The efficient operation of heavy-duty agricultural machines relies on the seamless interaction of numerous mechanical elements. Understanding how these elements are arranged and work together is essential for maintaining optimal performance and troubleshooting potential issues.
Each mechanical component plays a critical role, contributing to the overall functionality of the machine. From the engine system to hydraulic configurations, a detailed understanding of these structures can significantly improve maintenance routines and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
This section provides a clear and structured look at the internal and external mechanisms, helping users identify specific elements and their respective functions. With precise and easily accessible visual aids, operators and technicians can ensure better handling and maintenance of essential machinery.
Ford 1900 Tractor Overview
The model under discussion is a reliable and efficient piece of machinery designed to meet the needs of small to medium agricultural tasks. Built with durability in mind, this equipment offers flexibility and power, making it a popular choice for farmers and landowners who require dependable performance in diverse working conditions.
Its compact size and robust build allow it to handle a variety of jobs with ease, from tilling and plowing to hauling and mowing. The machine’s design ensures ease of use, allowing operators to accomplish their tasks with minimal effort while maintaining precision and control.
With a focus on versatility, the unit supports various attachments and tools, expanding its utility across multiple farming applications. Its user-friendly controls, combined with reliable performance, make it an essential asset for any agricultural setting.
Key Components and Their Functions
The equipment is built with numerous essential elements, each serving a unique purpose to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Understanding these integral parts is crucial for maintaining peak performance and addressing any potential issues.
Engine
The engine is the powerhouse of the machinery, converting fuel into mechanical energy. It drives the movement and operation of the entire system, allowing the equipment to perform tasks with power and reliability.
Transmission System
The transmission system manages the distribution of power from the engine to various mechanisms. It allows the operator to control speed, torque, and direction, ensuring flexibility and adaptability in different working conditions.
Hydraulic system is responsible for operating attachments and implements, providing the necessary force to lift or move heavy loads. This system plays a key role in making the equipment versatile in various tasks.
The cooling system ensures that the machinery operates at an optimal temperature by dissipating excess heat. This helps prevent overheating and ensures long-term durability.
Engine Assembly Breakdown
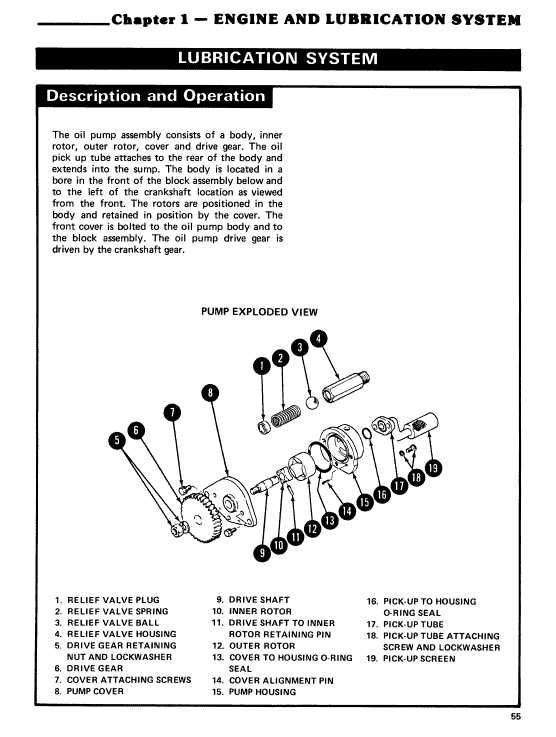
The internal power unit is a complex system composed of multiple interconnected components working in unison to deliver efficient performance. Each segment plays a vital role in the overall functionality, and understanding their structure is crucial for maintaining optimal operation. This section outlines the primary divisions and the key elements involved, providing insight into how everything fits together.
Cylinder Block and Pistons: At the core of the power mechanism lies the cylinder block, housing the pistons. These pistons are responsible for generating the necessary force through controlled movements, converting energy into mechanical work. Their alignment and precision are essential for smooth operation.
