
The structure of any mechanical system relies on a well-organized arrangement of individual elements. To ensure smooth operation and ease of maintenance, it is essential to have a clear overview of how different elements connect and function together. Knowing the layout of the components allows for efficient troubleshooting and helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate.
When dealing with complex machinery, recognizing the positioning and interaction between different sections is crucial. A detailed illustration of the individual segments can provide a visual representation, aiding in both repairs and regular upkeep. This organized overview is indispensable for anyone looking to maintain or upgrade their equipment with precision.
Having access to a reliable guide to the internal and external components of the machinery not only saves time but also ensures that each part is handled correctly. This comprehensive understanding makes the process of maintenance smoother, reducing the likelihood of errors and ensuring optimal performance.
John Deere 100 Series Overview
The lineup of lawn tractors has gained popularity due to its user-friendly design and efficiency. These machines are known for their durability, ease of use, and versatility, offering homeowners a reliable tool for maintaining their lawns. Whether you’re tackling a small garden or a larger property, this range provides an array of features suited for various needs.
Main Features
- Durable construction ensuring long-lasting performance
- Comfortable seating and ergonomic controls for ease of operation
- Efficient cutting systems designed for different types of grass and terrain
- Wide range of attachments available for year-round use
Performance and Usability
The models in this lineup are engineered with the user in mind, making yard work simpler and more efficient. High-powered engines provide sufficient torque for cutting, hauling, and towing. Moreover
Main Components Breakdown
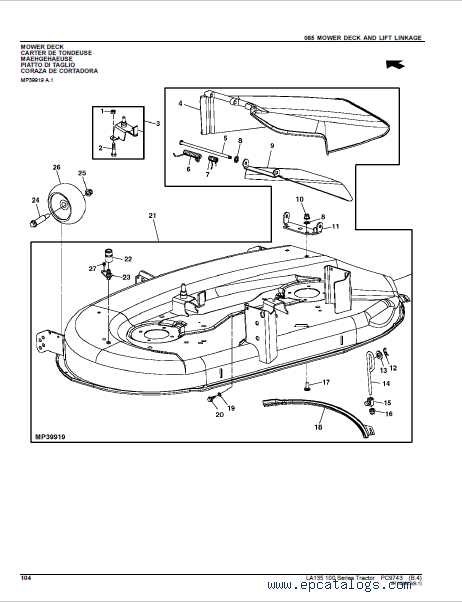
The essential structure of the machinery consists of several key elements that work in harmony to ensure smooth operation. Each part plays a distinct role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency. In this section, we will delve into the critical components that form the backbone of the system.
Engine and Power System
The central power source, typically an internal combustion engine, drives the entire mechanism. This engine is responsible for generating the necessary force to perform various tasks, from movement to specialized operations. The power system ensures that energy is efficiently transmitted to all other areas, making it a crucial aspect of the machinery’s performance.
Transmission and Steering
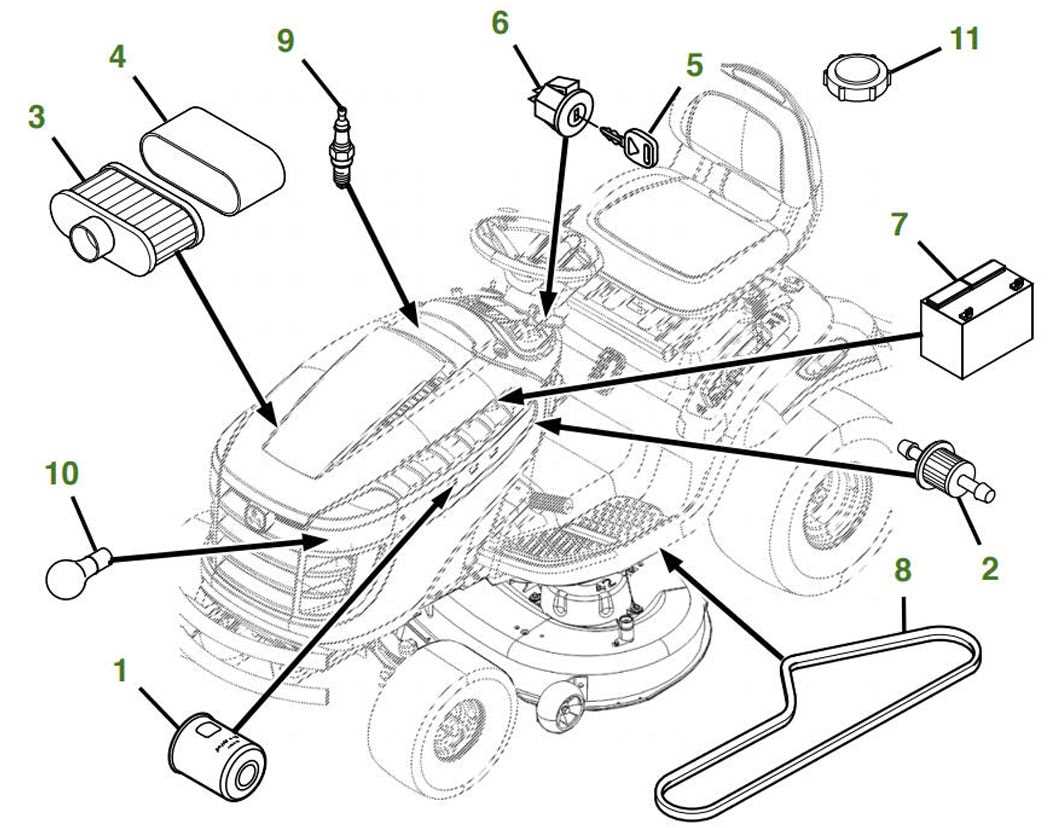
