Steering and Control Systems: The steering assembly integrates with various control systems, enabling the driver to easily manage direction, while secondary controls for lights, wipers, and other features are often mounted on or near the
Braking System Components Breakdown
The braking system is a critical aspect of vehicle safety, designed to ensure effective stopping power and control under various driving conditions. Understanding the individual elements that contribute to this system can provide insights into its functionality and help in diagnosing potential issues.
Brake Calipers play a central role in the mechanism, applying pressure to the pads to bring the vehicle to a halt. These components work in unison with rotors, which dissipate heat during the friction process, preventing overheating and ensuring consistent performance.
Another key element is the master cylinder, responsible for converting the force applied to the pedal into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is distributed through a network of brake lines, ensuring that all wheels receive the necessary force to slow down or stop the vehicle effectively.
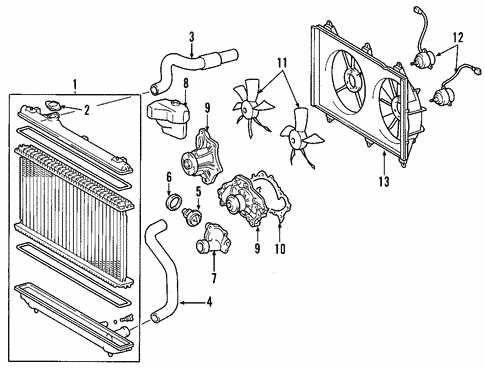
Cooling System Parts and Functionality
The cooling mechanism of an automobile plays a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the engine. This system is designed to prevent overheating and ensure efficient performance by regulating the heat generated during the combustion process. Understanding the components and their functions within this mechanism is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components:
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool before re-entering the engine.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating the coolant throughout the engine and cooling system.
- Thermostat: A temperature-sensitive valve that regulates coolant flow based on the engine’s temperature.
- Cooling Fan: Provides additional airflow through the radiator, especially during low-speed driving or idling.
Each of these elements works collaboratively to ensure that the engine operates within a safe temperature range, ultimately enhancing longevity and performance.
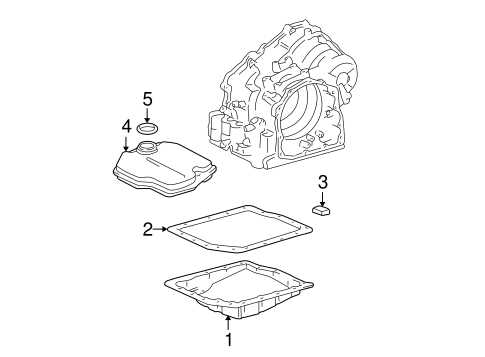
Transmission Assembly and Key Elements
The transmission assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of any vehicle, serving as the bridge between the engine’s power and the wheels. Understanding its essential components and their interconnections can enhance maintenance and repair processes, ensuring smoother operation and longevity of the vehicle.
Essential Components
This complex system includes several vital elements, each contributing to the seamless transfer of energy. Key components such as the gear set, torque converter, and control valve work in unison to regulate speed and power distribution. Familiarity with these parts allows for better troubleshooting and optimization of vehicle performance.
Importance of Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the transmission assembly is vital to prevent wear and potential failure. Inspecting fluid levels, replacing filters, and addressing any signs of leaks can significantly extend the lifespan of this critical system. Proper care ensures that the vehicle remains reliable and efficient on the road.
Exhaust System Diagram and Layout
The exhaust system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in directing harmful gases away from the engine, enhancing performance and reducing noise. Understanding its configuration is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section will explore the various components and their arrangement within this essential system.
Key Components of the Exhaust System
The exhaust system comprises several key elements, each serving a specific function. Here are the main parts:
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects gases from the engine cylinders.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting gases into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: Decreases noise produced by the exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Pipes: Channels gases away from the engine to the rear of the vehicle.
- Resonator: Works with the muffler to fine-tune sound frequencies.
Understanding the Layout
The arrangement of the exhaust components is designed to optimize efficiency and minimize emissions. Below is a simplified overview of how these elements are typically configured:
- Gases exit the engine through the exhaust manifold.
- They flow into the catalytic converter for treatment.
- After the converter, gases pass through the resonator.
- The muffler then reduces noise before exiting through the exhaust pipes.
A proper understanding of this layout aids in diagnosing issues and performing repairs effectively, ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly.
Electrical Wiring and Main Circuits
This section delves into the intricate system of electrical connections and primary circuits that facilitate the operation of various components within the vehicle. Understanding these connections is essential for diagnosing issues and ensuring proper functionality.
Overview of Electrical Systems
The electrical systems in vehicles comprise various pathways that enable the distribution of power to essential components such as lights, sensors, and the ignition system. Each circuit is designed to manage specific functions, contributing to the overall performance and safety of the automobile.