Crankshaft and Connecting Rods: Below the cylinders, the crankshaft transforms the vertical motion of the pistons into rotational energy. The connecting rods serve as the vital link between these two parts, ensuring the transfer of force is efficient and steady.
Camshaft and Valvetrain: Managing the timing of fuel intake and exhaust release, the camshaft regulates the movement of the valves. The valvetrain, a system of pushrods and lifters, ensures synchronization between the intake and exhaust cycles, contributing to the overall
Transmission System Parts Layout

The arrangement of the components within the transmission system is crucial for efficient operation and smooth power delivery. Understanding how these various elements interact allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring that the vehicle continues to perform optimally.
- Gears and Shafts: These elements are responsible for transferring torque and adjusting speed ratios, playing a key role in managing engine output.
- Clutch Assembly: This mechanism connects and disconnects the power flow, facilitating gear changes while minimizing wear on the system.
- Synchro Rings: These rings help align gears during shifting, ensuring smooth engagement and preventing grinding or damage.
- Shift Forks and Levers: These parts guide the movement of gears, allowing the operator to select the appropriate speed setting.
- Bearings and Seals: These components reduce friction between moving parts and prevent fluid leaks, thus maintaining the overall efficiency
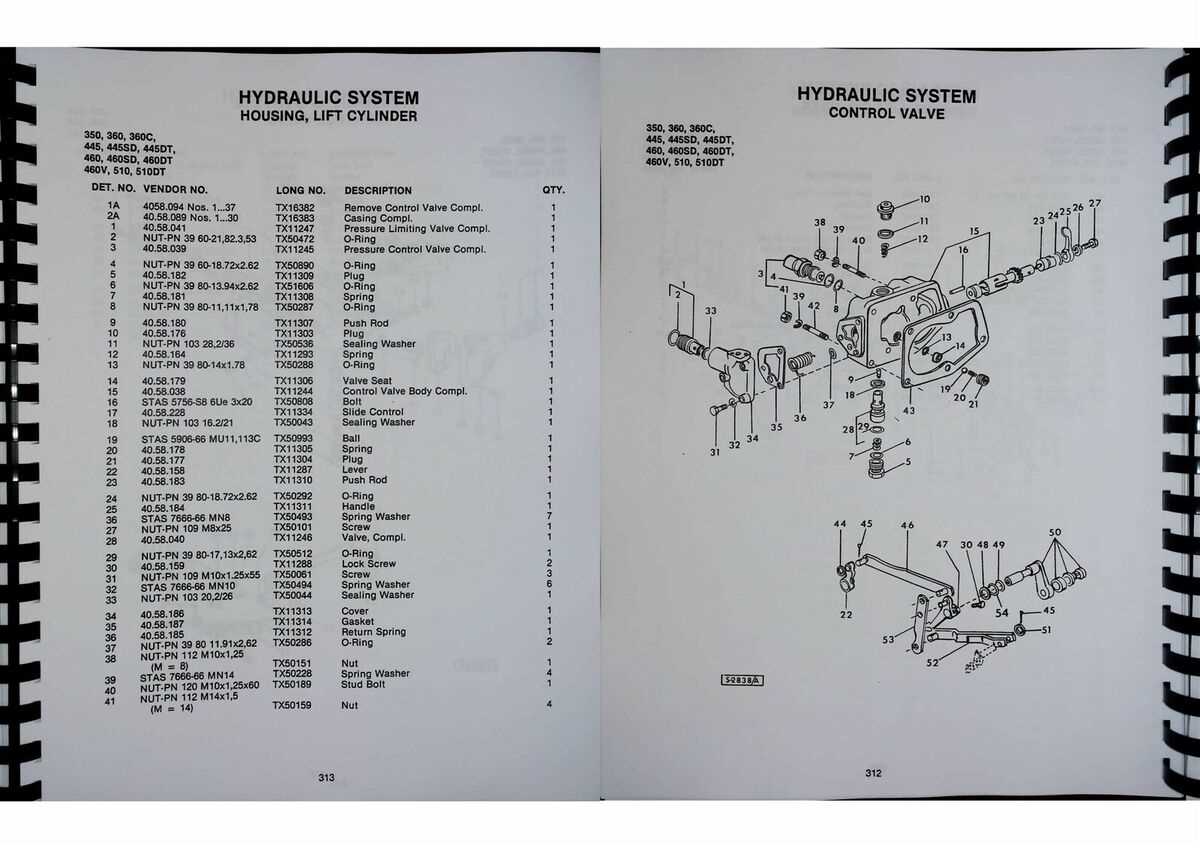
Hydraulic System Diagram and Features
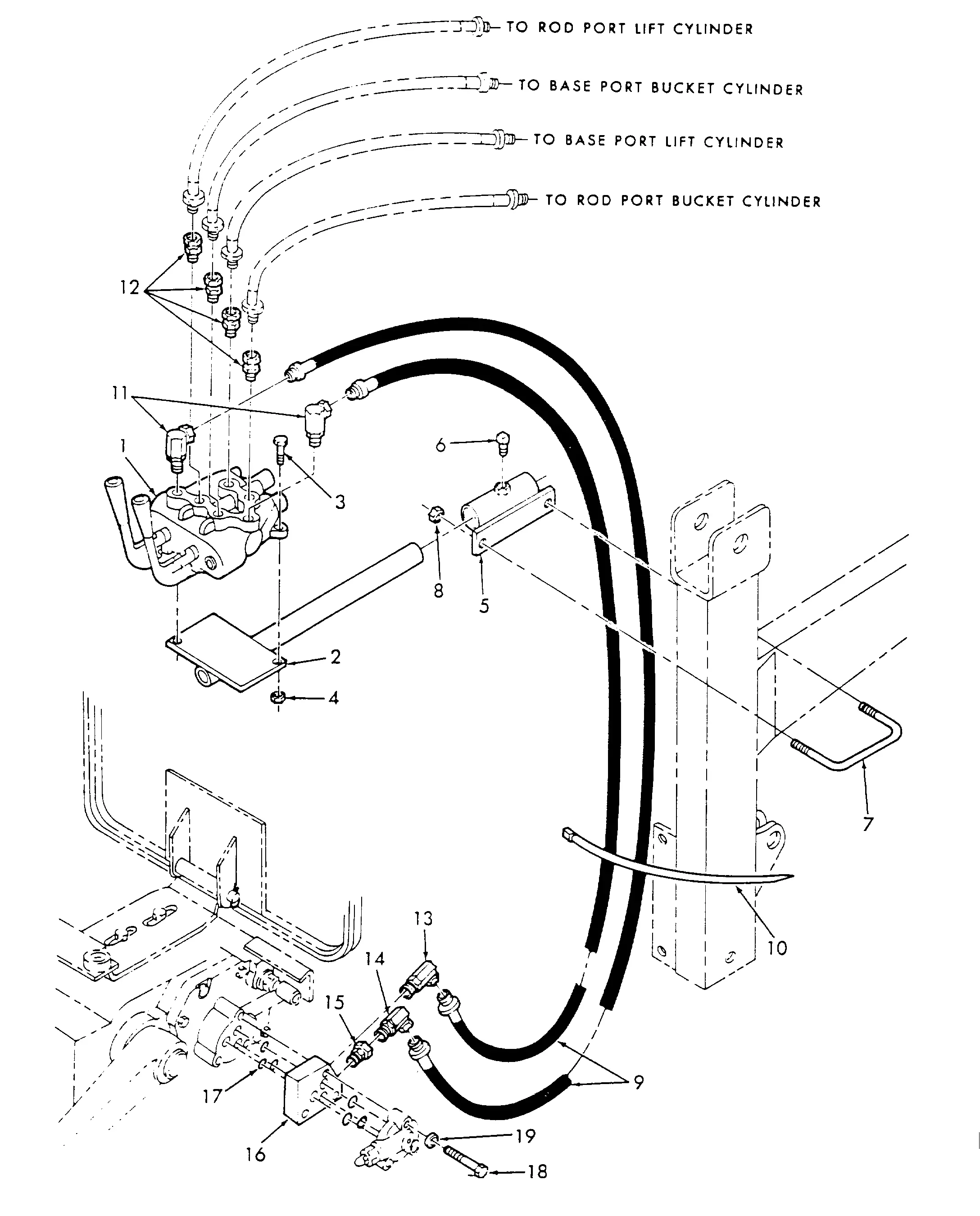
The hydraulic system plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency by transmitting power through fluid pressure. This technology allows various components to perform tasks that require significant force with minimal effort from the operator. Understanding the layout and functions of the hydraulic elements is essential for optimal performance and maintenance.
