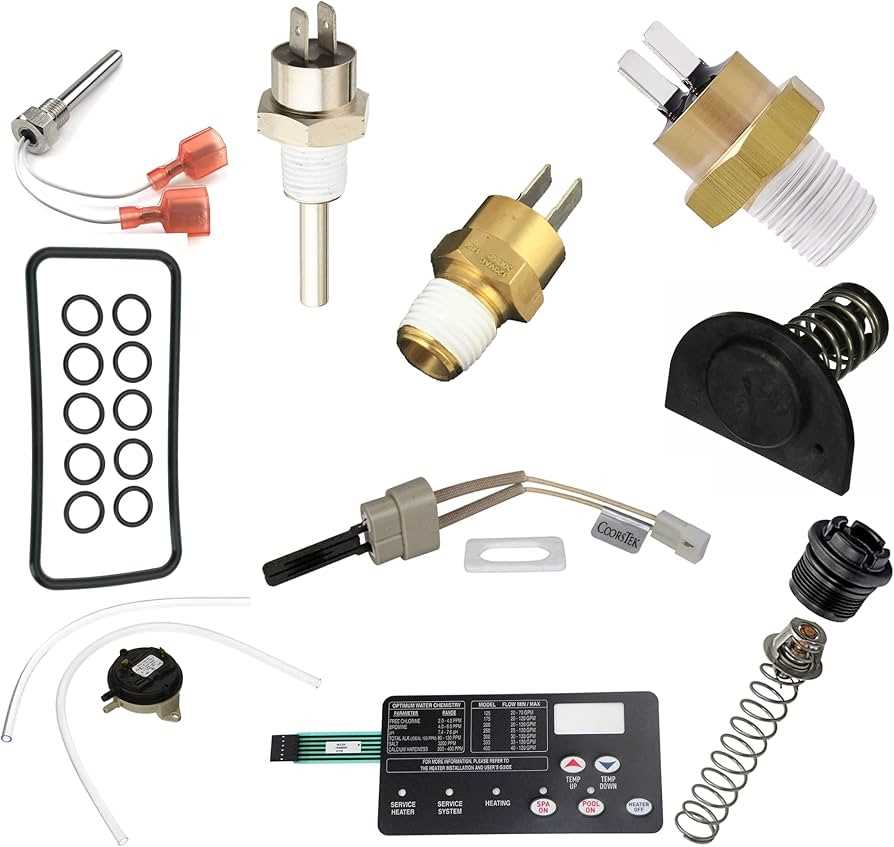
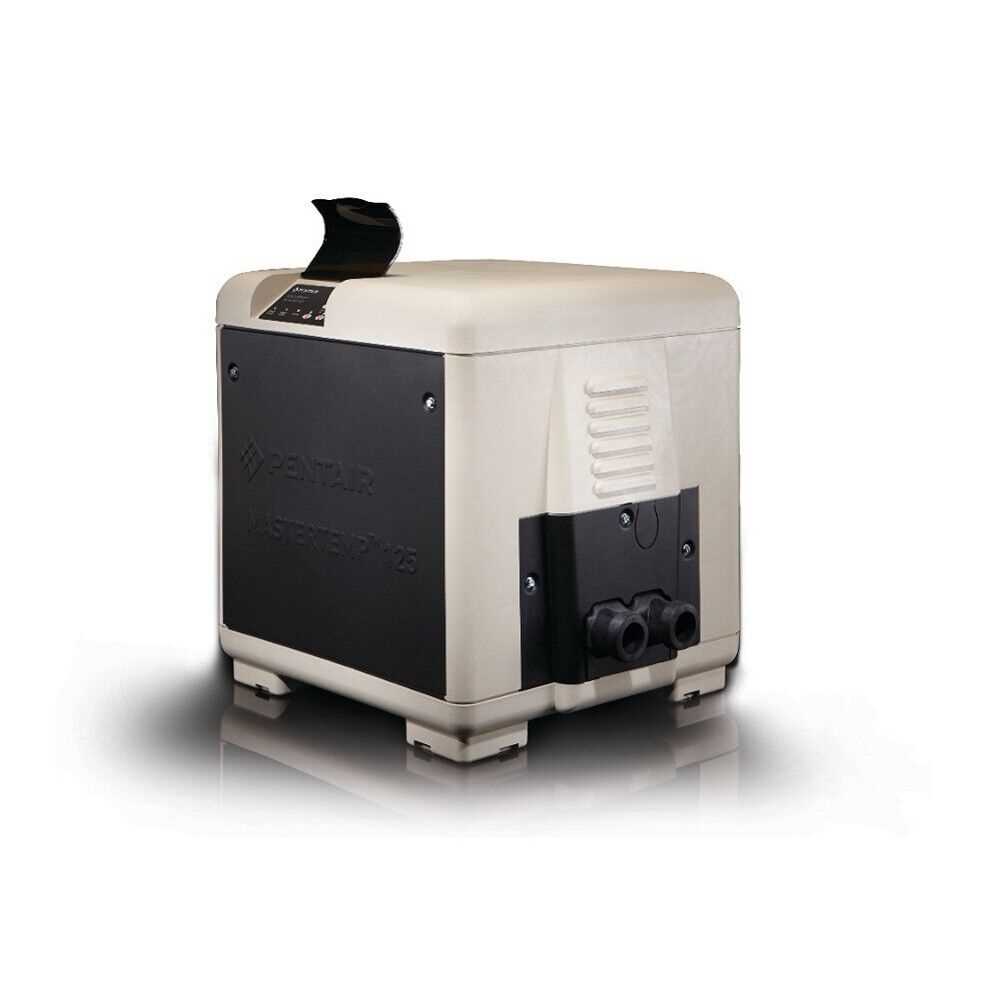
Every heating device relies on a series of interconnected elements that work together to provide efficient performance. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of specific components can significantly extend the lifespan of your equipment, ensuring optimal functionality for years to come. Whether dealing with repairs or upgrades, familiarizing yourself with the inner workings of such a system is essential.
