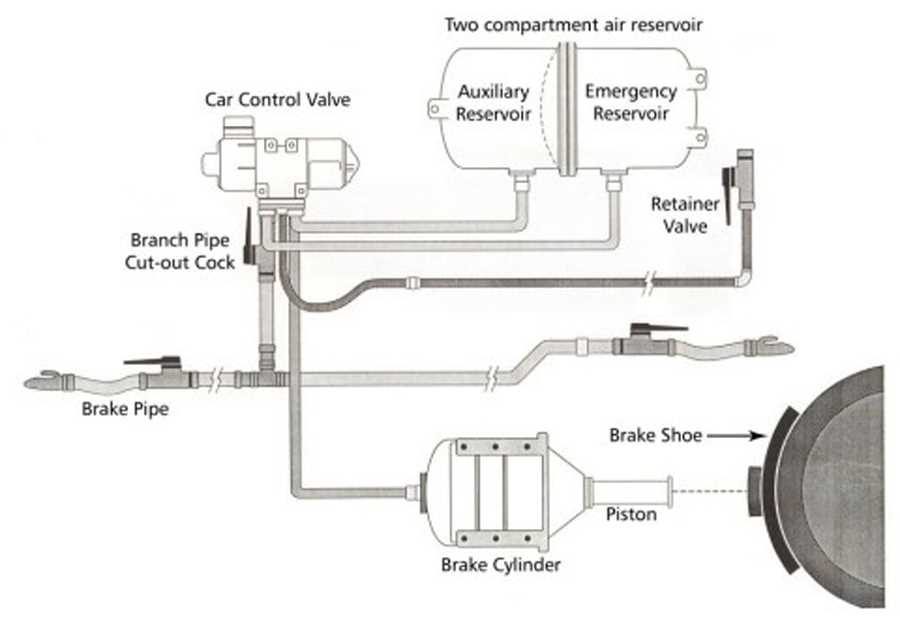
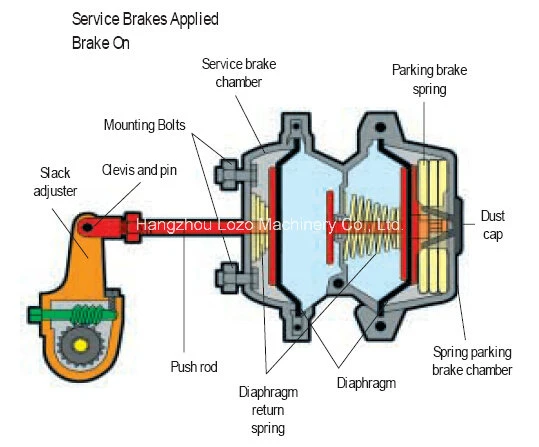
The functioning of heavy machinery relies heavily on specialized components that work in harmony to ensure safety and efficiency. This segment delves into the intricate relationships between these vital elements, emphasizing their roles and interactions. A thorough comprehension of these components is crucial for anyone involved in the maintenance and operation of large vehicles.
Each element in this assembly contributes uniquely to the overall performance, facilitating various functions essential for reliable operation. From controlling movement to ensuring stability, these components form a cohesive unit that enhances functionality. Understanding the nuances of each section allows operators to identify potential issues and optimize performance.
By exploring the design and arrangement of these elements, one can gain insights into their operational significance. A detailed overview reveals how each piece supports the larger mechanism, underscoring the importance of maintaining these critical features. This knowledge is invaluable for technicians and operators alike, fostering greater safety and efficiency in their work.
The components responsible for regulating pressure and flow play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and safety of pneumatic stopping mechanisms. Understanding the various categories of these devices is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring effective operation.
Different classifications of these elements are tailored to specific functions, allowing for a variety of applications. Below is a table summarizing the main types and their characteristics:
| Valve Type | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Relay Valve | Controls the delivery of pressure to the braking mechanism based on input from the driver. | Enhances responsiveness and modulation during operation. |
| Foot Valve | Serves as a control point for initiating braking by the driver. | Regulates the flow of compressed air to activate the stopping mechanism. |
| Protection Valve | Prevents damage by controlling excess pressure and providing a safety mechanism. | Ensures safe operation by managing pressure levels. |
| Quick Release Valve | Facilitates rapid exhaust of air to improve responsiveness. | Reduces lag time in the release of pressure for swift operation. |
Diagnostic Techniques for Air Brakes
Identifying issues in pneumatic stopping mechanisms is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Effective troubleshooting involves various methods and tools to assess functionality, pinpoint malfunctions, and implement necessary repairs. Understanding how to approach diagnostics can lead to more efficient maintenance and reduced downtime.