- Pump Mechanism: The primary force generator in the system, responsible for moving fluid throughout the network.
- Control Valves: These regulate the direction and amount of fluid flow, ensuring precise control over the system’s functions.
- Cylinders and Actuators: Convert fluid power into mechanical motion, providing the necessary force to lift, lower, or adjust various attachments.
- Reservoir: Stores the fluid and maintains pressure levels while preventing contamination through filtration.
- Hoses and Connections: These form the
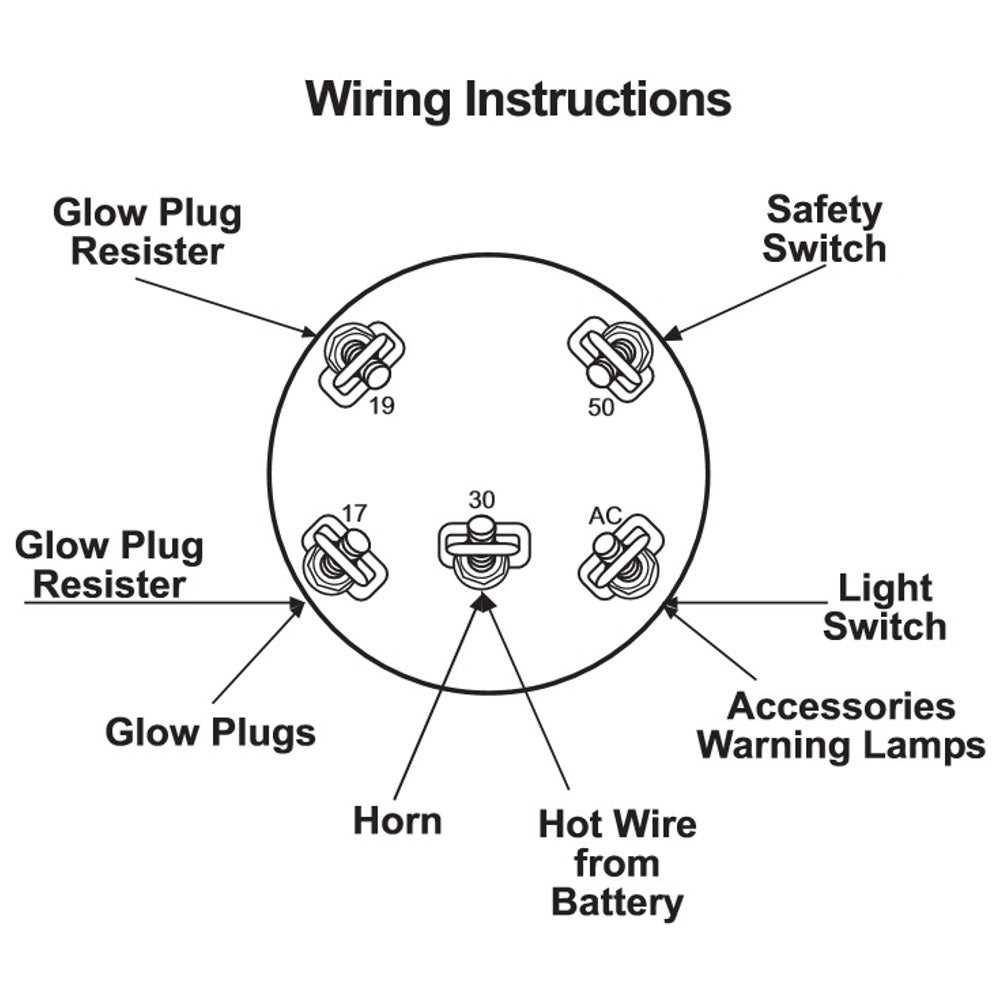
Electrical Wiring and Connections
The intricacies of wiring and connections in machinery play a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. Understanding the layout and function of each component allows for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Proper electrical configurations are essential for reliable operation, preventing malfunctions that could hinder functionality.
