
Heating systems play a crucial role in maintaining comfort during cold months. To ensure optimal functionality, it is essential to grasp the various elements that contribute to the operation of such systems. This guide will help you explore the key components, providing an overview of their roles and how they interact within the overall mechanism.
By familiarizing yourself with these crucial elements, you can gain a better understanding of how the heating system operates and identify any potential issues that may arise. This knowledge will empower you to maintain your equipment more effectively, ensuring it continues to function smoothly for years to come.
In the following sections, we will delve into the core elements of this heating solution, examining each piece and its significance in the system’s overall performance. Whether you are troubleshooting or simply curious about how everything works together, this comprehensive exploration will offer the clarity you need.
Overview of Key Components in Trane XR90

Understanding the primary elements of this system is crucial for optimal performance and maintenance. Each section within the unit plays a significant role in ensuring efficient functionality, from temperature regulation to air distribution. Below is a breakdown of the most critical pieces that work together to keep the unit running smoothly.
- Control Board: This acts as the brain of the system, managing and coordinating the operation of all other elements.
- Heat Exchanger: Converts energy into heat, ensuring that the space receives the desired warmth during operation.
- Blower Motor: Responsible
Understanding the Furnace Control Board

The control unit is a crucial component responsible for regulating and coordinating various functions of the heating system. It acts as the brain of the operation, managing everything from ignition to fan control. This electronic board ensures that the system operates safely and efficiently by handling the communication between sensors and mechanical parts. Without this coordination, the heating process could not be properly managed.
Main Functions
The primary role of the control board is to sequence the start-up and shutdown of the system. It monitors key sensors, controlling the flow of heat, air, and fuel. This ensures optimal temperature regulation and prevents overheating. Additionally, it provides error codes when a malfunction is detected, helping technicians diagnose
Exploring the Heat Exchanger Functionality