The transmission system allows for smooth transitions between different speeds and directions. It works closely with the steering mechanism, enabling precise control and maneuverability. Whether navigating tight spaces or operating on uneven terrain, these components provide the flexibility needed to handle diverse environments.
Engine Structure and Key Elements
The inner workings of a modern engine rely on a carefully designed system of components that work together to ensure optimal performance. Each part plays a crucial role in maintaining the functionality and efficiency of the machine. Understanding how these elements are arranged and interact with one another is vital for both maintenance and troubleshooting.
Core Components

- Cylinder Block: The foundation of the engine, housing the cylinders and providing support for other essential elements.
- Piston: Moves up and down within the cylinder to create the force needed to power the machine.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational
Essential Parts of the Power Unit
The power unit is a critical component, responsible for ensuring efficient energy transmission and operation. It is composed of several interconnected elements that work together to convert fuel into mechanical energy. Understanding the core elements involved is vital for maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the operational life of the equipment.
One of the primary elements is the combustion chamber, where fuel mixes with air and ignites, creating the energy needed to drive the machinery. Another essential part is the piston system, which transfers the energy produced into motion. These two systems must function seamlessly for smooth and efficient energy conversion.
Additionally, the cooling system plays a crucial role in regulating temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring the durability of the unit. The power unit also relies on a lubrication system to minimize friction and
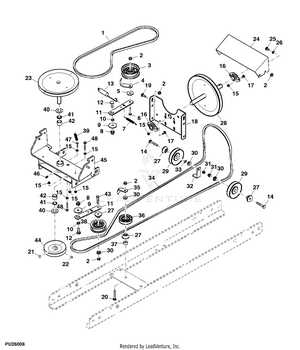
Transmission and Drive System Components

The transmission and drive system play a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth and efficient movement. These components work together to regulate speed and torque, allowing for optimal performance in various operating conditions.
- Transmission Assembly: This mechanism controls the application of power and is responsible for adjusting speed and direction. It includes multiple gears to manage engine output effectively.
- Drive Belt: The belt transfers energy from the engine to the wheels, ensuring continuous motion and proper function of the vehicle.
- Axles: These sturdy components bear the weight of the vehicle and connect the drive system to the wheels, enabling movement.