Key Components
- Battery: Provides the necessary power to start the engine and operate electrical systems.
- Alternator: Charges the battery and powers electrical devices while the engine runs.
- Wiring Harness: Connects various electrical components, facilitating the flow of electricity throughout the system.
- Fuses: Protect electrical circuits by preventing overloads and potential damage.
- Relays: Act as switches that control larger electrical loads with a smaller input signal.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect connections for corrosion and wear.
- Ensure that all wiring is securely fastened and free from abrasion.
- Replace any blown fuses promptly to avoid circuit damage.
- Test electrical components periodically to ensure proper functionality.
- Use the correct gauge of wire for specific applications to prevent overheating.
Maintaining the electrical system’s integrity is essential for smooth operation. By adhering to these guidelines, users can enhance the longevity and efficiency of their equipment.
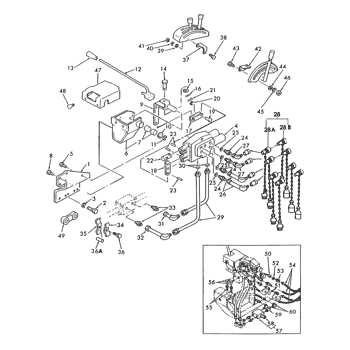
Steering and Control Mechanisms

The ability to maneuver effectively is crucial for any agricultural vehicle, ensuring precision in navigation across various terrains. This section delves into the intricate systems that govern directional movement and operational command, emphasizing their importance for efficient handling and user experience.
Directional Control: Central to any vehicle’s functionality is the steering assembly, which allows the operator to dictate the machine’s path. Various designs exist, ranging from traditional systems employing a mechanical linkage to advanced hydraulic solutions that enhance responsiveness. The choice of steering method significantly affects maneuverability, particularly in tight spaces.
Operational Interfaces: The control mechanisms encompass levers, pedals, and switches, all designed to facilitate smooth interaction with the vehicle. Each component plays a vital role in executing commands, whether it’s adjusting speed, engaging implements, or navigating obstacles. Understanding these controls is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Maintenance Considerations: Regular inspection and upkeep of steering and control systems are imperative to ensure reliability and longevity. Components such as linkages, joints, and hydraulic fluids should be routinely checked for wear and tear. Proper maintenance not only prolongs the life of these systems but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
Fuel System Components Map
This section provides an overview of the various elements that comprise the fuel system of agricultural machinery. Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The primary element responsible for storing the fuel is the reservoir, which ensures a steady supply to the engine. Connected to the reservoir is the fuel pump, which plays a vital role in delivering fuel at the required pressure. The system also includes filters designed to eliminate impurities, ensuring that only clean fuel reaches the engine.
Another important component is the fuel injector, which atomizes the fuel for optimal combustion within the engine cylinders. Additionally, various lines and hoses facilitate the transportation of fuel between components, contributing to the overall efficiency of the system. Understanding each of these parts and their interconnections is essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of the machinery.