The following techniques can aid in the evaluation process:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Regularly examine components for signs of wear, damage, or leaks, which can indicate potential issues. |
| Pressure Testing | Utilize pressure gauges to check for correct pressure levels and identify any inconsistencies that may affect performance. |
| Leak Detection | Employ soapy water or specialized leak detection solutions to identify any escaping gas from connections or components. |
| Functional Testing | Conduct operational tests under controlled conditions to observe behavior and responsiveness, ensuring proper functionality. |
By applying these strategies, one can effectively diagnose and resolve issues within pneumatic stopping mechanisms, enhancing overall reliability and safety.
Common Issues in Air Brake Systems
The functionality of pneumatic stopping mechanisms is crucial for safety in various vehicles. Regular maintenance and awareness of potential complications can significantly enhance performance and longevity. Understanding the typical challenges that may arise can aid in timely interventions and ensure efficient operation.
One frequent concern is leakage, which can occur in several areas, leading to a decrease in pressure and compromised efficiency. This can be caused by worn-out seals or connections. Regular inspections can help identify and rectify such issues before they escalate.
Another common problem involves contamination of components. Dust, moisture, and debris can hinder the performance of the mechanisms, affecting responsiveness and reliability. Keeping the system clean and properly lubricated is essential to mitigate these risks.
Worn-out components may also pose significant threats to functionality. Parts such as valves and diaphragms can degrade over time, resulting in impaired performance. Routine checks and timely replacements can prevent failures and enhance safety.
Finally, improper adjustments can lead to uneven force distribution, causing instability during operation. Ensuring that all components are correctly calibrated is vital for maintaining balance and control.
Maintenance Practices for Air Brakes
Proper upkeep of pneumatic stopping mechanisms is essential for ensuring vehicle safety and performance. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of components but also enhances the reliability of the overall assembly. This section discusses vital procedures that help maintain these crucial mechanisms in optimal condition.
Regular Inspections

Conducting frequent examinations of the entire setup is critical. Technicians should check for signs of wear, leaks, or damage in various components. Attention should be paid to connections, hoses, and cylinders to ensure everything operates smoothly. Documentation of these inspections aids in tracking performance over time and identifying potential issues before they escalate.
Fluid Management
Maintaining appropriate fluid levels and quality is essential for effective operation. Replacing or replenishing the fluid periodically helps prevent contamination and ensures efficient functioning. Draining condensation from reservoirs should also be a standard practice, as moisture can lead to corrosion and other complications that impair performance.
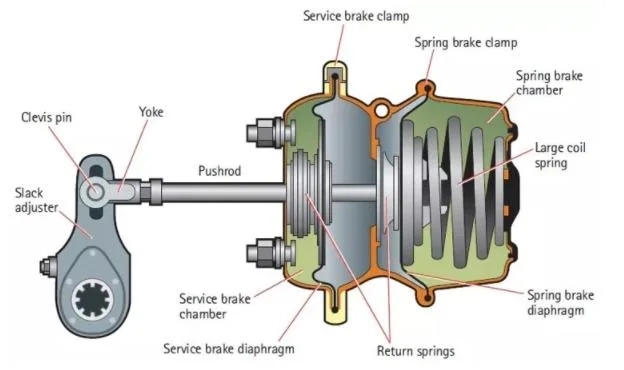
Air Brake System Safety Features
The mechanisms designed to enhance vehicle safety play a crucial role in ensuring reliable performance and preventing accidents. By incorporating various protective elements, these assemblies significantly improve operational integrity and user confidence.
Among the essential features are the fail-safe mechanisms that activate in case of unexpected issues, ensuring that the vehicle remains under control. Additionally, the incorporation of pressure monitoring systems allows for real-time assessment of functional parameters, alerting operators to any irregularities.