- Clutch Mechanism: Engages and disengages the power transfer from the engine to the transmission, offering
Diagram of the Drivetrain Parts
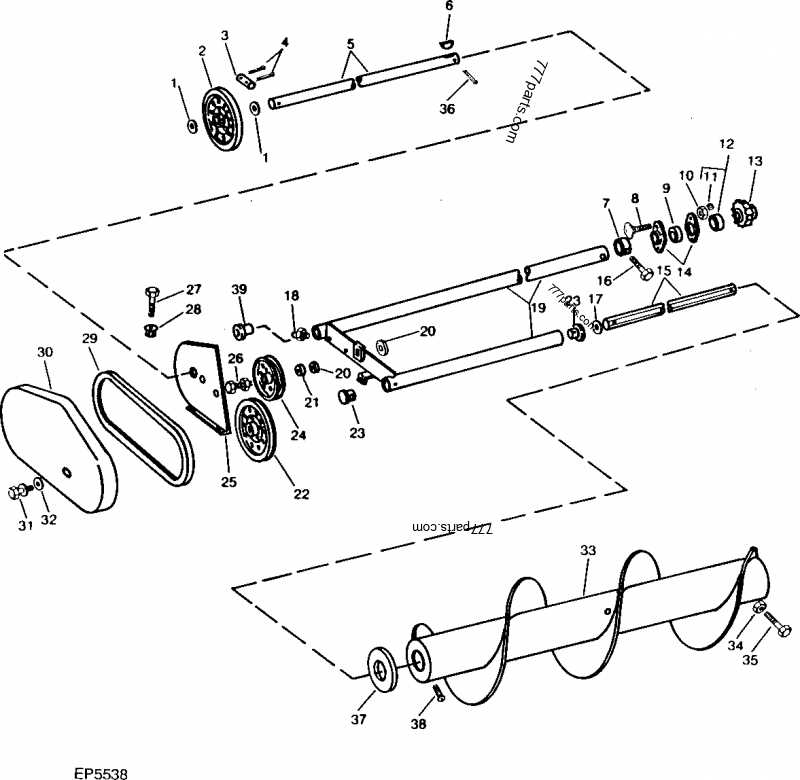
The drivetrain of a machine is responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels, enabling movement. Understanding how these components work together is essential for proper maintenance and repair. The following section provides an overview of the key elements involved in this system, outlining their function and relationships within the mechanical structure.
Key Components of the Drivetrain
Each part in the drivetrain plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and efficient power transfer. These components include the transmission, axles, and related elements that allow the vehicle to move forward or backward. Below is a breakdown of these essential parts and their connections.
Component Description Transmission Responsible for changing the speed and torque of the engine to suit different driving conditions. Drive Shaft Transfers rotational power from the transmission to the wheels. Axles Supports the weight of the vehicle and allows the wheels to rotate. Differential Helps distribute power to the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds during turns. How These Parts Work Together
Each element in the drivetrain works in tandem to achieve efficient motion. When the engine generates power, the transmission adjusts it before sending it through the drive shaft to the axles. The differential ensures that the wheels move in harmony, even when turning, offering optimal control and performance on various terrains.
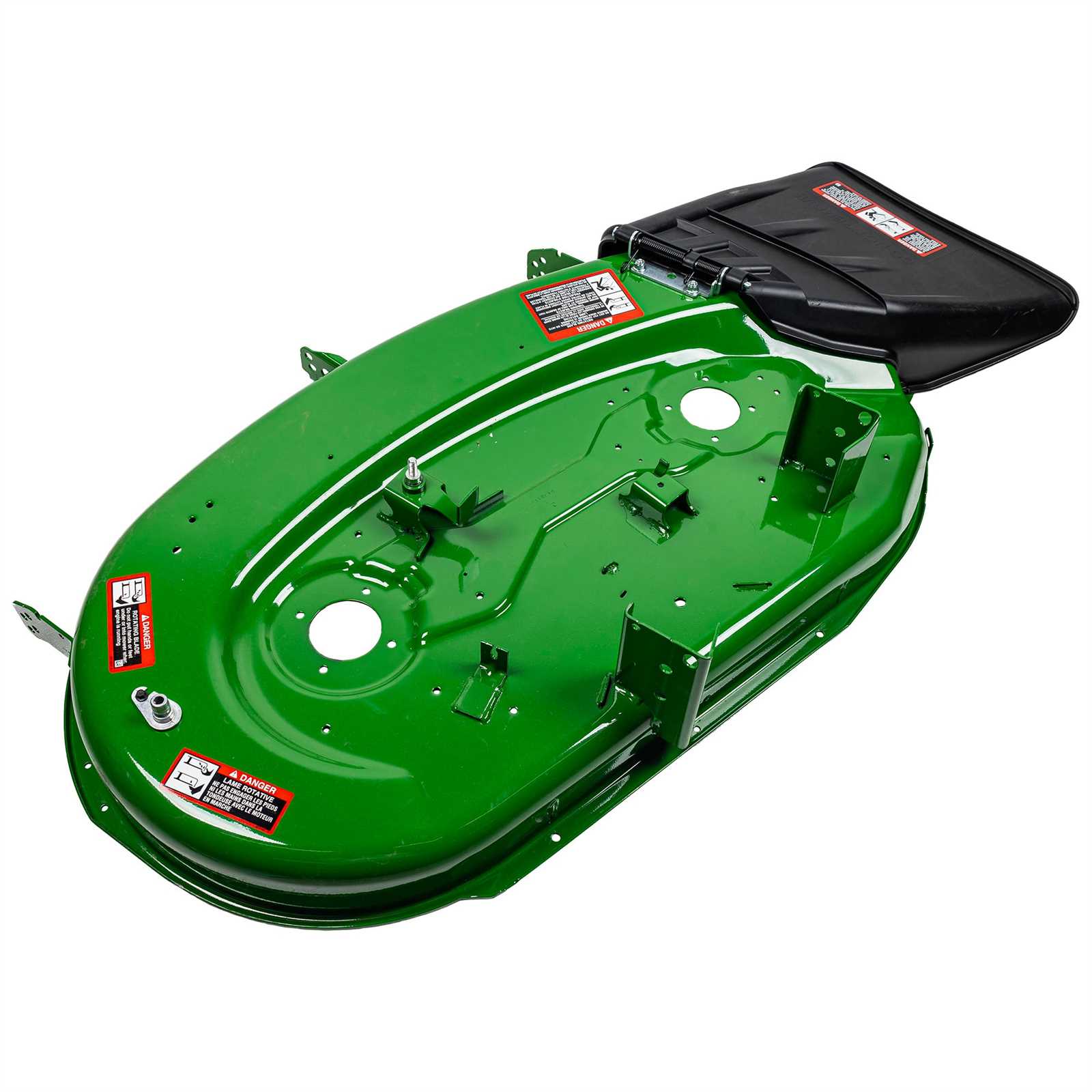
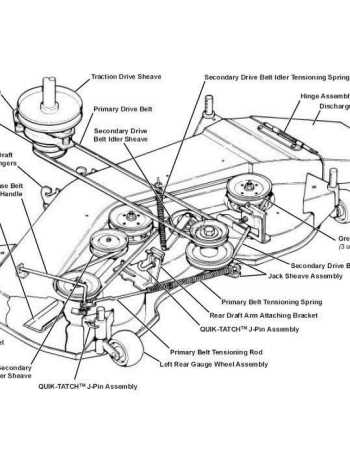
Deck Assembly and Cutting Mechanism
The deck structure plays a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the cutting process in a lawn care machine. It is the part that houses the blades and ensures an even cut across various terrains. Understanding how this assembly works and the mechanism behind the blade movement is essential for maintaining optimal performance and achieving the desired results in grass trimming.
Deck Components

- Chassis: The framework that supports the entire cutting assembly.
- Blades: Sharp rotating parts responsible for cutting the grass.
- Spindle: A central unit that drives the rotation of the blades.
- Deflector: A piece that guides the grass away from the blades during operation.
- Height Adjustment Mechanism: Allows the operator to control the cutting height.
Cutting Mechanism