Cooling System Layout and Parts
The efficient management of temperature is crucial for the longevity and performance of any engine. A well-designed cooling mechanism ensures that the operating temperatures remain within optimal limits, preventing overheating and potential damage. Understanding the arrangement and components involved in this system can significantly aid in maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
- Radiator: This essential unit dissipates heat from the coolant.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating the coolant throughout the system.
- Thermostat: Regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature.
- Hoses: Flexible conduits that transport coolant between various components.
- Coolant Reservoir: Stores excess coolant and allows for expansion.
System Layout Overview
The arrangement of the cooling assembly typically follows a streamlined path:
- The water pump draws coolant from the reservoir.
- Coolant is circulated through the engine block, absorbing heat.
- Heated coolant flows to the radiator for cooling.
- Once cooled, the coolant returns to the engine to repeat the cycle.
Brake System Design and Components
The braking mechanism in agricultural machinery is crucial for ensuring safety and control during operation. This system is engineered to provide effective stopping power, enhance maneuverability, and ensure reliable performance under various conditions. Understanding the components and their arrangement helps in maintaining and troubleshooting the system effectively.
At the core of this mechanism, several key elements work in harmony:
- Brake Pedal: The interface for the operator, allowing for easy activation of the braking process.
- Master Cylinder: Converts the force applied on the pedal into hydraulic pressure, initiating the braking action.
- Brake Lines: Tubes that transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the braking units.
- Brake Shoes: Components that press against the drum to create friction and slow down the movement.
- Brake Drums: Rotating elements that work with brake shoes to facilitate stopping.
- Hydraulic Fluid: A special fluid that transfers force and allows for smooth operation of the braking system.
Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the system. Proper maintenance and timely inspection of these parts are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the braking mechanism. Understanding how each piece contributes to the system allows for more efficient troubleshooting and repairs, thereby enhancing operational safety.
Exhaust System and Muffler Configuration
The exhaust mechanism is a crucial aspect of any engine setup, playing a significant role in managing emissions and enhancing performance. Properly configured, this system ensures efficient expulsion of gases, minimizes noise, and contributes to the overall longevity of the engine. Understanding its components and their arrangement can greatly aid in maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