The mechanism responsible for transferring thermal energy within a system plays a crucial role in maintaining efficiency and safety. This component ensures that heated air is effectively utilized, optimizing the system’s overall performance. It serves as a bridge between the energy source and the distribution of warmth, controlling the balance between input and output temperatures.
One of its essential functions is to prevent the escape of harmful gases by containing the combustion process within sealed chambers. This controlled process not only improves energy efficiency but also enhances the environmental safety of the heating system, making it a key factor in both residential and industrial applications.
Blower Motor and Its Role
The air circulation mechanism plays a critical function in ensuring efficient heating and cooling within any system. At the core of this mechanism is a powerful component responsible for driving air movement throughout the entire structure. This ensures that the environment remains comfortable, regardless of temperature fluctuations. By directing airflow consistently, it optimizes overall system performance, contributing to energy efficiency and maintaining balanced indoor conditions.
Function Impact Air Distribution Ensures even airflow to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the space. System Efficiency Reduces energy consumption by maintaining a smooth Significance of the Ignitor in Heating Systems
The ignitor plays a crucial role in the functionality of heating units by initiating the combustion process. It serves as the catalyst that transforms the fuel into heat, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and safely. Without this essential component, the heating mechanism would be unable to produce the necessary warmth, rendering the entire system ineffective.
Types of Ignitors
There are various types of ignitors utilized in heating systems, each designed to suit specific operational requirements. Understanding the differences can aid in selecting the right component for optimal performance.
Type Description Common Applications Hot Surface Ignitor Uses a resistive heating element to ignite fuel. Furnaces, Boilers Intermittent Pilot Ignitor Creates a flame only when needed, improving efficiency. Gas Furnaces, Water Heaters Continuous Pilot Ignitor Maintains a constant flame for immediate ignition. Older Heating Systems, Commercial Applications Impact on System Efficiency
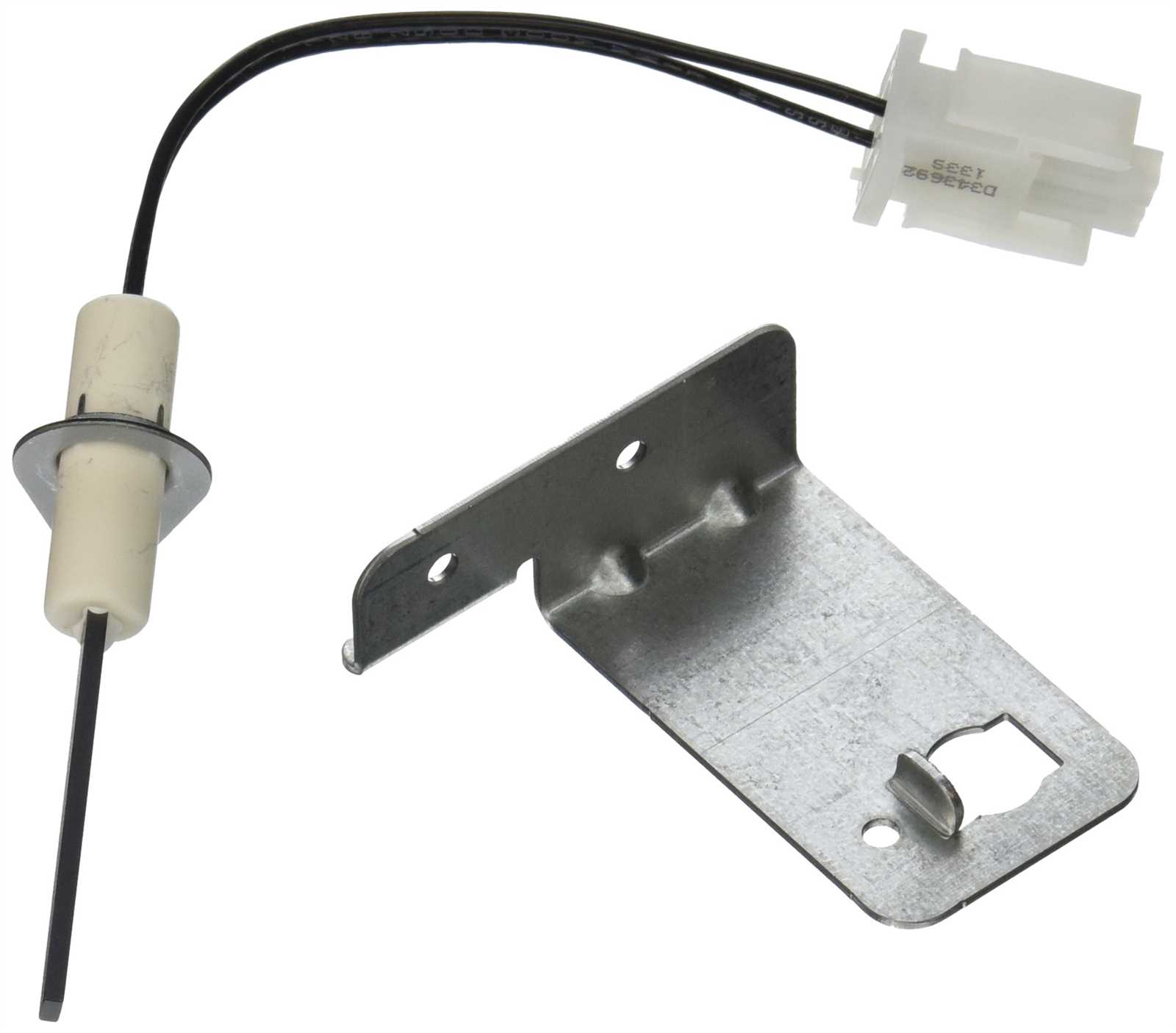
The performance of an ignitor directly influences the efficiency of heating systems. A well-functioning ignitor ensures that combustion occurs promptly and completely, minimizing wasted fuel and maximizing heat output. Conversely, a malfunctioning ignitor can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in reduced efficiency and potential safety hazards.
Importance of Gas Valve in Furnace Operation

The gas valve is a crucial component in the functioning of heating systems, playing a vital role in ensuring safe and efficient operation. This device regulates the flow of gas to the burner, enabling the combustion process necessary for generating heat. Its functionality directly impacts the overall performance and reliability of the heating appliance.
One of the primary functions of the gas valve is to control the supply of fuel, ensuring that the right amount is delivered to maintain optimal temperatures. A properly functioning valve prevents excess gas from escaping, which not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the risk of hazardous situations, such as gas leaks.
Additionally, the gas valve contributes to the safety mechanisms of the heating system. It is equipped with various features, such as safety switches and automatic shutoff capabilities, which activate in case of malfunctions or irregularities. This ensures that the system can safely shut down, preventing potential accidents.
In summary, the gas valve’s significance cannot be overstated. Its role in regulating fuel flow and ensuring safety makes it an indispensable part of any heating system. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of this component are essential to ensure uninterrupted and secure operation.
Analyzing the Pressure Switch Mechanism