Key Components and Connections
Central to the electrical framework are several critical elements, including fuses, relays, and wiring harnesses. These components work together to create a reliable network that supports the vehicle’s operations. The following table outlines some of the essential components and their roles:
| Component |
Function |
| Fuse |
Protects circuits by breaking the connection during overloads |
| Relay |
Controls high-current devices with low-current signals |
| Wiring Harness |
Bundles wires together, facilitating organization and protection |
Steering Mechanism and Related Parts
The steering system is a crucial element in ensuring the smooth navigation and control of a vehicle. It comprises various components that work in harmony to enable precise handling and responsiveness while driving. Understanding this system can aid in maintenance and repairs, ensuring safety and efficiency on the road.
Key components involved in the steering mechanism include:
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for the driver to control the vehicle’s direction.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the mechanism, allowing the transfer of movement.
- Rack and Pinion: A widely used gear mechanism that converts rotational motion into linear motion for steering.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic assistance to reduce the effort needed to turn the wheel.
- Tie Rods: Connect the steering gear to the wheels, facilitating movement during turns.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal performance. Common issues can arise from wear and tear, affecting the overall handling and safety of the vehicle. Keeping the steering mechanism in good condition enhances driving experience and extends the lifespan of related systems.
In summary, the steering mechanism is essential for effective vehicle control. Familiarity with its components and their functions contributes to better maintenance practices and informed decision-making regarding repairs.
Fuel System Diagram and Components
The fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of any vehicle. This network of components is responsible for transporting the necessary energy source from the tank to the engine, enabling combustion and power generation. Understanding the various elements involved in this system can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key components of the fuel delivery mechanism include:
| Component |
Description |
| Fuel Tank |
Stores the fuel and provides a reservoir for the system. |
| Fuel Pump |
Moves fuel from the tank to the engine under pressure. |
| Fuel Filter |
Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Injector |
Atomizes the fuel and delivers it into the combustion chamber. |
| Pressure Regulator |
Maintains the correct fuel pressure within the system. |
By familiarizing oneself with these essential elements, one can ensure the longevity and reliability of the fuel system, ultimately contributing to the vehicle’s overall performance.
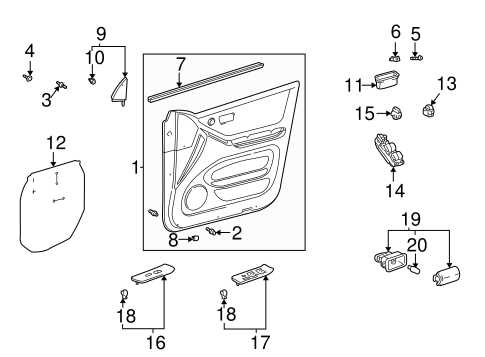
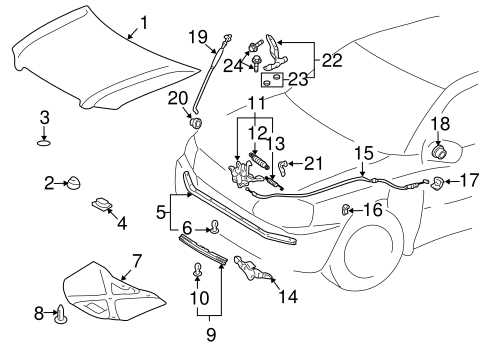
Body Structure and Exterior Elements

The outer framework of a vehicle is crucial for its overall integrity and aesthetic appeal. This section delves into the various components that comprise the shell and exterior features of the automobile. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance and modifications, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Key Components of the Exterior
The exterior structure consists of several important parts, each playing a vital role:
- Chassis: The main support structure that underpins the vehicle, providing stability and strength.
- Fenders: Panels that cover the wheel wells, protecting the tires and enhancing the overall look.
- Doors: Access points that offer entry and exit, equipped with locking mechanisms for security.
- Hood: The cover over the engine compartment, crucial for engine protection and aerodynamics.
- Roof: The top structure that contributes to the vehicle’s profile and provides shelter for passengers.
Exterior Features and Accessories
In addition to the core components, numerous accessories enhance both functionality and appearance:
- Lighting: Headlights, taillights, and turn signals are essential for visibility and safety.
- Mirrors: Side and rearview mirrors provide crucial visibility for the driver.
- Windshield: The front glass panel that protects occupants from elements while providing visibility.
- Trim: Decorative elements that enhance the vehicle’s aesthetics and protect edges.
Air Conditioning System Parts Layout
The air conditioning setup within a vehicle is a complex network designed to provide comfort by regulating temperature and humidity. Understanding the components involved can assist in troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance during operation.
Key elements of the air conditioning system include:
- Compressor: This component circulates refrigerant throughout the system, compressing it to raise its temperature and pressure.
- Condenser: Typically located at the front of the vehicle, it dissipates heat from the refrigerant, allowing it to transition from a gas to a liquid state.
- Expansion Valve: This part regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, lowering its pressure and temperature.
- Evaporator: Located inside the cabin, it absorbs heat from the interior air, cooling it before circulating back into the vehicle.
- Receiver/Drier: This component filters and stores refrigerant, ensuring that moisture and debris do not enter the system.
Proper functioning of each component is crucial for the efficiency and effectiveness of the cooling system. Regular checks can prevent issues and prolong the lifespan of these essential elements.