At the heart of this configuration lies the muffler, designed to dampen sound produced during combustion. Connected to the exhaust manifold, it channels gases through a series of chambers and tubes, which work to reduce noise levels before they exit the vehicle. Additionally, the system may include catalytic converters, which aid in converting harmful emissions into less harmful substances, playing a pivotal role in environmental compliance.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
When installing or inspecting the exhaust framework, ensure that all joints are secure to prevent leaks, which can lead to performance issues or safety hazards. Regular checks for rust or corrosion are also advisable, as these can compromise the effectiveness of the system. Proper maintenance not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to a quieter operation, making it essential for optimal performance.
Axles and Drive Train Diagram
This section focuses on the crucial components involved in the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, emphasizing the structural and functional elements that ensure efficient movement. Understanding the layout and interaction of these elements is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components Overview
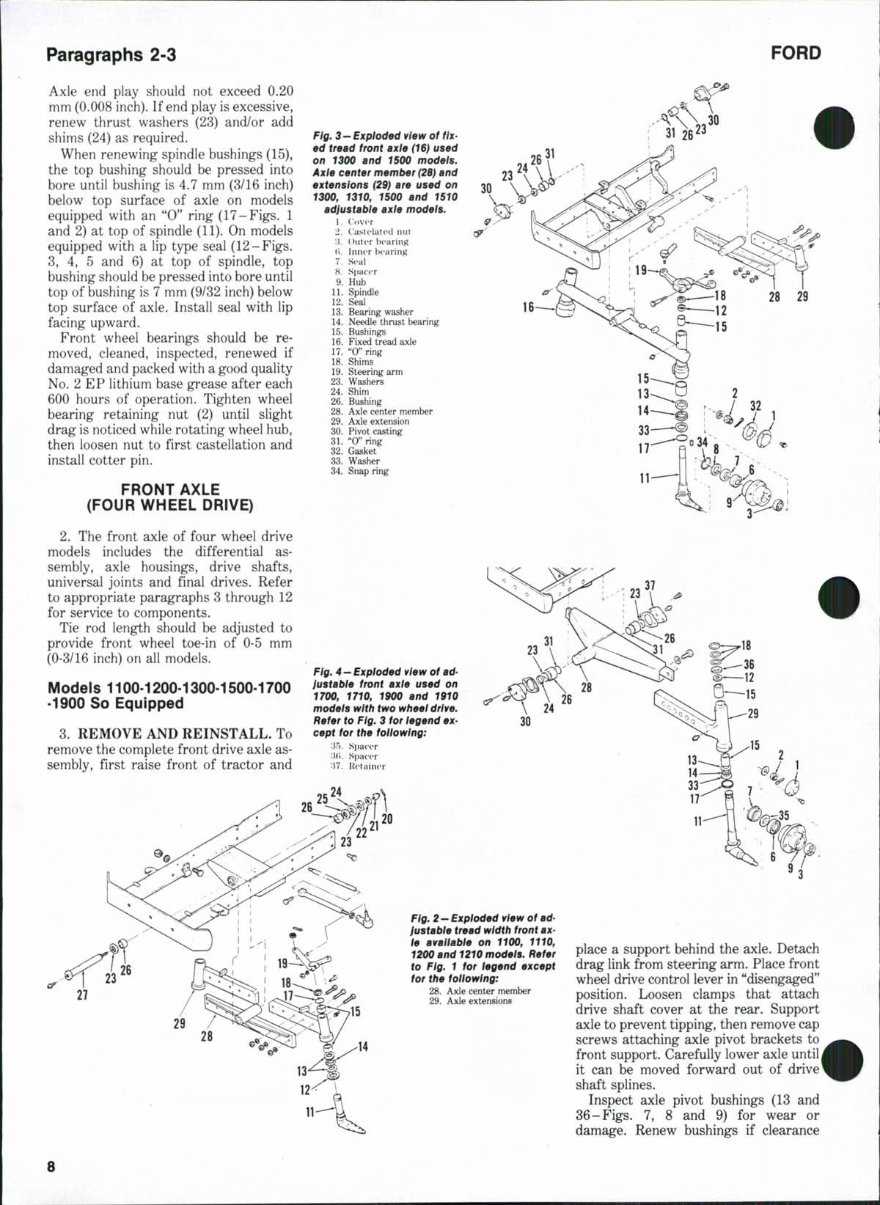
The system comprises various vital components that work in unison to facilitate mobility. These include the axle assemblies, differential units, and associated transmission parts, which collectively contribute to the overall functionality of the vehicle.
Component Specifications
Component Description Axle Housing Encloses the axle shaft and provides structural support for wheel mounting. Drive Shaft Transfers torque from the engine to the differential, allowing for wheel rotation. Differential Distributes power to the wheels while allowing for differences in wheel speed during turns. Wheel Hub Connects the wheel to the axle, providing a mounting point and enabling rotation. Universal Joint Allows for flexibility in the drive shaft, accommodating movement and angle changes. Routine Maintenance Parts Identification
Proper upkeep of machinery involves recognizing and understanding the various components that contribute to its efficient operation. Regular maintenance not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. Familiarity with essential elements is crucial for effective service and timely replacements.
During routine inspections, it is vital to identify key elements such as filters, belts, and fluids. Filters play a critical role in keeping the engine clean by removing impurities, while belts ensure proper power transmission between different systems. Regular checks of these components can prevent potential issues and reduce the risk of breakdowns.
Moreover, fluids such as oil, coolant, and hydraulic fluids must be monitored to maintain optimal functionality. Each of these liquids serves specific purposes, including lubrication, temperature regulation, and operational efficiency. Keeping a record of fluid levels and replacing them as needed is essential for the longevity of the machinery.
By developing a keen understanding of these vital components, operators can ensure their equipment remains in top condition. This proactive approach not only minimizes downtime but also enhances overall productivity in various tasks.