The pressure switch serves as a crucial component in regulating the operation of heating and cooling systems. It functions by monitoring the pressure levels within the system and ensures that these levels remain within safe operational boundaries. If the pressure deviates from the established thresholds, the mechanism activates safety protocols to prevent potential damage and ensure efficient functioning.
Understanding the Functionality of the pressure switch is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. When the system operates normally, the switch engages and allows the unit to run smoothly. However, in cases of pressure anomalies, the switch triggers a shutdown, protecting the equipment from undue stress and preventing potential malfunctions.
In addition, the location of the pressure switch within the system is significant, as it directly impacts its responsiveness. Typically positioned in a strategic area, it can quickly detect changes in pressure and react accordingly. Regular checks and calibration of this component are vital to maintain optimal performance and prolong the lifespan of the heating and cooling systems.
Moreover, understanding the relationship between the pressure switch and other components, such as the compressor and blower, enhances the overall efficiency of the system. By ensuring that the pressure switch is functioning correctly, users can prevent costly repairs and improve the energy efficiency of their units.
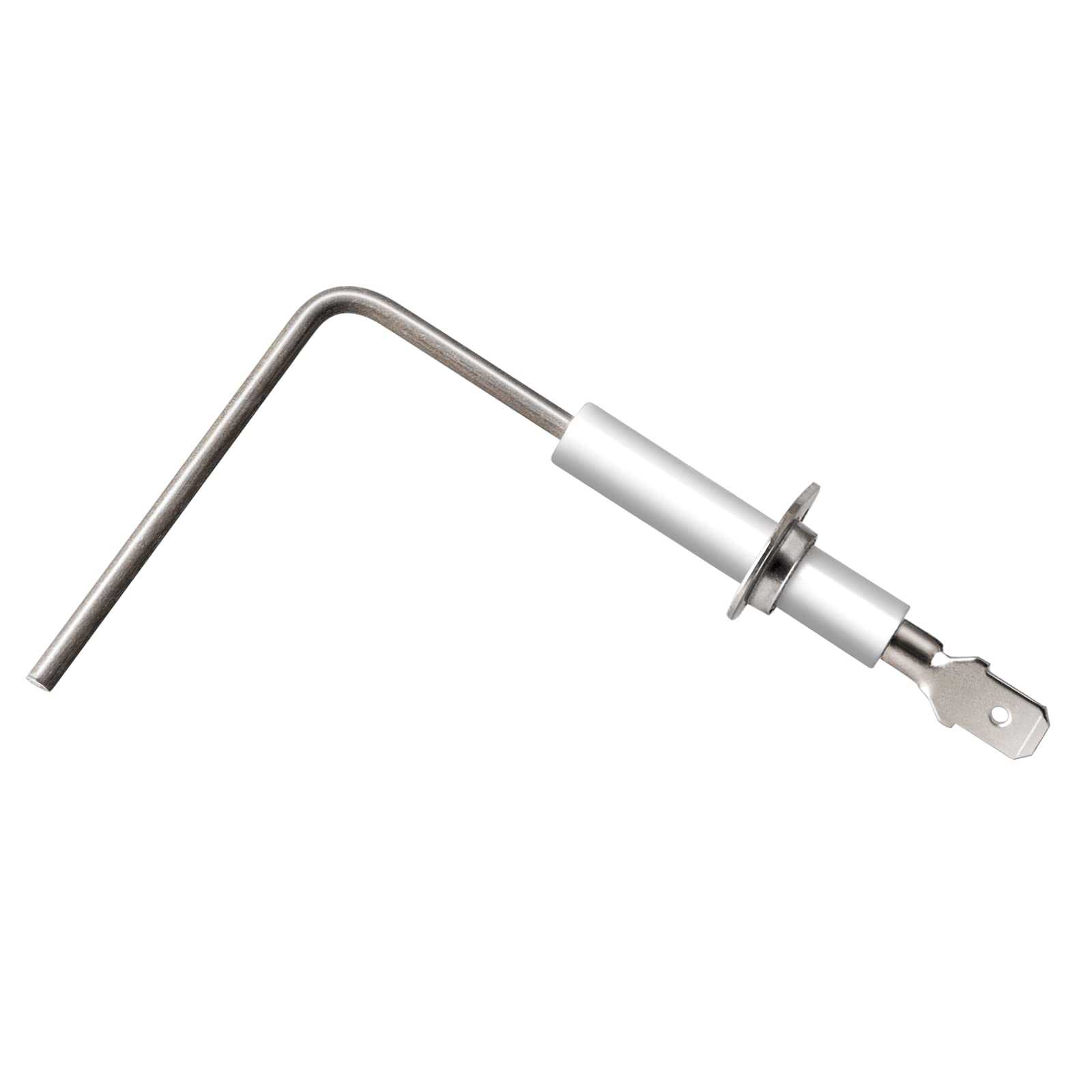
Flame Sensor and Its Operational Use

