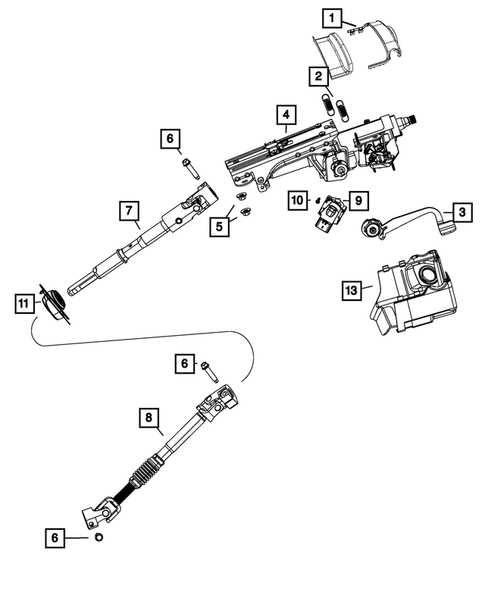
Delving into the inner components of an iconic off-road vehicle’s navigation system can provide insights into the mechanisms that guide its smooth maneuvering. This system is crucial for ensuring precise control, whether navigating rugged trails or urban streets. By exploring its structural layout, enthusiasts and repair professionals can gain a deeper appreciation of how each element contributes to the overall functionality.
Each segment of this navigation framework plays a role in maintaining stability and control, especially under challenging conditions. Recognizing the connection between these elements is key for those aiming to maintain or enhance the vehicle’s response capabilities. A well-informed approach to understanding these components can ensure both safety and performance during outdoor adventures.
This guide focuses on revealing the intricate layout, emphasizing the interactions between various elements. By understanding how each part contributes to the overall system, drivers can better diagnose potential issues, make informed upgrades, and appreciate the engineering that makes these vehicles a reliable choice for enthusiasts.
Overview of Steering Components
Understanding the key mechanisms that contribute to the control of a vehicle’s direction is crucial for maintaining safe and responsive handling. These mechanisms work together to ensure smooth navigation, providing stability and precision during movement. Let’s explore the primary elements involved in this system, highlighting their roles and interactions.
Key Elements of the System
- Rotary Linkage: Connects the central turning device with various pivot points, allowing the transfer of motion and direction to the wheels.
- Guidance Arm: This component ensures the correct angle is maintained when the main control device is turned, translating adjustments to the ground contact points.
- Hydraulic Assist Unit: Provides additional force to make turning the central control device easier, especially at lower speeds or when stationary.
- Axle Support: Holds the wheels in place while allowing them to pivot, ensuring they follow the directional input provided by the operator.
Interaction Between Elements
The coordination between these components ensures a reliable response to directional inputs. The rotary linkage sends movement signals, while the guidance arm ensures precise angle adjustments. The hydraulic assist reduces effort during turns, making it easier to navigate challenging terrains or tight spaces. Together, they offer a seamless driving experience, balancing control and comfort.
Main Functions of Steering System
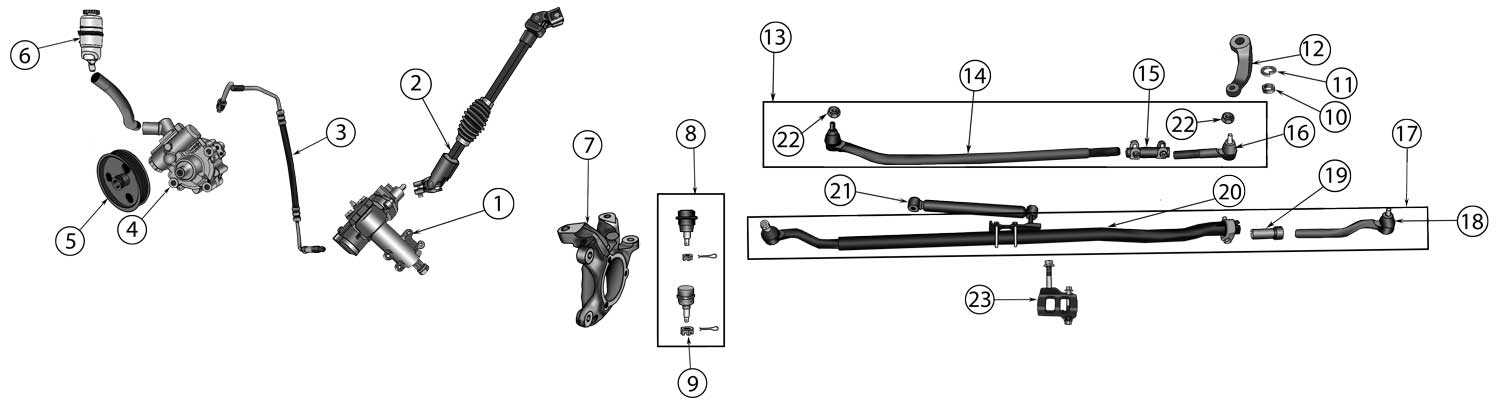
The mechanism in question plays a crucial role in guiding the movement of a vehicle. It ensures smooth navigation, maintaining control and direction during various driving conditions. Its design is essential for safety and efficiency, contributing to a comfortable experience for the driver.
