ecosystems and the health of plant communities. Their activities support not only their survival but also benefit a wide range of other organisms.
Contribution to Ecosystem Health
Insects like these serve multiple functions within their environments, including:
- Decomposition: They aid in breaking down organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil.
- Food Source: Many animals rely on them as a key source of nourishment, supporting diverse food webs.
- Waste Reduction: By consuming decaying matter, they help mitigate the spread of disease and maintain hygiene in ecosystems.
Role in Pollination
These creatures also play a critical role in the pollination process, which is essential for plant reproduction. Their interactions with various flora include:
- Transfer of Pollen: While foraging for food, they inadvertently transport pollen from one bloom to another, facilitating fertilization.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Their activity supports the growth of diverse plant species, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
- Food Production: Many crops benefit from their pollination, enhancing agricultural yields and food security.
Through their diverse contributions, these insects are indispensable allies in maintaining ecological balance and promoting the growth of healthy plant life. Their presence underscores the interconnectedness of all living organisms within ecosystems.
Housefly Feeding Behavior Patterns
The feeding habits of this common insect are fascinating and play a crucial role in its survival. These creatures exhibit a variety of behaviors when consuming food, influenced by their sensory perception and environmental factors. Understanding these behaviors provides insight into their ecological roles and interactions with their surroundings.
| Behavior Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Sampling | Using their sensory receptors to test food sources before ingestion. |
| Liquid Feeding | Utilizing a specialized mechanism to consume liquids, including nectar and decaying matter. |
| Regurgitation | Releasing digestive enzymes onto solid food to facilitate breakdown before consumption. |
| Grooming | Cleaning their bodies to remove food residues and maintain hygiene for effective feeding. |
| Foraging | Scouting for various food sources in diverse environments, showcasing adaptability. |
These behaviors highlight the adaptability and resourcefulness of the species, which enables it to thrive in various habitats. Observing these feeding strategies can enhance our understanding of their ecological significance and their impact on the environment.
Impact on Human Health
Insects that feed on organic matter can significantly influence human well-being. Their activities often facilitate the spread of various pathogens and diseases, raising concerns for public health. Understanding how these creatures interact with our environment is essential for mitigating potential risks.
One of the primary concerns associated with these insects is their role as vectors for numerous harmful microorganisms. As they traverse unsanitary surfaces, they can pick up and transfer bacteria, viruses, and parasites to food and living spaces. This transmission can lead to outbreaks of gastrointestinal diseases and other infections, posing a threat, particularly in densely populated areas.
Prevention of these health risks involves maintaining cleanliness in our surroundings and being aware of food safety practices. By minimizing exposure to these insects and implementing effective pest control measures, we can reduce the likelihood of disease transmission and safeguard public health.
Awareness and education about the risks associated with these insects are crucial. Public health initiatives aimed at informing communities about the importance of hygiene and pest management can play a vital role in reducing the impact of these insects on human health.