The flame sensor plays a critical role in the safety and efficiency of combustion systems. Its primary function is to detect the presence of a flame, ensuring that the heating system operates smoothly and prevents dangerous situations, such as gas leaks or explosions. By monitoring the flame, this component helps maintain optimal performance and energy usage.
Understanding how the flame sensor operates is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are some key points about its functionality:
- Detection Mechanism: The sensor utilizes infrared or ultraviolet light to identify the presence of a flame.
- Response Time: Quick detection allows for immediate adjustments in the system, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Integration: It works in conjunction with the ignition system and gas valves to control fuel flow.
Regular checks and cleaning of the flame sensor are vital to its proper functioning. Neglecting this component can lead to system malfunctions, including:
- Failure to ignite the burner.
- Frequent system shutdowns.
- Increased energy consumption due to inefficient operation.
By ensuring the flame sensor is in good working condition, users can enhance the overall reliability of their heating systems, promote safety, and reduce operational costs.
Examining the Inducer Motor System

The inducer motor system plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of heating appliances by facilitating proper airflow through the combustion chamber. This mechanism is designed to optimize the process of gas combustion while ensuring safety and reliability in operation. Understanding the components and functionality of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Inducer Motor System
The primary elements of the inducer motor system include the motor, housing, and associated wiring. Each component works in harmony to ensure that the system operates smoothly. Below is a detailed overview of these components:
Component Description Inducer Motor This motor generates the necessary airflow to support efficient combustion by drawing air into the system. Housing The casing that encases the inducer motor, protecting it from external elements while aiding in airflow direction. Wiring Electrical connections that power the inducer motor and allow it to communicate with the control board. Functionality of the Inducer Motor
The operation of the inducer motor system is critical for maintaining optimal performance. By ensuring the correct air pressure within the combustion chamber, the inducer motor enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions. It also plays a significant role in safety by preventing the buildup of harmful gases. Regular inspection and maintenance of this system are essential for long-lasting operation and efficiency.
Safety Features and Limit Switch Overview
Understanding the mechanisms that ensure safe operation in heating systems is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Safety features are designed to protect both the equipment and the users by monitoring various operational parameters and intervening when necessary. Among these features, limit switches play a vital role in regulating system performance and preventing potential hazards.
Key Safety Features
- Overheat Protection: This feature automatically shuts down the system if excessive temperatures are detected, preventing damage to internal components.
- Flame Rollout Switch: A device that monitors the combustion area and will trigger a shutdown if it detects flame movement beyond the designated zone.
- Pressure Switch: Monitors the pressure levels within the system and ensures they remain within safe operating limits.
Limit Switch Functionality

Limit switches are critical components that monitor the operational status of heating units. They are activated when specific conditions are met, providing an essential safety net.
- High-Temperature Limit Switch: Activates when temperatures exceed preset levels, halting the operation to prevent overheating.
- Low-Temperature Limit Switch: Ensures that the system operates only within a safe temperature range, preventing damage during low-temperature conditions.
Incorporating these safety features and limit switches significantly enhances the reliability of heating systems, ultimately contributing to safer environments for users and improved longevity for the equipment.
Detailed Look at the Capacitor’s Purpose
Capacitors play a vital role in various electrical systems, serving as components that store and release energy. They help regulate voltage and improve the performance of electrical circuits. Understanding their function is essential for anyone involved in maintaining or repairing heating and cooling systems.
Energy Storage and Release
At its core, a capacitor acts as a temporary energy reservoir. It can accumulate charge when the electrical supply is stable and release it when needed. This ability to store energy is crucial during the startup phase of motors, where a sudden demand for power occurs. By providing an extra burst of energy, capacitors help ensure smooth operation and prevent system strain.
Enhancing Circuit Performance
Another important function of capacitors is to enhance the overall performance of circuits. They can filter out unwanted noise and smooth fluctuations in power supply, leading to more reliable operation. This stability is particularly important in systems that require precise control over their electrical environment, as it helps prevent damage to sensitive components.
In summary, capacitors are essential in electrical systems, providing both energy storage and performance enhancement. Their role in ensuring efficient operation cannot be overstated.
Replacing or Maintaining Air Filters

Regular upkeep of air filtration systems is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your heating and cooling units. Proper maintenance not only enhances air quality but also contributes to energy efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Filters should be inspected frequently, typically every 1-3 months, depending on usage and environmental factors. When dirt and debris accumulate, airflow is restricted, leading to increased energy consumption and potential system failure. Here’s a guideline for effectively managing your air filters:
- Check the filter’s condition regularly.
- Replace disposable filters as needed.
- Clean reusable filters according to manufacturer instructions.
Choosing the right type of filter is essential for maintaining system efficiency. Consider the following options:
- Fiberglass filters: Affordable but need frequent replacement.
- Pleated filters: More effective in trapping particles and have a longer lifespan.
- HEPA filters: Ideal for capturing small particles, excellent for allergy sufferers.
To ensure a smooth replacement process:
- Turn off the heating or cooling system.
- Locate the filter compartment.
- Remove the old filter carefully.
- Insert the new or cleaned filter, ensuring proper orientation.
- Turn the system back on.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can significantly enhance the performance of your air handling equipment while maintaining a comfortable environment in your space.