- Direction Control: This system allows precise management of the vehicle’s path, enabling turns and adjustments with ease. It provides the necessary response to driver inputs, helping the vehicle follow the intended route.
- Stability Maintenance: By keeping the vehicle aligned during straight-line movement, this system enhances stability. It counteracts external forces, such as uneven road surfaces or wind, maintaining consistent performance.
- Safety Assurance: A well-designed mechanism helps prevent unexpected movements, reducing risks during sudden maneuvers. It ensures that the vehicle remains stable even in challenging conditions like slippery or rough terrains.
- Feedback Provision: This function offers the driver a sense of the road, delivering tactile information through the wheel. This feedback helps in understanding the conditions of the surface, allowing for timely adjustments.
- Efficiency Enhancement: Through
Common Issues with Steering Mechanism
Many vehicles experience challenges related to the handling and control system over time. These complications can range from minor inconveniences to significant safety concerns, often requiring timely attention and repairs. Below are some of the frequent problems drivers encounter with the control mechanisms, which can affect maneuverability and overall driving stability.
- Vibration or Shaking: A common symptom that something might be wrong is noticeable shaking or vibration, especially at higher speeds. This issue can stem from alignment problems, worn components, or unbalanced wheels.
- Difficulty in Turning: If more effort is needed to navigate curves or corners, it could indicate low fluid levels, a malfunctioning pump, or worn-out linkages, all of which reduce ease of movement.
- Unusual Noises: Clunking or squeaking sounds during motion can signal worn joints or bushings. These noises might become more pronounced when maneuvering through tight spaces or over uneven terrain.
- Poor Responsiveness: When the vehicle fails to respond quickly to directional input, it may point to issues like loosened connections or aging components. This lack of response can be
Identifying Different Types of Linkages
Understanding the various connections within a control mechanism is essential for maintaining effective motion and stability. These connections ensure that movements are accurately transferred, making the overall system more responsive and reliable. Below are some common types that play a crucial role in this setup.
Control Rods
These components act as intermediaries that transfer motion between different elements. Their design is often rigid, allowing for precise alignment and smooth operation. They help maintain the structure’s balance by controlling the direction and position of moving parts.
- Fixed length designs provide stability in movement.
- Adjustable models allow for fine-tuning and calibration.
Ball Joints and Tie Rods
These versatile connectors offer flexibility while maintaining firm connections between moving sections. They enable rotation and pivoting, which are crucial for directional adjustments. Ball joints work with tie rods to ensure smooth transitions in motion.
- Ball joints provide a pivot point, allowing for multi-directional movement.
- Tie rods serve as connectors, maintaining the alignment during changes in direction.
By understa
Maintenance Tips for Better Steering

Ensuring smooth and responsive movement control is essential for a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Regular upkeep and attention to key components can greatly extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s maneuvering system. Here are some practical tips to keep the system performing optimally and avoid potential issues.
Regular Inspections
Frequent checks help detect early signs of wear or damage. Pay attention to unusual sounds, stiffness, or vibrations while turning. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more serious problems. A thorough visual inspection can often reveal cracks, leaks, or loose connections that might compromise performance.
Lubrication and Fluid Checks
Proper lubrication reduces friction, ensuring smoother operation. Periodically check the condition and level of the hydraulic fluid, as insufficient or old fluid can lead to stiff or unresponsive movements. Using the right grade of lubricant is crucial to maintaining efficiency and preventing premature wear of components.
Maintenance Task Frequency Benefit Inspect Key Joints Every 6 months Prevents unexpected breakdowns Check Fluid Levels Monthly Ensures consistent Replacing Damaged Parts Effectively
Addressing issues with damaged components in your vehicle is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and safety. Ensuring that all elements function properly not only enhances driving experience but also prevents further complications that could arise from neglect. This section provides guidance on the best practices for efficiently replacing these components.
Assessing Damage
Before proceeding with any replacement, it’s essential to evaluate the extent of the damage. This assessment will help determine the necessary steps for replacement and whether professional assistance is required.
- Inspect the component for visible signs of wear or breakage.
- Check for unusual noises or handling issues during operation.
- Consult the owner’s manual for specific maintenance recommendations.
Replacement Process
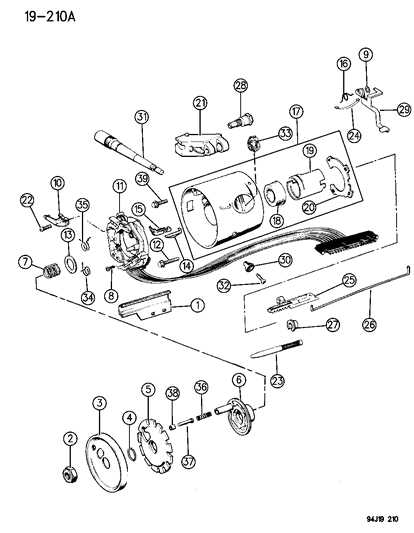
Once the damaged item has been identified, follow these steps for effective replacement:
- Gather the necessary tools and replacement components.