Another vital aspect is the use of advanced materials and technology, which contribute to durability and reliability, reducing the likelihood of component failure. This innovation enhances overall safety and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Activation | Ensures immediate response in case of primary failure. |
| Pressure Monitoring | Continuously checks pressure levels and alerts for discrepancies. |
| Durable Materials | Utilizes high-strength materials to withstand wear and tear. |
| Redundancy Systems | Incorporates backup features to maintain functionality during failures. |
Innovations in Air Brake Technology
Recent advancements in braking technology have significantly enhanced vehicle performance and safety. These innovations focus on improving reliability, efficiency, and responsiveness, providing a safer driving experience across various transportation modes.
Key developments include:
- Advanced materials: The use of lightweight composites and heat-resistant materials enhances durability and performance.
- Electronic controls: Integration of electronic systems for better monitoring and response times, allowing for precise modulation of braking forces.
- Automated diagnostics: Systems that can self-check and diagnose issues in real-time, ensuring optimal functionality.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring:
- Regenerative technologies: Innovations that allow energy recovery during braking, improving overall efficiency.
- Smart connectivity: Linking braking systems with other vehicle technologies to enhance coordination and response times.
- Modular designs: Components designed for easy replacement and upgrades, facilitating maintenance and customization.
These breakthroughs aim to create a more efficient and safer environment for all road users, showcasing the ongoing evolution of braking technologies.
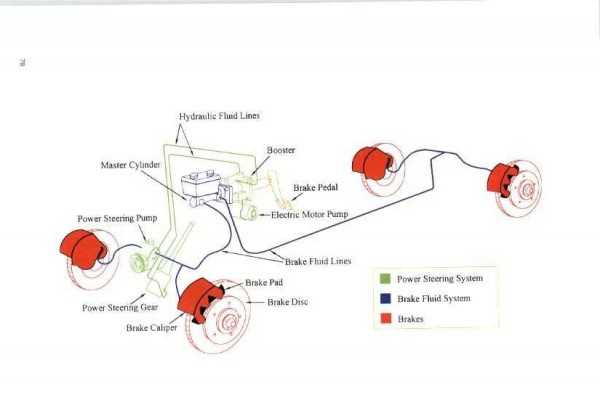
Comparison of Air and Hydraulic Brakes
The choice between two common stopping mechanisms often comes down to specific requirements and application scenarios. Both options utilize different methods to create stopping power, which significantly affects their performance and reliability in various conditions.
Operating Principles
One mechanism operates by utilizing compressed gas to engage friction surfaces, while the other relies on fluid pressure to achieve the same result. This fundamental difference leads to unique characteristics in terms of responsiveness and control.
Applications and Performance
The selection of either mechanism often depends on the intended use. For instance, one option is frequently found in larger vehicles due to its ability to handle heavy loads effectively. In contrast, the alternative is commonly utilized in smaller vehicles, providing adequate stopping power with more compact design benefits. Durability and maintenance requirements also vary, impacting overall operational efficiency.
Impact of Air Brakes on Performance
The utilization of pneumatic stopping mechanisms significantly influences overall vehicle functionality and efficiency. Their design allows for effective control over motion, enhancing safety and responsiveness during operation.
Several factors contribute to the positive effects of these mechanisms:
- Quick Engagement: The rapid activation enables prompt responses, improving handling during critical situations.
- Consistent Performance: These mechanisms maintain effectiveness over time, ensuring reliability in diverse conditions.
- Reduced Weight: Lightweight components contribute to better fuel efficiency, optimizing the vehicle’s operational capacity.
- Enhanced Modulation: The ability to finely tune the force applied allows for smoother deceleration, improving overall driving comfort.
Moreover, their impact extends to maintenance aspects. Regular upkeep is straightforward, promoting longevity and sustained performance. This reliability ultimately fosters trust among users, encouraging wider adoption in various transportation sectors.
In summary, the integration of these stopping technologies plays a crucial role in shaping vehicle dynamics, balancing performance, safety, and efficiency for enhanced user experience.
Training for Air Brake Technicians
Proper education and skill development are crucial for professionals working with pneumatic stopping mechanisms. These individuals must grasp the fundamentals of operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting to ensure safety and efficiency in their roles.
Comprehensive training programs offer in-depth knowledge of various components and their functions. Participants learn about the essentials of diagnosis, repair techniques, and effective inspection methods. Hands-on experience, alongside theoretical instruction, equips trainees with the expertise needed to address common challenges.
Additionally, staying updated on industry standards and technological advancements is vital. Continuous education helps technicians adapt to changes and improve their problem-solving capabilities. By engaging in workshops and seminars, they can enhance their proficiency and maintain high safety standards in their work environment.