The cutting action is powered by a spindle that rotates multiple blades. These blades are designed to spin at high speeds, cutting the grass cleanly as they pass through. The rotation is typically powered by the engine of the machine, with the speed and sharpness of the blades being crucial factors in achieving an even and professional-looking lawn. The height adjustment feature allows for flexibility, letting the user adapt to different grass lengths and terrains.
Understanding the Mowing System

The mowing mechanism is the heart of any grass-cutting machine, ensuring efficient and precise trimming. This system consists of multiple interconnected components that work together to create an even cut across varying terrain. The performance of this system is heavily influenced by the design of the cutting deck, the blade system, and the power delivery from the engine. Each part must function seamlessly for optimal results and durability.
At the core of the mowing system is the rotating blade assembly, which is powered by the engine’s drive system. The blades spin at high speeds to ensure clean and consistent cuts. The cutting deck housing, which encloses the blades, is designed to channel grass into a collection system or direct it back to the ground as mulch. Proper adjustment and maintenance of these components play a critical role in achieving uniform cutting performance.
The efficiency of the system is also determined by how well the components are aligned and the condition of the blades. Over time, wear and tear can reduce cutting efficiency, which is why regular maintenance is essential to keep the mowing system in peak working condition. Keeping the blades sharp and ensuring that all parts are properly lubricated and adjusted will extend the lifespan of the system and enhance the overall mowing experience.
Electrical System and Wiring Diagram
The electrical network of a machine plays a crucial role in ensuring that all components work efficiently. This section focuses on the intricate wiring that connects the various electrical parts, providing the necessary power for smooth operation. Understanding the connections between the different elements is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Overview of the Electrical Network
This system includes the main components that power essential functions, such as the ignition, lighting, and control circuits. The wiring structure connects all the necessary components to allow seamless operation, ensuring that electrical flow is stable and reliable. The careful routing of wires helps prevent interference and potential shorts, ensuring that each element gets the correct voltage.