In this guide, we will explore the arrangement of key mechanisms within a compact and effective heater. Knowing the exact placement of each essential unit allows for smoother troubleshooting and enhances your ability to perform routine upkeep. This approach not only boosts performance but also ensures the longevity of your equipment.
By gaining insight into the core structure, you’ll be better equipped to identify any malfunctions, locate essential elements, and make informed decisions when it comes to replacements or enhancements. Stay ahead of potential issues by understanding the detailed layout and role of each crucial component in your heating system.
Overview of Key Components

The following section will explore the various elements that make up the core of this heating system. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient functionality, from temperature regulation to safety mechanisms. Understanding the primary elements will help in maintaining and troubleshooting the device effectively.
Temperature Control Mechanisms
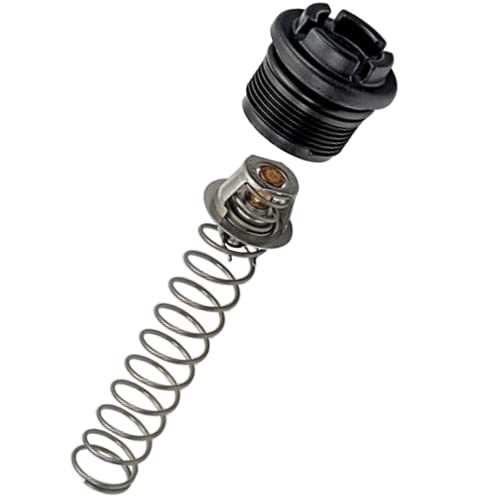
A primary feature of the system includes sophisticated mechanisms for maintaining desired heat levels. These components ensure that the system operates within optimal temperature ranges, preventing overheating or underperformance. Their accurate control is vital for the overall performance.
Safety Features and Sensors
Safety elements, including various sensors, are built into the system to monitor operation and prevent hazardous conditions. These sensors detect irregularities in performance, allowing the system to shut down or adjust automatically if needed, ensuring user safety and equipment longevity.
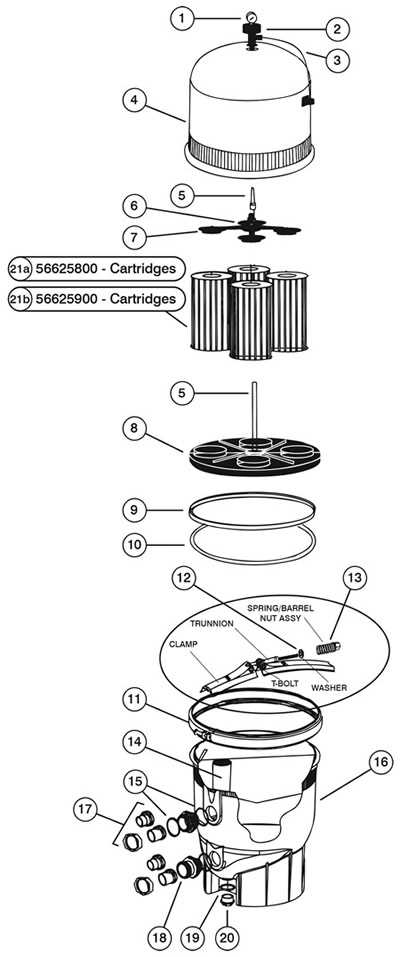
Key Internal Elements and Their Functions
The internal structure of this equipment contains a variety of crucial components designed to work together to ensure efficient operation. Each part has a specific role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the system. Understanding these elements and their functions helps in maintaining, troubleshooting, and enhancing the device’s longevity.