- Carefully remove the damaged item, following safety protocols to avoid injury.
- Install the new component, ensuring a secure fit and proper alignment.
- Test the newly installed item to confirm functionality and performance.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure a smooth replacement process, enhancing the reliability and safety of your vehicle.
Understanding Steering Gear Functionality
The mechanism responsible for directing the wheels is essential for vehicle maneuverability. Its operation involves converting the driver’s input into motion, allowing for precise control of the vehicle’s trajectory. This system ensures that the direction of travel aligns with the driver’s intentions, enhancing both safety and handling.
Key Components of the Mechanism
- Input Shaft: Connects to the steering wheel and transmits the driver’s commands.
- Output Shaft: Converts rotational movement into lateral movement to turn the wheels.
- Sector Gear: Engages with the output shaft to facilitate the turning action.
- Pitman Arm: Transmits movement from the sector gear to the linkage system.
- Linkage System: Connects various components, ensuring synchronized movement of the wheels.
How the Mechanism Operates
- The driver turns the wheel, causing the input shaft to rotate.
- This rotation engages the sector gear, which pivots around its axis.
- The pitman arm moves in response, pushing or pulling the linkage system.
- The linkage system transmits the movement to the wheels, resulting in a change of direction.
This intricate interplay of components ensures a responsive and accurate directional change, allowing for effective navigation and control during operation.
Steering Column Components Explained
The assembly responsible for directing the vehicle’s trajectory encompasses various elements that contribute to its functionality. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and repair.
- Column Housing: The outer casing that protects the inner mechanisms and provides structural integrity.
- Upper Bearing: This element allows the shaft to rotate smoothly within the housing, ensuring minimal friction.
- Lower Bearing: Positioned at the base, this part supports the shaft and maintains its alignment during operation.
- Steering Shaft: The central rod that transmits the driver’s input to the linkage, translating rotational motion into directional control.
- Ignition Lock Cylinder: This component secures the ignition system, preventing unauthorized access while allowing the driver to start the engine.
- Turn Signal Switch: Located on the column, this switch operates the vehicle’s indicators and often integrates additional functions such as headlights.
- Wiper Control Switch: Typically found on the same assembly, this control manages the windshield wipers, enhancing visibility during adverse conditions.
Understanding each of these components facilitates better troubleshooting and aids in the overall comprehension of the vehicle’s directional control system.
Upgrading to Aftermarket Steering Parts
Enhancing the handling and control of your vehicle often leads enthusiasts to consider superior alternatives to factory components. Aftermarket options provide the opportunity to improve responsiveness, durability, and overall performance. This upgrade can significantly enhance the driving experience, especially for those who navigate rugged terrains or engage in off-road adventures.
Benefits of Aftermarket Components
- Improved Durability: Many aftermarket solutions are designed to withstand harsher conditions, offering longer lifespans than stock components.
- Enhanced Performance: Upgraded options often feature advanced materials and engineering, resulting in better handling and response.
- Customization: A wide variety of choices allows owners to select components that align with their specific needs and preferences.
- Weight Reduction: Lighter alternatives can help improve overall vehicle agility and fuel efficiency.
Considerations When Choosing Alternatives
- Compatibility: Ensure that the selected upgrades fit your vehicle’s specifications and intended use.
- Quality: Opt for reputable brands known for producing high-quality and reliable alternatives.
- Installation: Assess whether professional installation is necessary or if you can manage the process independently.
- Warranty: Review any warranties associated with aftermarket components to protect your investment.
Importance of Regular Steering Alignment
Maintaining proper alignment in a vehicle’s directional control system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Misalignment can lead to a variety of issues that not only affect handling but also result in uneven tire wear and reduced fuel efficiency.
Consistent checks are essential for identifying any deviations in alignment. Regular assessments can prevent more serious mechanical failures down the road. When the directional system is not properly adjusted, it can cause the vehicle to pull to one side, making driving more challenging and increasing the risk of accidents.
Moreover, proactive maintenance can extend the lifespan of tires and other related components. By keeping the directional system in proper condition, owners can save on costly replacements and repairs in the long run. Overall, prioritizing alignment checks fosters a safer and more efficient driving experience.
Visual Guide to Steering System Layout

This section offers a detailed overview of how the essential components of a vehicle’s turning mechanism are arranged and interact. Understanding this structure helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance more effectively, as it clarifies the connections between various elements involved in direction control.
Key Components Overview
The arrangement includes several critical elements that work in unison to allow the vehicle to change direction smoothly. These include the control arm, which supports the wheel hub, and the assembly that adjusts the wheel alignment. Additionally, linkages connect these parts to ensure consistent movement during adjustments.
Component Arrangement Table
Element Description Function Control Arm Metal link connecting the wheels to the frame Ensures the wheels move in sync with the vehicle’s body Linkage Assembly