Wiring Connections and Components
Component Function Connection Battery Power supply for all electrical components Connected to the main fuse and starter motor Fuse Protects the system from overloads In line with the battery and other key circuits Ignition Switch Controls the start of the engine Wired to the battery and starter motor Lights Provide visibility for operation Connected to the main electrical bus Alternator Charges the battery during operation Wired to the battery and electrical system Components of the Electrical Circuit
The electrical system of any machinery is composed of several vital elements that work in tandem to ensure smooth operation. These components are responsible for transmitting power, controlling various functions, and ensuring safety and efficiency during use. Understanding the structure and role of these parts helps in troubleshooting, maintenance, and overall performance optimization.
Power Source and Distribution
- Battery: Provides the initial electrical energy necessary to start the engine and power other components.
- Alternator: Recharges the battery and supplies power to the system while the engine is running.
- Fuses: Protects the circuit from excessive current by breaking the connection in case of a fault.
- Relays: Act as switches that allow electrical current to flow to specific components when needed.
Control and Safety Features
- Switches: Enable the user to control various functions like lights, ignition, or other accessories.
- Wiring Harness: The network of wires that carries electrical signals and power throughout the system.
- Grounding System: Ensures safety by directing excess electricity away from sensitive parts.
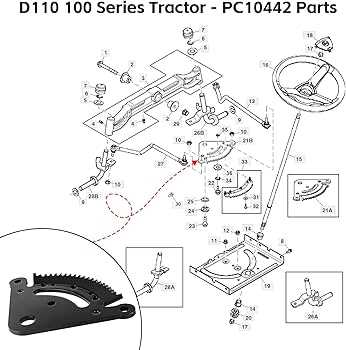
Steering and Control System Parts
The steering and control mechanism of a machine plays a critical role in ensuring smooth handling and maneuverability. This system is designed to provide the operator with precise control, allowing the vehicle to respond accurately to movements. Understanding the key components involved can greatly improve the ease of operation and the efficiency of the equipment.
Key Components
- Steering Wheel – the primary interface for directing movement.
- Steering Shaft – transfers rotational motion from the wheel to the steering mechanism.
- Linkage Assembly – connects various parts of the system for coordinated movement.
- Hydraulic Cylinder – assists in providing power to steer the machine with less effort.
- Pivot Points – enable the wheels to turn smoothly in response to steering commands.
Control Mechanisms
- Throttle Control – regulates the engine speed, affecting overall movement.
- Brake Pedal – used for halting or slowing down the vehicle.
- Gear Lever – allows the operator to switch between different speeds and gears for enhanced control.
- Clutch Pedal – disengages the transmission to facilitate smooth gear changes.
Diagram of Steering Mechanism Components
The steering mechanism of a lawn tractor is a critical part that ensures smooth navigation and control. This system integrates various components that work together to direct the movement of the vehicle, providing stability and maneuverability during operation. Understanding the layout of these parts is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Component Description Steering Wheel The primary control interface that allows the operator to steer the vehicle. Steering Shaft A vertical shaft that connects the steering wheel to the steering linkage. Steering Gear A gear mechanism that translates the rotation of the steering wheel into linear motion. Linkage A series of rods and joints that connect the steering gear to the front wheels, transmitting the steering action. Front Axle The component that supports the front wheels and allows them to pivot in response to steering input. Pivot Points Joints that enable the front wheels to rotate smoothly, allowing for directional changes. Fuel System and Related Components
The fuel delivery mechanism plays a crucial role in the performance of any engine. Proper fuel supply ensures smooth operation and efficient combustion, minimizing the risk of issues like stalling or reduced power. This section covers the essential elements involved in fuel management, including the various components that contribute to the process of storing, transporting, and injecting fuel into the engine.
Fuel Tank: The storage vessel that holds fuel until it is required by the engine. It is typically designed to prevent leaks and ensure a steady fuel supply. Many tanks also include features for easy refueling and secure closure.
Fuel Pump: This component ensures that fuel is delivered from the tank to the engine at the correct pressure. Depending on the system, the fuel pump may be mechanical or electric, with each type designed to suit specific engine requirements.
Fuel Filter: A critical component that prevents contaminants in the fuel from entering the engine. It filters out dirt, debris, and other impurities, helping to prolong the lifespan of the engine and maintain its efficiency.
Fuel Injectors: These components play a key role in delivering a precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. Their function is crucial for maintaining optimal fuel-air mixture, ensuring maximum power output and fuel efficiency.
Carburetor (if applicable): In some systems, the carburetor mixes air and fuel before it enters the engine. It helps control the engine’s air-fuel ratio, which is critical for smooth acceleration and maintaining steady operation.