Main Operational Components
Several core mechanisms are responsible for the primary operation of the unit. These components regulate essential processes, ensuring smooth functionality. Their efficiency directly impacts how well the system performs under various conditions.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Module | Manages overall operation and ensures that all internal processes are running smoothly. | ||||||||||||||
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers heat effectively, playing a key role in temperature regulation. | ||||||||||||||
| Valve Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Ball Valve | Offers quick on/off control with minimal pressure drop. |
| Gate Valve | Provides full flow with low resistance when fully opened. |
| Check Valve | Prevents backflow and maintains system integrity. |
Importance of Seals
Seals are crucial in preventing leaks and ensuring the efficient operation of the heating apparatus. They are designed to withstand varying temperatures and pressures, thus maintaining the integrity of the system.
| Seal Type | Application |
|---|---|
| O-Rings | Used in various fittings to prevent fluid leakage. |
| Gaskets | Provide a sealing surface between flanged connections. |
| Mechanical Seals | Used in pumps to prevent leakage of fluids. |
Power Supply Components and Connections
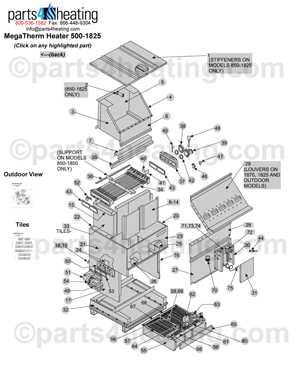
The functionality of heating units relies significantly on their electrical supply systems. Understanding the various components involved in the power supply and their interconnections is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. This section delves into the essential elements that form the backbone of these systems, ensuring reliable energy delivery for optimal performance.
Key Components of the Power Supply System
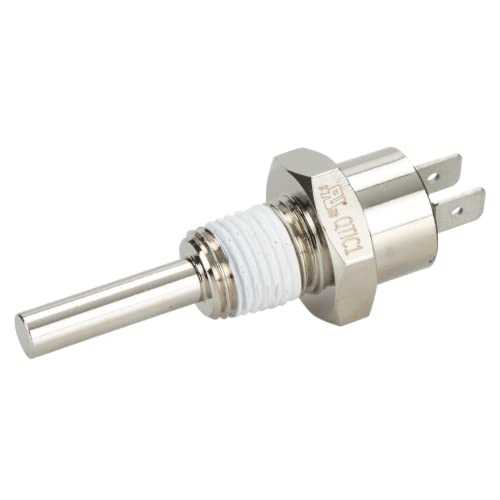

- Transformers: These devices convert voltage levels to the appropriate values required by the heating unit.
- Circuit Breakers: Essential for protecting the system from overloads, these components interrupt the electrical flow when necessary.
- Relays: These electromagnetic switches control the power to various parts of the system, allowing for automated operation.
- Capacitors: Used to store electrical energy, capacitors help maintain voltage stability and improve system efficiency.
- Wiring: Properly insulated and rated wires are crucial for safe and effective power distribution within the unit.
Connections and Wiring Practices
Effective connections between components are vital for the safety and functionality of the heating system. Here are some best practices:
- Ensure all connections are tight to prevent arcing and energy loss.
- Use wires of appropriate gauge to handle the expected current load without overheating.
- Regularly inspect connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for wiring layouts and configurations to maintain system integrity.
Common Replacement Parts and Their Usage
In maintaining heating units, understanding the essential components that may require replacement is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Regular wear and tear can affect various elements of the system, leading to inefficiencies or malfunctions. Here, we will explore several key components that are frequently replaced and their respective functions.
- Heating Element: This component is responsible for generating heat within the unit. Over time, it may become less efficient or fail completely, necessitating a replacement to restore proper operation.
- Thermostat: Serving as a temperature control mechanism, the thermostat regulates the heating process. A malfunctioning thermostat can lead to incorrect temperature readings, affecting the system’s efficiency.
- Pressure Switch: This safety feature ensures that the heating unit operates under appropriate pressure conditions. If it becomes faulty, it may prevent the unit from turning on or off as needed.
- Filter: Essential for maintaining clean water flow, the filter can become clogged or damaged over time. Regular replacement helps prevent debris from circulating through the system, ensuring longevity and performance.
- Water Pump: This component circulates water through the heating system. A failing pump can lead to inadequate heating and may require immediate attention to prevent further issues.
Being aware of these components and their functions can help users make informed decisions regarding maintenance and replacements, ultimately prolonging the life of their heating units.
Troubleshooting Diagram for Quick Repairs

When dealing with heating units, having a clear understanding of common issues can greatly enhance the efficiency of repair efforts. A structured approach to troubleshooting can help identify problems swiftly, minimizing downtime and ensuring the unit operates smoothly. Below are some steps and considerations that can assist in resolving typical malfunctions.
Common Issues and Solutions
- No Heat Production:
- Check power supply and connections.
- Inspect thermostat settings to ensure they are correct.
- Examine the heating elements for signs of wear or damage.
- Inconsistent Temperature:
- Verify the calibration of the temperature sensor.
- Inspect for blockages in water flow that could affect heating.
- Ensure the unit is properly vented to avoid overheating.
- No Water Flow:
- Check for clogged filters or debris in the plumbing.
- Inspect the pump for operational issues.
- Verify that valves are open and allowing water to flow.
Steps to Follow for Repairs

- Identify the symptom and gather relevant information.
- Refer to the operational guide for troubleshooting guidance.
- Test components systematically to isolate the issue.
- Perform necessary repairs or replacements as needed.
- Restart the unit and monitor performance closely.
By following these structured steps and utilizing this guide, quick repairs can be made efficiently, ensuring that the heating system remains reliable and effective.