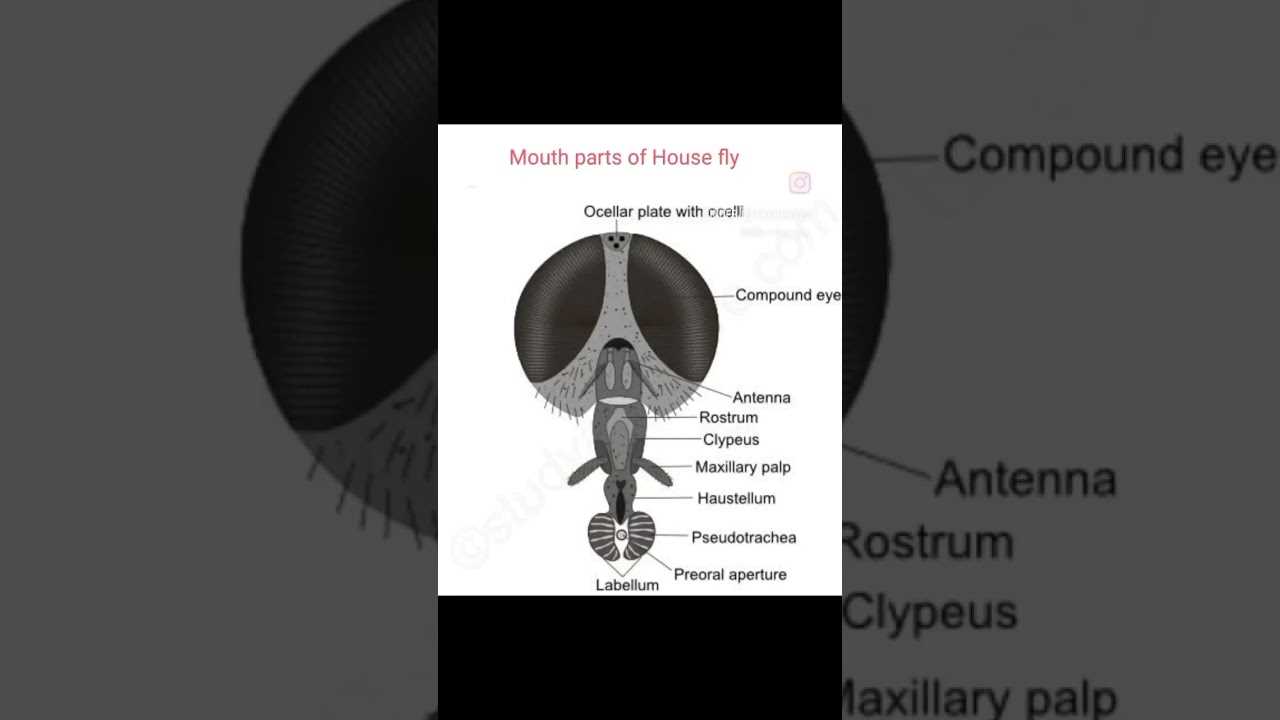
Diagram of Housefly Mouthparts
This section provides an overview of the specialized structures used by these insects for feeding and interaction with their environment. Understanding these unique tools is essential for comprehending how they obtain nourishment and interact with their surroundings.
Feeding Mechanism
The feeding mechanism consists of a combination of elongated and flexible components that allow for effective liquid consumption. These structures are designed to penetrate various surfaces, enabling access to a wide range of nutrients.
Role in Sensory Perception
In addition to feeding, these specialized tools play a crucial role in sensory perception. They help the insect detect flavors and textures, enhancing its ability to locate food sources efficiently. Ultimately, these adaptations are vital for survival in diverse environments.
Evolution of Housefly Mouth Structures
The transformation of feeding mechanisms in certain insects illustrates their adaptability and ecological niches. Over time, these adaptations have enabled them to thrive in diverse environments, leading to unique structural developments that facilitate their dietary needs.
Key Adaptations
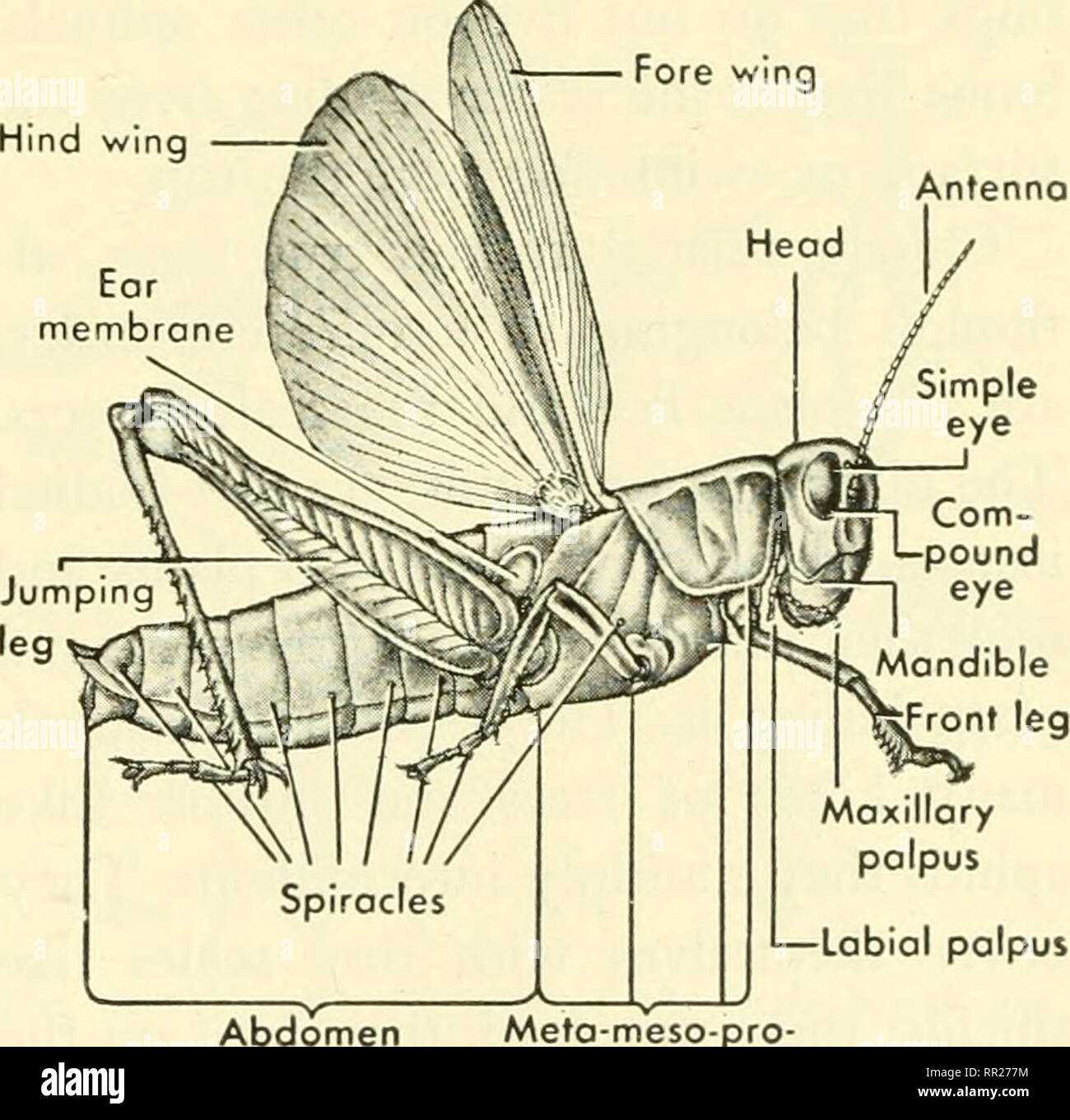
- Evolution of sponging mechanisms for liquid intake
- Development of specialized appendages for nutrient absorption
- Modification of sensory receptors for detecting food sources
Significance of Evolutionary Changes
- Enhanced survival through efficient feeding strategies
- Improved interactions with various food sources
- Influence on ecological relationships and roles
Interesting Facts About Houseflies
These common insects possess a range of remarkable characteristics that often go unnoticed. Their adaptations enable them to thrive in diverse environments, making them a subject of fascination for many. Understanding these features reveals the complexity of their biology and behavior.
One striking fact is their impressive flight capabilities. With the ability to beat their wings at around 1,000 times per minute, they can maneuver with incredible agility, allowing them to evade predators and navigate through tight spaces effortlessly.
Additionally, their sensory receptors are highly developed. Equipped with thousands of taste and smell sensors, they can detect food from great distances, guiding them to suitable sources of nourishment quickly and efficiently.
Their rapid reproduction cycle is another noteworthy aspect. Under optimal conditions, a single female can lay up to 500 eggs in just a few days, leading to exponential population growth. This ability allows them to adapt swiftly to changing environments.
Finally, these creatures play a vital role in ecosystems. They are essential decomposers, helping break down organic matter and contributing to nutrient recycling in nature. Despite being often viewed as pests, their ecological contributions are significant and worthy of recognition.